Unit 4 Test Review
advertisement

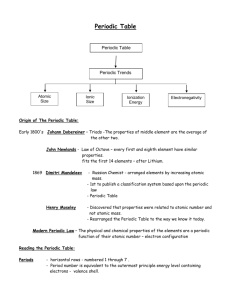
Name:_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Unit 4 Test Review Target 1: I can describe how Medeleev set up the periodic table and define periodic law. 1) How did Mendeleev set up his periodic table? 2) How was Mendeleev able to predict the properties of undiscovered elements? 3) Define periodic law. 4) How is the periodic table arranged today? Target 2: I can decide what elements have similar properties to a given element and explain why these elements have similar properties. 1) What elements have properties similar to Bromine? 2) Why do these elements have similar properties? Target 3: I can find and describe the following groups on the periodic table: alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, noble gases, lanthanides, actinides and main block elements. 1) Which group is Bromine a part of? _____________________ 2) Which group is Neon a part of? _____________________ 3) Which group is Potassium a part of? _____________________ 4) Which group is Strontium a part of? _____________________ 5) Which side of the periodic table are metals located? 6) Where are metalloids located? List 2 properties of a metalloid. Name:_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7) List three properties of metals and three properties of non-metals. 8) Which group of elements are the most reactive non-metals? Why? 9) Which columns on the periodic table contain the transition metals? Name 2 properties of transition metals 10) Which group of elements are the most reactive metals? Why? 11) Which groups of elements are always found in nature as part of a compound? In other words, which elements are not pure elements in nature? 12) Which elements are radioactive and synthetic? 13) Which group of elements are always found in nature as pure substances because they are very unreactive? 14) Which groups are the main block elements? Target 4: I can describe how transmutation creates synthetic elements. 1) How do we create synthetic elements? 2) What happens to the synthetic elements after they are created? 3) What is the process of changing one or two elements into another element? Target 5: I can describe what an alloy is and explain why they are stronger than most pure metals. 1) What is an alloy? 2) Why are alloys stronger than the 2 metals that make it up? Name:_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Target 6: I can define the following terms: electron shielding, ionization energy, atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electronegativity. 1) What is electronegativity? 2) What is ionization energy? 3) What is atomic radius? 4) What is nuclear charge? 5) What is electron shielding? Target 7: I can describe the patterns of the following on the periodic table: atomic number, electron configurations, electron shielding, ionization energy, atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electronegativity. Use assignment #13 to help you. 1) What element has the noble gas notation of [Ne]3s23p4? 2) What group does the element belong to if its electron configuration ends with 4s1? 3) What is the last part of an electron configuration for a Halogen like Bromine. In other words, what would its electron configuration end with? 4) Down a group what happens to electron shielding? Why? 5) Across a period what happens to ionization energy? Why? 6) Across a period what happens to the atomic number? Why? 7) Across a period what happens to electronegativity? Why? 8) Across a period what happens to electron shielding? Why? Name:_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9) Across a period what happens to the atomic radius? Why? 10) Down a group what happens to ionization energy? Why? 11) Down a group what happens to electronegativity? Why? 12) Down a group what happens to atomic radius? Why? 13) Which has a larger radius O or F? 14) Which has a larger radius Be or Mg? 15) Which has a higher ionization energy O or F? 16) Which has a higher ionization energy Be or Mg? 17) Which has a higher electronegativity O or F? 18) Which has a higher electronegativity Be or Mg?