USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Gene Mapping and Cloning 386075
advertisement

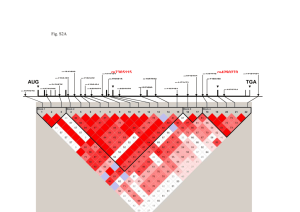
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Gene Mapping and Cloning 386075 >>> 00:00:00 SLIDE 1 of 13 Chapter 4 Gene Mapping and Cloning 386080 >>> 00:00:45 SLIDE 2 of 13 Gene Mapping: Linkage Analysis Determining: Where a gene is located How far apart two genes are Syntenic loci - on the same chromosome Linked loci - close enough together so that chance of recombination is less than 50% o o 386085 >>> 00:03:56 SLIDE 3 of 13 Gene Mapping: Linkage Analysis Importance: Cloning Genes Genetic Diagnostic Tests 386090 >>> 00:05:20 SLIDE 4 of 13 386095 >>> 00:12:53 SLIDE 5 of 13 386100 >>> 00:18:37 SLIDE 6 of 13 386105 >>> 00:25:19 SLIDE 7 of 13 Recombination Frequency In our example: 1/6 = 17% Provides measure of genetic distance between linked loci One centimorgan = 1% recombination One centimorgan = 1 million base pairs 386110 >>> 00:28:55 SLIDE 8 of 13 LOD (Log of Odds) Scores LOD = log10 P (recombination frequency = θ) P(recombination frequency of 50%) LOD score greater than 3 means loci are linked LOD less than -2 means there is no linkage 386115 >>> 00:29:42 SLIDE 9 of 13 How could the USMLE test your understanding of LOD scores? Interpret the following table of LOD scores and recombination frequencies (θ): θ LOD 0.0 -inf 0.5 1.7 0.1 3.5 0.2 2.8 0.3 2.2 0.4 1.1 0.5 0.0 The highest LOD score is at a recombination frequency of 10%, so the two loci are most likely to be 10 cM apart. 386120 >>> 00:34:00 SLIDE 10 of 13 Linkage Disequilibrium Specific alleles at two linked loci are observed together as a haplotype more (or less) frequently than predicted by chance alone The greater the linkage disequilibrium, the more closely linked the loci 386125 >>> 00:36:56 SLIDE 11 of 13 386130 >>> 00:42:12 SLIDE 12 of 13 386135 >>> 00:51:52 SLIDE 13 of 13 Gene Cloning Find linkage to a known marker Identify protein-coding regions Compare DNA sequences of these genes in affected and unaffected individuals