Supplementary Materials

Supplementary Materials
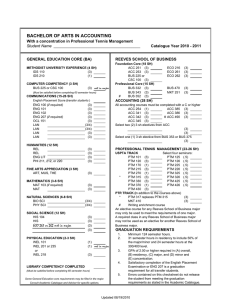
Table S1: Primers used for PCRs on DNA and cDNA
Name
1
1’
3
2
4
V5R
Mex2F
Mex4F
Mex6R
BD1 a b c d
49F
BDhDysf-4
51R
Sequence
5’ GGCTAAGAATTTCCACGGCC 3’
5’CATTTTGTCCCTCGTTAATGTTTTG 3’
5’ CACCATGGGAATTCCGCCTAAAAT 3’
5’ CCACCACAGGATTTTTCTTTCACT 3’
5’ CTTGTCATCGTCATCCTTGTAGTCG 3’
5’ CGTAGAATCGAGACCGAGG3’
5’ GCTATTGCACAAGGCAGTAAATAC 3’
5’ CATTTCTTCAAATATCAGTGTGAGTCG 3’
5’ AATCGATCGAATATGTATATTCACAGTGGC 3’
5’CCATGATTGAGAGTCTCGACAACG 3’
5’ CTGGCAGACTCCCAAACCCACACC 3’
5’ CCGAGGAGAGGGTTAGGGATAGGC 3’
5’ CCTGGATGACCTGAGCCTCACG 3’
5’ CCTTGTCATCGTCATCCTTGTAGTCGC 3’
5’ CCT GGATGACCTGAGCCTCACG 3’
5’AAGAGGACTCGATGCCTGCC 3’
5’ CAGATCTGGAAGACCACACGTGCTG3’
Table S2: Sequence of the different BD PTM Mex6 titin
PTM1
PTM2
PTM3
PTM Mex6
δISEF
δISER
δESSF
CCTGTGGCCAACGCGTACCTCCAAACATATTTACATTACGACTCATAAAGT
TAGCAAAATTACAGTTGGGAAGTAGCAACAAAAATAATTTCATG
GGAATTCCTTTATGAAACAGCAGGGTCACCGAAAACAAGAAATCCTATTC
GCTTTCTATTGACTTTTAATGCACTAAGACAGTGTTCTCAACATGTGGGCC
GTGACCCCTGTGGCCAACGCGTACCTCCAAACATATTTACATTACGACTCA
TAAAGTTAGCAAA
CGAAAACAAGAAATCCTATTCGCTTTCTATTGACTTTTAATGCACTAAGAC
AGTGGTTCTCAACATGTGGGCCGTGACCCCTGTGGCCAACG
CATGATTGAGAGTCTCGACAACGTGAGGAACTGTATTAAAGGGTCGCAGC
ATTAGGAAGGCGGAGAACCACTGCTCTAGAACGATGCCATGC
CCGCGGAACATTATTATAACGTTGCTCGAATACTAACTGGTATTCTCTTCCT
CTTCTTTT
CTGCAGGATATCAAAAAAAAAGAAGAGGAAGAGAATACCAGTTAGTATTC
GAGCAACGT
CCCCAGAAGTAACATGGTCCTGTGGAGGAAGAAAAATCCAC
δESSR GTGGATTTTTCTTCCTCCACAGGACCATGTTACTTCTGGGG
Table S3: Oligonucleotides used for mutagenesis. The mutated bases are indicated in red.
ATG PTM Mex6 5’ GACCTGACAACCCTGATCATCA C GGACAGAAACAAGATG 3’
ATG1 PTM Mex4-6 5’ CAGTGTTCAGCTACAGCTTCCTTAA C GGTCCTTCCTCTAGTTGAAG 3’
ATG2 PTM Mex4-6 5’ GCTTCTCGTCTCAGTCAGTCCAAA C GTCTGCCTCCAAGCAGG 3’
ATG1-2 PTM Dysf 5' GGGAGAAGA C GAGCGACATTTATGTGAAAGGTTGGA C GATTGGCTTTG 3'
ATG3 PTM Dysf 5' GCTCGATCTCAACCGCA C GCCCAAGCCGCCAAGACAGC 3
ATG4 PTM Dysf 5' GGCAAGCTGGAAA C GCCTTGGAGATTGTAGC 3'
PTM Mex6-DS1 5' CGACAACG A GAGGAACTGTATTAAAGGGACGCAGCATTAGG 3'
Supplementary Materials and Methods
Directed mutagenesis for Exon Splicing Enhancer (ESE) and Intron Splicing Enhancer (ISE) modifications
For PTM Mex6, site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the QuickChange sit-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene) to insert an ISE sequence (ttctctt) determined by [23] to be an
ISE sequence highly present in splicing regulation sequences of the pmRNA in the muscle.
This sequence was inserted by using the primeurs δISE (
Table S2 ) in the intronic sequence.
Moreover, ESS sequences were found using FAS-ESS website ( http://genes.mit.edu/fas-ess/ ) and ESE determined using ESE finder ( http://rulai.cshl.edu/cgibin/tools/ESE3/esefinder.cgi?process=home ). After selection, one ESS sequence was modified by one ESE sequence using directed mutagenesis according to this modification: tcc tgt ggT gga aga aaa > tcc tgt ggA gga aga aaa using the primers δESS ( Table S2 ).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
FIGURE S1
Figure S1.
Exon Splicing Enhancer (ESE) and Intron Splicing Enhancer (ISE) modifications. a/ Representation of the ISE and the ESE modifications of the PTM Mex6.
The ISE sequence was inserted in the chimeric intron of the PTM. A prominent ESS sequence present in the Mex6 exon carried by the PTM was removed by modifying a T in a A, leading to the creation of 3 ESE recognized by different factors. b / Western Blot on cell extracts obtained 48h after cotransfection of the different modified PTMs Mex6 (with the ISE, ESE or both). Upper panel: presence of the V5 and Flag tagged proteins. Middle panel: presence of the unexpected protein due to the expression of the PTM at 16 kDa. Lower panel: Actin as control. Images were cropped to focus on the proteins of interest.
b/ Ratio of V5/FLAG staining in Arbitrary Unit (AU) for cotransfection of the PTMs with BD domains and splicing modifications.
Quantification was performed on 3 experiments using the Odyssey software.
*=p<0.05 compared to PTM2. Localization of the PTM BD is indicated on Figure 3.
FIGURE S2
Figure S2.
Human and mouse dysferlin intron 48 homology. a/
Alignment of the human and the mouse dysferlin intron 48 targeted sequences in the trans -splicing strategy using multalin software (http://multalin.toulouse.inra.fr/multalin/) [1]. Arrows show the beginning and the end of the sequence recognized by the BD of the PTM hDysf. The result shows that 155 bp of the BD sequence of the PTMhDysf are similar to the mouse intron sequence, corresponding to 62% of homology between BD of the PTM hDysf and the mouse intron 48.