tissues, integument
advertisement
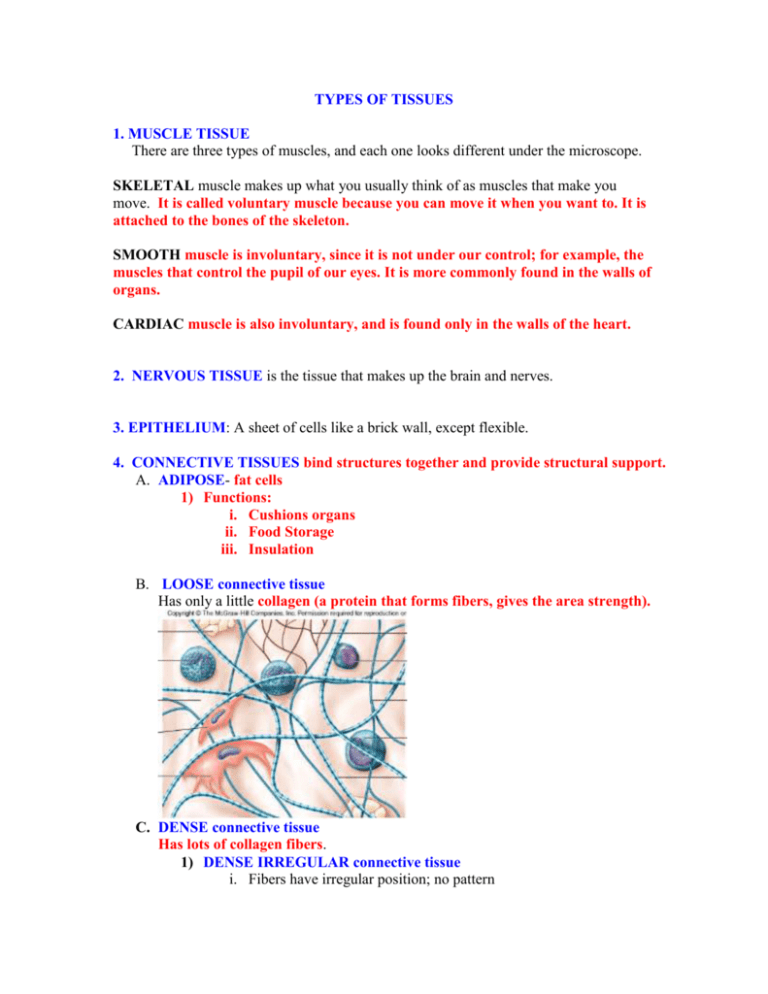
TYPES OF TISSUES 1. MUSCLE TISSUE There are three types of muscles, and each one looks different under the microscope. SKELETAL muscle makes up what you usually think of as muscles that make you move. It is called voluntary muscle because you can move it when you want to. It is attached to the bones of the skeleton. SMOOTH muscle is involuntary, since it is not under our control; for example, the muscles that control the pupil of our eyes. It is more commonly found in the walls of organs. CARDIAC muscle is also involuntary, and is found only in the walls of the heart. 2. NERVOUS TISSUE is the tissue that makes up the brain and nerves. 3. EPITHELIUM: A sheet of cells like a brick wall, except flexible. 4. CONNECTIVE TISSUES bind structures together and provide structural support. A. ADIPOSE- fat cells 1) Functions: i. Cushions organs ii. Food Storage iii. Insulation B. LOOSE connective tissue Has only a little collagen (a protein that forms fibers, gives the area strength). C. DENSE connective tissue Has lots of collagen fibers. 1) DENSE IRREGULAR connective tissue i. Fibers have irregular position; no pattern ii. Extremely strong in all directions iii. Found in areas of body where strength is needed, such as the skin 2) DENSE REGULAR connective tissue i. Fibers have a pattern, and run in same direction ii. Even more strong than irregular, but only in one direction iii. Found in ligaments, tendons, etc. D. SPECIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUES (discussed later in semester) 1. Cartilage a. Main cell type is CHONDROCYTE (“cartilage) b. Dense collagen; almost solid, very rigid c. Avascular (no blood vessels. Torn cartilage won’t heal). 2. Bone tissues a. Main cell type is OSTEOCYTE = “bone” b. The cells are almost solid, full of minerals (instead of fluid) c. Minerals are mostly the calcium that’s the same as limestone. 3. Blood tissue a. Main cell type is ERYTHROCYTE (red cell) b. PLASMA is the fluid the red blood cells float in. 4. Nerve tissue a. Main cell type is NEURON (nerve cell) b. Nerve cells are covered with a sheath made of fat, called myelin, which helps the nerve impulses to travel faster. c. specialized for conduction of impulses ORGAN SYSTEMS Now everything so far has been just an introduction. Now Anatomy class begins! DIRECTIONAL TERMS (Describe where things are) 1) Superior: towards the head 2) Inferior: towards the feet These are comparative terms, so you can’t say “He is taller than.” You have to say “He is taller than she is”. So you would say, “The neck is superior to the pelvis” 3) Anterior: towards the front of the body 4) Posterior: towards the back of the body 5) Superficial (external): Towards the external surface of the body “The skin is superficial to the muscles.” 6) Deep (internal): Toward the internal surface of the body “Bones are deep to the muscles.” 7) Proximal: Toward the heart 8) Distal: Toward the fingers or toes OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY We’ll discuss the organ systems of the body one by one. For each system, we’ll discuss its function, the individual organs, its tissues, and clinical significance. The tissue of the body can form systems, which are tissues and organs that work together for a similar function. We are going to study most of the rest of the course according to body systems. 1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 2. CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM RESPIRATORY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM (TAKE-HOME WORK) NERVOUS SYSTEM (TAKE-HOME WORK) ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 3. CANCER REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM GENETICS 4. BIOTECHNOLOGY ECOLOGY HEALTH We are going to start with the integument system, and then we’ll cover the digestive system. As soon as we are done with that, we’ll have the first exam. INTEGUMENT SYSTEM: Does anyone know what integument means? Integrity? Holding things together? What part of the body do you think this refers to? 1. Organs a. Skin b. Nails c. Hair d. Glands 2. Functions a. Protection 1) Abrasions 2) Infections from pathogens 3) UV light 4) Dehydration b. Thermal regulation (maintaining proper body temp) 1) Insulation = adipose layer 2) Cooling = sweat glands c. Sensory reception (touch, temp, pain, etc) d. Vitamin D production e. To separate one region from another; e.g. skin, stomach lining, blood vessel lining, intestine, heart. 1. ORGANS OF THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM A. SKIN (has three layers): Epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. 1) EPIDERMIS (outermost layer. “epi” means above). We talked about this layer when we talked about the tissues. Remember it has epidermal cells on top of a basement membrane. BASEMENT MEMBRANE joins an epithelium to underlying connective tissue. The connective tissue beneath the basement membrane is very important because it supplies O2 and nutrients. i. If you rub the skin, it stimulates cell division = callous NOTE: If you rub the skin too hard, the basement membrane tears away from the epidermis, and causes a gap, which fills with fluid. What’s this called? A BLISTER. The epidermis then dies because it’s too far away from nutrients. That’s why the top of a blister dries up. FUN FACTS ABOUT EPITHELIUM The 'bone' in a rhinoceros' horn is simply a mass of epithelium. 2) DERMIS (deep to epidermis) This is the layer underneath the epidermis that is loose and spongy and contains the hair follicles, nerve endings, a lot of blood vessels and collagen, which is a protein that forms fibers that give the area strength. In the fingers and toes, the dermis also has friction ridges that make fingerprints. The function of the dermis is to give support, strength, and shape to the skin, and to provide nutrients to the epidermis by their blood vessels. If you shave off the epidermis, like in a callous, it won’t bleed, but if you get a cut that goes through the basement membrane and into the dermis, it will bleed. 3) HYPODERMIS (“hypo” means below. Hypodermic needle) Varies tremendously in thickness: Shins = thin; Buttocks = thick. Functions 1) Stores fat 2) Cushions 3) Insulation of heat from blood vessels in this layer. Hypodermis is not connected to underlying tissue, such as muscle. Therefore, exercising muscle will not burn off fat only in that area. Fat is burned off equally over entire body. Losing 10 lbs is like loosing ¼” off whole body. More noticeable in face than in hips. By the way, there’s no such thing as cellulite. The term was invented by marketers. It’s just fat, the same as every other fat. No such thing as a cream to get rid of adipose. Liposuction is dangerous because hypodermis is very vascular, can bleed too much. SKIN COLOR; Caused by four things: 1) MELANIN: (dark brown pigment made by special cells called melanocytes in the skin). The more melanin you make, the darker the skin. 2) CAROTENE: (a yellowish/orange pigment). Common in Asian skin types. 3) SKIN THICKNESS: thinner skin see blood vessels, looks pinker 4) HEMOGLOBIN: Even veins are red because blood is red. But when you look at veins through the adipose layer, they look blue. SKIN DISORDERS BURNS: Three types: FIRST DEGREE: Minor burn to the epidermis; sunburn SECOND DEGREE: Dermis separates from epidermis; blister THIRD DEGREE: Hypodermis is burned. 2˚ and 3˚ burns over a large part of the body gives a survival chance proportional to the amount of skin left. 60% burn = 60% chance of dying. Why are deep burns so dangerous? 1) Infection 2) Dehydration: nothing to keep fluid in body. SKIN CANCER: Three major types: 1) BASAL CELL CARCINOMA: Cancer of the dermis. Almost never metastasizes or invades the hypodermis. Looks like shiny nodules 2) SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA Cancer of the epidermis. 25% of all cancers Will metastasize if not treated. 3) MELANOMA When the melanocytes (that produce the pigment melanin seen in freckles and moles) divide uncontrollably. Highly metastatic. DECUBITUS ULCERS Epidermis is destroyed, underlying tissue is exposed. How decubitus ulcers form: If you’re sitting down, weight of the body presses against blood vessels, no blood flow to skin of buttocks. In you, it’s ok, because you’ll be walking around again in a half hour. But if it there is no circulation for longer than a couple of hours because one can’t move, tissues can’t get oxygen. Ulcer forms, can get gangrene or go systemic and die of infection. That’s how Christopher Reeve died. PSORIASIS: An autoimmune disease of the skin, hereditary; causes flaking skin; not a cancer. No cure. CONTUSION: “Bruise” Why does a bruise look black and blue? The vessels in the hypodermis is ruptured, and the blood leaks upward; looks blue. As it gets pushed upwards, it appears green/yellow. The depth determines the color of the bruise. WRINKLES Over time, collagen fibers align themselves more and more as they are always being pulled in the same direction: smile, frown. Skin begins to sag because body makes less collagen. Pinch your grandma’s skin. Does it bounce back, or ooze back? What can be done about wrinkles? Not much. Face lift clips off extra skin. Creams don’t work. Trying to fix a collagen problem with a cream is like trying to shampoo your carpet by putting the cleaner on the roof! BOTOX This is a deadly poison which paralyses the muscles, making them sag. That releases the tension, and relaxes the skin line. In 3 months, new muscle cells are made, so wrinkles come back, and need new injection. COLLAGEN INJECTION Collagen is injected into hypodermis. Can last a couple of years. MOISTURIZER CREAMS The secret ingredient of all moisturizers is WATER. They work superficially on the epidermis. The top layer of skin is dead, it just hasn’t flaked off yet. Although it is waterproof, it swells when wet. So, if you put a moisturizer on skin, the dead cells on top will expand and hide wrinkles. Get the same effect by soaking in the tub, and that’s cheaper. If you soak in water a long time, it over-swells, and fingers appear deeply wrinkled. Moisturizers work best if you soak in the tub so the natural water gets into the cells, then the cream prevents evaporation. If you wait more than 10 minutes after drying off, the cream doesn’t have much effect because the water has already evaporated. Once the water in the skin evaporates, it takes more water with it, so you’ll wind up with dryer skin if you don’t put moisturizer on it. TATTOOS Pigment is injected into the dermis. If the needle is sterile, there’s no health risk. However, the pigment diffuses with time. What looks good in your 20’s will look like a blob when you’re 50. Laser treatment is just burning the tattoo off all the way to the dermis; leaves scar. I used to laser off a lot of gang tattoos in my last year of medical school at USC. NOSE PIERCING Let me warn you about nose piercing: There is a region of the face called the “Danger Triangle” which goes from between your eyes to your upper teeth. All of the blood in this region drains into the brain, so infection there can cause meningitis and death in 24-48 hours. A cut on the forehead isn’t so bad, but a cut on the cheek near the nose is considered very dangerous and needs immediate antibiotics. A nose piercing can become a serious infection because some of the worst bacteria in the body is in the nose…that’s why your mother always told you not to pick your nose. Can you imagine if you put a hole in your nose and it got infected? WARTS Warts are caused from a virus that can only get in if there is a break in the skin. It starts multiplying itself, forming a benign local tumor. Therefore they are found on the hands of people who get a lot of scratches and the feet of those who go outside without shoes. That’s it for the organ called skin; now we’ll move on to the organ called NAILS NAILS At the nail root, there is rapid division of skin cells, and as they die, the skin moves up and creates the nail, similar to hair formation. Taking calcium won’t make the nails any stronger because there is no calcium in skin cells. HAIR There are about 2 million hairs on the body; 200,000 on the scalp. Hair follicles are found in the dermis layer. The hair bulb is skin cells which are rapidly dividing. When they die, the new ones push them out, forming the hair. Hair is just dead skin cells. Each hair has its own tiny muscle that makes the hair stand up like when you get “goose bumps”. HAIR FOLLICLES If follicle is round, it makes straight hair. If it is oval, makes wavy hair. If it is oblong, makes curly hair. Laser treatment or electrolysis to remove unwanted hair is a beam that tries to kill the root of the hair. But if the hair is not in the cell division phase, it will not die; that’s why the procedure has to be repeated weekly in an attempt to get the hair while it’s dividing. Also, if the follicle is curved, the beam might not reach the root, and the treatment will never be successful on that hair. Chemotherapy kills cells which are rapidly dividing (cancer cells), so hairs in follicles die as well as bone marrow cells. That’s why chemotherapy patients are bald. GLANDS 1. SEBACEOUS GLANDS produce sebum, which is OIL that coats the hair and epidermis. IT IS NOT A SWEAT GLAND. It keeps the skin from getting dry and brittle. The problem is that when you wash the oil away, the skin gets dry. Has anyone heard of moisturizers with the ingredient lanolin? It is made from sheep sebum. Some of the largest sebaceous glands are associated with the smallest hairs (face). When they get clogged, the gland swells PIMPLE. In puberty, there is an increase in hormones, and an increase in gland production leading to pimples. A blackhead is sebum which has bound to an oxygen molecule. 2. ECCRINE SWEAT GLANDS form the SWEAT when you exercise. 3. APOCRINE SWEAT GLANDS coat the pubic hairs. The hairs function as a wick to draw the secretions to the surface. These glands also produce hormones called PHEROMONES. Pheromones function to regulate menstrual cycles of females. If you put several women in one room for months, their menstrual cycles will all start to occur at the same time. Pheromones also function for sexual attraction. There is no conscious odor. The smell from the axilla is from bacteria that are attracted by the gland. Expensive perfumes have pheromones. Guess where they get them from? The anal glands of male cats! They are designed to attract females. They are used so women will buy expensive perfume. 4. MAMMARY GLANDS secrete milk. 5. CERUMINUS GLANDS are only found in the ear, and they produce wax. E. They keep the ear canal from drying out F. They prevent insects from crawling in; they don’t like walking on the wax.









