Pediatric Airway Exam
advertisement

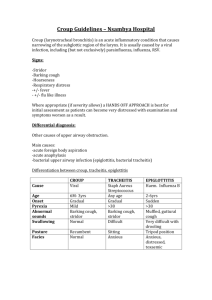
Pediatric Airway Exam 1. Which fact makes it more important to suction secretions in infants? a. They have large passages b. They are nose breathers c. They have harder cartilage d. They are displaced easily 2. How would you describe the shape of the epiglottis in children? a. T b. L c. U d. O 3. Where is the narrowest portion of the airway in children up to the age of 8 years? a. Cricoid cartilage b. Pharynx c. Trachea d. Vocal chords 4. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases is caused by the influenza virus? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 5. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases is caused by the Haemophilus influenza type B? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 6. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases is caused by a virus and is generally seen in children under the age of two? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 7. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases presents with a hoarse voice and a bark-like cough and wheezing? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 8. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases presents with a sore throat, fever, muffled voice and drooling? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 9. Which of the following common childhood airway diseases presents with the symptoms of a cold that worsens over a few days coupled with tachypnea? a. Epiglottitis b. Asthma c. Croup d. Bronchiolitis 10. How many back blows should be performed when clearing an obstructed airway in an infant? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 11. How should you position a child more than 1 year old if they become unconscious while trying to clear an obstructed airway? a. On their back with arms by their side b. On their back with arms above their head c. On their side with arms by their side d. On their side with arms above their head 12. How many chest thrusts should be administered to an infant when clearing an obstructed airway? a. 5 chest thrusts b. 2 chest thrusts c. 2 chest thrusts d. 1 per second 13. How should you characterize your approach to pediatric patients? a. Airway management in children is the same as in adults b. Children are just little adults c. Children have features that make their care unique d. Children’s tongues are smaller in comparison to adults 14. You arrive at the scene of a 4 year old whose mom states he was fine 4 hours ago, but now has a temperature of 105 degrees. Upon examination, you find he is drooling and has high pitched noisy respirations. How would you transport this patient: a. Place the patient on the stretcher and transport after establishing an IV. b. Allow the patient to transport on his mother's lap after establishing an IV. c. d. Transport by air ambulance. Transport in the most non-threatening position and not attempt to place an IV. 15. You arrive at the scene of a 6 y/o with difficulty breathing. You note that the patient is retracting and has nasal flaring. Pulse oximeter reads: 89% on room air. What does this tell you? a. This is a sign of impending respiratory failure. b. This child should be transported by air ambulance. c. This child has asthma and this is a normal finding. d. This child is in complete respiratory failure. 16. You are preparing a nebulizer with Albuterol for a 10-year-old child who is wheezing. 1 cc of Albuterol= 5 mg. According to the article, how much should this patient receive? a. 0.25 cc. b. 2.5cc. c. 0.50 cc. d. 1.5 cc. 17. As you listen to the lung sounds of an ill child, you hear expiratory wheezing with a prolonged expiratory phase. You advise the receiving emergency department that your patient is experiencing breathing problems probably due to _________ airway disease. a. lower b. upper c. inner d. outer 18. Your patient is a child who has had cold-like symptoms for several days and suddenly developed a barking cough. What do you think the barking cough is from? a. asthma b. croup c. epiglottitis d. pneumonia 19. Which of the following conditions would produce drooling, rapid onset of fever and stridor? a. asthma b. Croup c. epiglottitis d. pneumonia 20. Intercostal retractions occur: a. Between the ribs b. Below the ribs c. Above the clavicle and sternum d. Below the xiphoid process 21. Pre-hospital treatment of asthma includes ventilatory support, administration of ________________, and administration of an anti-bronchospasm medication such as Albuterol, Metaproterenol or subcutaneous epinephrine and rapid transport to the hospital. a. humidified oxygen b. non-humidified oxygen