MAPPING MODEL
advertisement

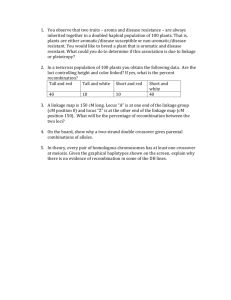
MAPPING MODEL When modeling recombination as a Poisson process (and neglecting crossover interference) the recombination fraction r between two loci is related to the distance between them by: (1) clog(1 2r) (LIU 1998) When c = -1/2 this equation results in (HALDANE 1919) mapping function (2) r 1 1 e2 2 and describes the probability of one or more crossover events occurring between two loci separated by physical distance . A related function describes the expected frequency of haploids having no apparent recombination between loci at distance : (3) h( ) 1 4 1 e 3 2 This value is equivalent to the expected frequency of haploids in which two loci separated by a physical distance share the alleles of one of the parents. Assuming that recombination rate is uniform over a chromosome, the distance between two loci can be rescaled to an average recombination rate so that: (4) h() 1 4 1 e 3 2 The expected frequency of haploids for which a locus at a physical position xi on chromosome j has the same parent as the locus at position is then given by: (5) x 4 i 1 h(x i ) 1 e 3 j 2 The scaled microarray data for polymorphic features can be fit to this function, and the parameters and can be estimated numerically for each chromosome by likelihood maximization. If all haploids in a pool share some trait, the maximum likelihood estimate of estimates the physical location of the cosegregating locus.