procedure
advertisement

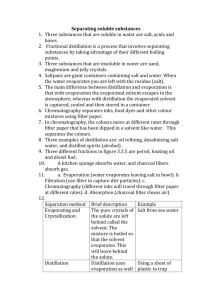
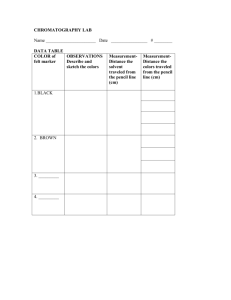
EXPERIMENT 10 TRANSAMINATION (ROUND PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY EVALUATION) PRINCIPLE Transamination reactions are catalyzed by transaminases (aminotransferases). In this process the α -amino group of most amino acids is transferred to α -Ketoglutarate to form glutamate and the corresponding new α-Keto acid. Every transamination reactions are catalyzed by specified transaminase. Transaminases are widespread in each organs of organism. In this experiment, liver homogenate is under water bath with glutamate and pyruvate,while alanine aminotransferase catalyzes the transfer of the amino group of glutamate to pyruvate, thus alanine yields. Using Round paper chromatography to evaluate the existing of alanine and to prove transamination in the tissue. In order to prevent pyruvate would be oxidized or reduced by other enzymes in the tissue, iodoacetic acid may be added to inhibite some enzymes of glycolysis pathways. PROCEDURE 1 The preparetion of liver homogenate:Obtain fresh animal liver 1g, add precooling 0.01mol/L(Ph7.4) 5ml phosphate buffer saline ,triturate it in a morta. 2 Transamination reactions:Get 2 tubes, perform according to the following table: addition(drops) determination tube control tube liver homogenate 10 10 (bath in boiling water for 10 minutes) 0.25% iodoacetic acid solution 5 5 1% glutamate solution 10 10 bath in 40℃ water for 10 minutes 5% trichloroacetic acid solution 2 2 bath in boiling water for 5 minutes After cooling the tubes, filter with filter paper or 2000 rpm centrifuge for 3-5 minutes, transfer the upper liquid to the new tubes marked with the same number. 3 Paper chromatography evaluation: (1) Obtain a sheet of 12 cm diameter round filter paper.Draw two 2 cm vertical lines passing its center . Use the terminal point of the two lines as spot application and mark “determination”、“control” 、“glutamate” 、“alanine” on the edge of the paper corresponding to each point. 1 (2) Use 4 capillary tubes, absorb one drop of determination solution、0.1% glutamate solution、control solution、0.1% alanine solution respectively. Dot the solution at the corresponding points of the lines. Pay attention to the diameter of the spot less than 0.3 cm. While the spot is dried, dot the solution again, Each spot may dot for 2-3 times. (3) Stab a hole (1mm diameter) through the center of the filter paper using a pin, Get another filter paper strip (0.5×2.5cm). Roll it into a cylinder and twist it tightly as a lampwick, insert it into the hole from the reverse side of the dotting spot. (4) Add about 1 ml chromatography solvent to a 5 cm diameter watch-glass placed in a 10 cm diameter Petri dish. Put filter paper flatly on the Petri dish in order to soak the lampwick in the chromatography solvent. Cover the Petri dish with another one of the same size . Solvent rise along the lampwick to the filter paper and diffuse in a circle.( chromatography time is approximately 45-60 minutes).Allow the solvent diffuse to about 1 cm distance from the edge of the filer paper.Remove it from the Petri dish. Draw the edge of the solvent with a pencil.Dry it on a electric stove. (5) Development: Put filter paper flatly on the Petri dish.Spray 0.1% indene-triketon ethanol solvent.Dry it on the electric stove.. Purple arc patches then appear on the filter paper. (6) Draw the outline of the patches with a pencil. Record relevant data according to the following table. Calculate the Rf values. determination the distance from the spotting point to the center of the patches(cm) glutamate alanine control the distance from the spotting point to the edge of the solvent(cm) Rf value Contrast the Rf values of the patches of “determination”and“control” with the Rf values of the known amino acids, infer what amino acid they are. Explain transamination reactions on these grounds. 2