Proposal for the optional course:
advertisement
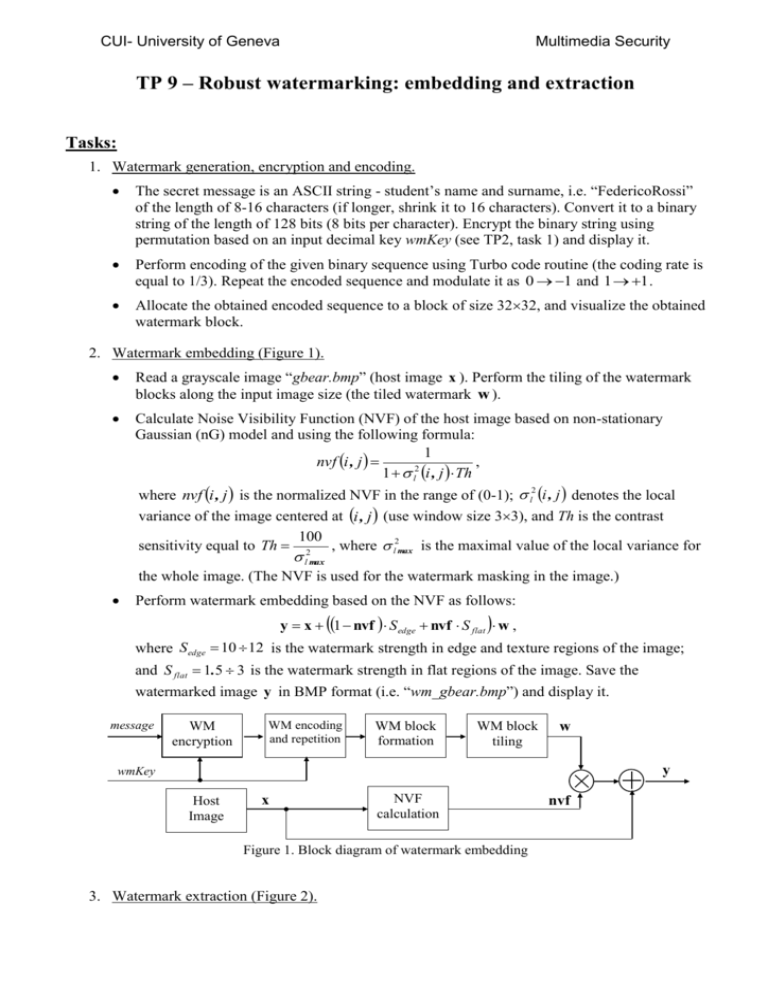
CUI- University of Geneva Multimedia Security TP 9 – Robust watermarking: embedding and extraction Tasks: 1. Watermark generation, encryption and encoding. The secret message is an ASCII string - student’s name and surname, i.e. “FedericoRossi” of the length of 8-16 characters (if longer, shrink it to 16 characters). Convert it to a binary string of the length of 128 bits (8 bits per character). Encrypt the binary string using permutation based on an input decimal key wmKey (see TP2, task 1) and display it. Perform encoding of the given binary sequence using Turbo code routine (the coding rate is equal to 1/3). Repeat the encoded sequence and modulate it as 0 1 and 1 1 . Allocate the obtained encoded sequence to a block of size 3232, and visualize the obtained watermark block. 2. Watermark embedding (Figure 1). Read a grayscale image “gbear.bmp” (host image x ). Perform the tiling of the watermark blocks along the input image size (the tiled watermark w ). Calculate Noise Visibility Function (NVF) of the host image based on non-stationary Gaussian (nG) model and using the following formula: 1 , nvf i , j 2 1 l i , j Th where nvf i , j is the normalized NVF in the range of (0-1); l2 i , j denotes the local variance of the image centered at i, j (use window size 33), and Th is the contrast 100 sensitivity equal to Th 2 , where l2max is the maximal value of the local variance for l max the whole image. (The NVF is used for the watermark masking in the image.) Perform watermark embedding based on the NVF as follows: y x 1 nvf S edge nvf S flat w , where S edge 10 12 is the watermark strength in edge and texture regions of the image; and S flat 1.5 3 is the watermark strength in flat regions of the image. Save the watermarked image y in BMP format (i.e. “wm_gbear.bmp”) and display it. message WM encryption WM encoding and repetition WM block formation rep WM block tiling w y wmKey Host Image x NVF calculation Figure 1. Block diagram of watermark embedding 3. Watermark extraction (Figure 2). nvf CUI- University of Geneva Multimedia Security Extract the watermark from the watermarked image y using the following formula: ˆ blind y xˆ W iener , w where ŵ blind is the estimated watermark, and x̂W iener is the result of Wiener filter applied to the watermarked image (use window size 33). Visualize the extracted watermark. Perform the untiling of the estimated watermark (inverse operation to the tiling based on data averaging) to the watermark block of size 3232 and convert to a vector. Shrink the vector twice (inverse operation to repetition) by data averaging and normalize it with respect to its standard deviation. Perform the decoding of the obtained sequence using Turbo code routine (use the same coding rate). Decrypt the decoded binary string using inverse permutation and retrieve the secret message (convert to ASCII string). Compare the obtained decoded binary string and secrete message with the corresponding input ones. Apply several attacks to the watermarked image y (i.e. filtering, JPEG compression, cropping, scaling) and try to retrieve the hidden message. Explain why the different operations and data manipulations (such as encoding/decoding, tiling/untiling, encryption/decryption, sequence repetition/shrinking, etc.) were used for given robust watermarking technique. Make the conclusions. Wiener filter x̂W iener WM image y ŵ WM block untiling WM sequence formation WM decoding WM decryption retrieved message wmKey Figure 2. Block diagram of watermark retrieval Useful information: The necessary files for data encoding/decoding using Turbo code routines are placed at http://cui.unige.ch/~ms/TP/Software/TurboCode. The images for testing are placed at http://cui.unige.ch/~ms/TP/Images/.