University of Missouri
advertisement

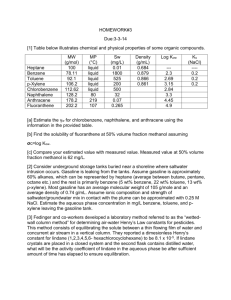
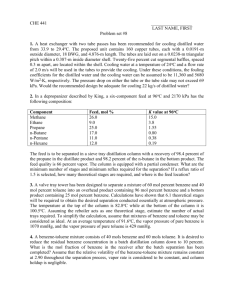
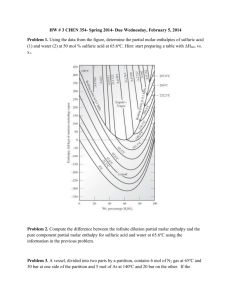
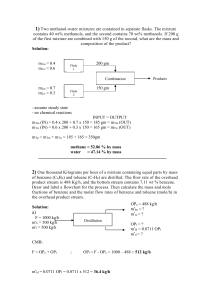
University of Missouri-St. Louis Department of Chemistry Chemistry 1111 Name ___________________ Final Examination May 10, 2007 There is a Periodic Table and some other useful information attached to the end of this examination. You may leave once you have completed the examination. 1. Nickel has a face-centered cubic unit cell. How many Ni atoms are there in a unit cell? (Diagrams of some typical unit cells are provided at the end of the exam) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 5 2. If the edge of a Nickel unit cell is 3.54 x 10-10 m in length, what is the radius of a Ni atom? a. 1.76*10-10 m b. 1.25*10-10 m c. 4.98*10-10 m d. 3.54*10-10 m e. not enough information to tell 3. Calculate the molality of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.0 g of sodium chloride in 500 g of water a. 0.34 molal b. 0.17 molal c. 0.428 molal d. 0.856 molal e. cannot be determined without the density of the solution 4. Which of the following processes does not result in an increase in entropy? a. dissolving NaCl in water b. the movement of electrons in their orbitals around the nucleus. c. the evaporation of water. d. the melting of ice at 298 K. e. the burning of jet fuel. 5. What is the mol fraction of benzene in a solution containing 7.8 g of benzene, C6H6, 9.2 g of toluene, C7H8, and 5.3 g of xylene, C8H10. a. 0.35 b. 0.40 c. 0.333 d. 0.2 1 6. Consider the molecules CH3CH2CH3, CH3CH2OH, C2H6, and CH3OCH3. Which is the most polar? a. CH3CH2CH3 b. CH3CH2OH c. CH3OCH3 d. CH3CH3 7. One can purify water by a method known as "reverse osmosis", which consists of forcing the pure solvent through a semi-permeable membrane with a pressure that exceeds the osmotic pressure of the solution. Which of the following aqueous solutions would require the greatest pressure to purify by reverse osmosis? a. 1.0 mol Cu(ClO4)2 per liter of water b. 1.0 mol NaCl per liter of water c. 1.0 mol FeCl3 per liter of water d. 5.0 mol glucose (C6H12O6) per liter of water 8. Which of the following best describes a solution? a. a homogeneous mixture b. a heterogeneous mixture c. a heterogeneous pure substance d. a homogeneous pure substance. 9. The solid p-dichlorobenzene melts (and freezes, of course) at 53.1 °C. It is often used to determine the molar mass of an unknown substance by freezing point depression measurements because it has a very large Kf value, 7.10 °C kg mol-1. A solution of 1.52 g of the drug sulfanilamide in 10.0 gram of p-dichlorobenzene freezes at 46.7 °C. What is the molar mass of sulfanilamide? 10. Circle which of the following compounds are likely to have a permanent dipole moment. a. CH2=CH2 b. Br2 c. CHCl3 d. CCl4 2 11. Which phase transition is represented in this diagram? a. b. c. d. liquid to gas solid to gas liquid to solid solid to liquid 12. For most gases, decreasing the temperature generally a. increases the solubility of the gas. b. decreases the solubility of the gas. c. has no effect on the solubility of the gas. d. causes the gas in solution to fizz. 13. Which of the following compounds has polar bonds but no net dipole moment? a CCl4 b. NH3 c. H2O d. Br2 14. The fusion enthalpy of sodium is 2.64 kJ/mol, its vaporization enthalpy is 89.6 kJ/mol and the melting and boiling temperatures are 97.8 °C and 883 °C, respectively. Calculate the fusion entropy of sodium. 3 15. The vapor pressures of pure benzene and pure toluene at 93 °C are 500 mm and 260 mm Hg, respectively. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with the liquid if the composition of the liquid is in the ratio of 2 mol of toluene for every mol of benzene? a. benzene/toluene = 1.92 b. benzene/toluene = 0.52 b. benzene/toluene = 0.96 d. there is no vapor because the solution is not boiling Supplemental material Some typical cubic unit cells. 4