Geophysical Data Acquisition
advertisement
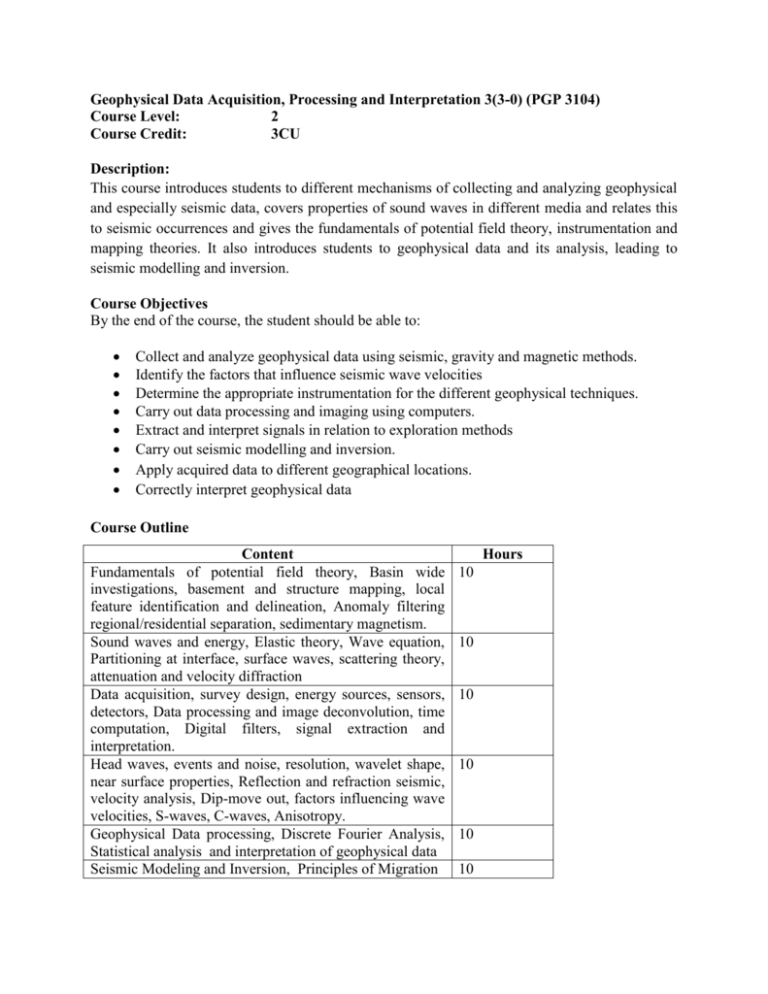
Geophysical Data Acquisition, Processing and Interpretation 3(3-0) (PGP 3104) Course Level: 2 Course Credit: 3CU Description: This course introduces students to different mechanisms of collecting and analyzing geophysical and especially seismic data, covers properties of sound waves in different media and relates this to seismic occurrences and gives the fundamentals of potential field theory, instrumentation and mapping theories. It also introduces students to geophysical data and its analysis, leading to seismic modelling and inversion. Course Objectives By the end of the course, the student should be able to: Collect and analyze geophysical data using seismic, gravity and magnetic methods. Identify the factors that influence seismic wave velocities Determine the appropriate instrumentation for the different geophysical techniques. Carry out data processing and imaging using computers. Extract and interpret signals in relation to exploration methods Carry out seismic modelling and inversion. Apply acquired data to different geographical locations. Correctly interpret geophysical data Course Outline Content Fundamentals of potential field theory, Basin wide investigations, basement and structure mapping, local feature identification and delineation, Anomaly filtering regional/residential separation, sedimentary magnetism. Sound waves and energy, Elastic theory, Wave equation, Partitioning at interface, surface waves, scattering theory, attenuation and velocity diffraction Data acquisition, survey design, energy sources, sensors, detectors, Data processing and image deconvolution, time computation, Digital filters, signal extraction and interpretation. Head waves, events and noise, resolution, wavelet shape, near surface properties, Reflection and refraction seismic, velocity analysis, Dip-move out, factors influencing wave velocities, S-waves, C-waves, Anisotropy. Geophysical Data processing, Discrete Fourier Analysis, Statistical analysis and interpretation of geophysical data Seismic Modeling and Inversion, Principles of Migration Hours 10 10 10 10 10 10 Mode of Delivery: This course is mainly lecture based, with exercises, assignments and tests. Assessment Assignments, exercises and tests Final Examinations 30% 70% Reading list BLAKELY R. J. (1995). Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications. Cambridge University Press, New York. BURGE H. R. SHEEHAN A. F. and JONES C. H. (2006). Introduction to Applied Geophysics: Exploring the Shallow Subsurface. CLAERBOUT, J. F., (1976): Fundamentals of Geophysical Data Processing. Blackwell. KEAREY, P. BROOKS B. M. and HILL I. (2000). An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration 3rd edition. Blackwell Science Ltd. SIMAAN, M. & AMINZADEH F., (1989). Advances in Geophysical Data Processing: Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems in Petroleum Exploration. JAI Press, Greenwich. NIKRAYESH M., ZADEH L. A. and AMINZADEH (2003), Soft Computing and Intelligent Data Analysis in Oil Exploration, Volume 51 (Developments in Petroleum Science), Elsevier Science. KEAREY, P., BROOKS, B.M. & HILL, I., (2002). An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration. 3rd edition. Blackwell Science Ltd. SHARMA, P.V. (1986). Geophysical Methods in Geology. Prentice Hall, Englewood, New Jersey. 442pp. SHERIFF R. E. & GELDART, (1995). Exploration Seismology. Cambridge University Press, New York. TELFORD W. M., (1976). Applied Geophysics. Cambridge University Press, New York. UPADHYAY S.K., (2004). Seismic Reflection Processing: With Special Reference to Anisotropy. Springer-Verlag. 636pp. PEMBERTON S. G. (1992), Applications of Ichnology to Petroleum Exploration: A Core Workshop (S E P M Core Workshop) (Paperback), Sepm Society for Sedimentary.