Vocabulary Unit Four The Ecosystem and the Environment # 1-10
advertisement

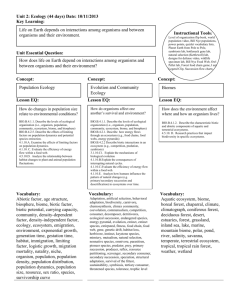
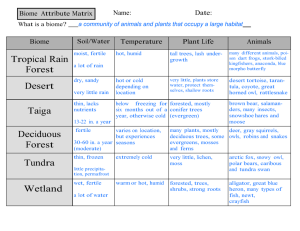
Vocabulary Unit Four the Ecosystem and the Environment 7th Science NPMS Mr. Giordano/Ms. Bellitti Name: __________________________________________ Date: __________ Per: ____ Vocabulary Words 1. Population Size – total number of species living in a defined area 2. Population Density – the number of a species in a specific area (measured based on that area- surface or cubic) 3. Limiting factors – anything that has impact which changes the population of a species (land, food water sources, mates, predators, human encroachment) 4. Competition – interaction between species fighting for survival; to battle for dominance – food sources, living space, mates 5. Predator – carnivore- predator attacks, hunts or kills other animals (prey) 6. Prey – an organism, plant or animal consumed, hunted, attacked by the predator 7. Symbiosis – cooperation of the species to assist another species for survival (certain birds on buffalo eat the parasites off the buffalo) 8. Parasitic – relationship between two organism -attaches itself to a host for food or shelter (flee on dog) 9. Climate – pattern of average of year round temperature, rain, snow – etc… (not daily weather) 10. Biomes – specific climate area contains living and nonliving things – forest, grass lands, marine (salt water), fresh water 11. Tundra – permafrost, severely cold biome, limited growth of tress and plants (no deep roots) due to the climate 12. Deciduous Forest – continuous growth seasonally, near coast and no extreme climate predominately trees that loose their leaves 13. Coniferous Forest – evergreen/cone bearing predominately and deciduous tress as well. 14. Rain Forest – over 100 inches of rain fall within one year - very diverse plant/animal life (70-85% of all plant/animal life on Earth) 15. Grassland – area that has sporadic/seasonal rainfall, heavy or no rain…extremes- rain and temperature (limited or no trees due to lack of water) 16. Desert – sandy terrain, very little rain/vegetation (plant life) extreme temperatures 17. Marine Biome – salt water area; climate area contains living and nonliving things 18. Still Water – water that does not flow; land locked; no outlet or inlet 19. Running Water – water that continuously flows/moves to larger main body of water; inlet and outlet 20. Shallow Seas – oceans and continents meet; sunlight reaches the bottom levels to create diverse life in the water (photosynthesis) 21. Deep Ocean – area of ocean that sunlight does not reach; depth about 1 mile (down) 22. Coral Reef – part of the shallow seas, sunlight reaches area bottom, skeletal sea life remains; greatest diversity of sea life in the seas/oceans 23. Natural resources – non-man made; provided or found in nature; examples: earth, land, air 24. Conservation – wise and careful use of natural resources, to preserve natural resources; planting trees after cutting trees down (to replace resource) 25. Biosphere – all areas of earth that supports life (biome) --large area (NJ forest) 26. Ecosystem – specific system area that interacts with multiple organisms – middle area (Union County) 27. Communities - ecosystems living in a specific location – small area (New Providence) 28. Populations – total number of organisms that belong to a specific species in a specific area 29. Habitats and Niches – location or living environment; role that organism take or plays in that environment (rabbit lives in grassy field- eats plants– prey to predators ) 30. Food Chain – series transfer of energy through organisms in an ecosystem 31. First-Level Consumer – herbivore – plant eating animal 32. Producer – plants or plant like which makes own food (herbivore) 33. Second-Level Consumer - eats a first-level consumer 34. Decomposers – energy from once living organisms ( fungi) 35. Food Web – relationships of organism and energy transfer 36. Energy Pyramid – shows the energy levels -plants (producers) at bottom…apex predator (humans) at top 37. Third-Level Consumer – apex predator ( polar bear) - eats whatever chooses 38. Water Cycle – process of evaporation( liquid to gas), condensation( water droplets form ) and precipitation (water released into the atmosphere- liquid) rain/snow/sleet/hail 39. Evaporation – water from liquid to gas 40. Condensation – gas returns to liquid - water droplets formed 41. Precipitation- liquid released into atmosphere 42. Nitrogen Fixation - % of air made of nitrogen - bacteria aids in plant use- absorb for growth 43. Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Cycle – plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis; humans absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide 44. Succession – slow or gradual change of biome to another biome (maybe due to climate change or human impact ) Population size: The amount of organisms and species in and area Population density: The number of a particular species who live in an area Limiting factors: A change in an environment that impacts the population size Competition: contest between organisms to fight for food, shelter, life Predator: kills for a living (orders from the menu) Prey: An animal eating another animal (is on the menu) Symbiosis: when two different species interact to survive (cap buffalo with the help of ox peckers to help clean) Parasitic: one organism attaches to the host when the host gets harmed but then ides (tic on the buffalo) Climate: the average conditions throughout the year in a particular area Biomes: an area that is characterized by the animals that lived there Tundra: A treeless area having a permanently frozen subsoil and supporting low-growing vegetation (lichens, mosses, and stunted shrubs) Deciduous forest: a type of forest in which the dominant species of trees and other woody vegetation that make up the forest are those species that shed their leaves during the cold months of the year and re-grows new leaves the next spring in time for the growing season. Coniferous forest: largest biome, mostly cone baring trees with seeds, soil is not fertile, small vegetation (softwood is very popular which produces paper) Rain forest: a tropical woodland with an annual rainfall of over 100 inches marked by big leaves from evergreen making a canopy over the Grassland: an area the is dry for long periods in the summer and freezes in the winter (grasses, herbs, not too many trees or shrubs) Desert: A dry, often sandy region of little rainfall, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation. It is permanently cold that is largely or entirely lack of life. Marine biome: the water that is on the earth's surface which covers three fourths of the earth. There are thousands of animals and plants in the biome. These plants and animals are affected by events in the waters. Still water: a flat or leveled area of a stream where no flow or motion of the current Running water: water that is always moving (river) Shallow seas: the majority of ocean. Shallow seas are rich with coral reefs, mangrove swamps, kelp forests and sea-grass plains, and include open waters off icy islands, thick with penguins, krill and whales. Deep ocean: the lowest layer of the sea (over a mile deep), low temperatures, intense pressure, dark (no light) Coral reef-marine biomes with the greatest diversity of life for their tiny area, sunlight gets to the bottom, animals that keep building on each other. Natural resources supplies directly from the environment used for animal for survival (without human interaction) Conservation: having resources for a time of need (wise use) Biosphere: all the parts of the earth in which they study all living things. Ecosystem: all living things living together and get along Communities: a part of the ecosystem Population: number of (animals, plants, etc) that number of a particular item. Habitat: some place where you live Niche: What is your environment Food chains: a series of animals how they are eating and who is eating them (energy transfer) First-Level Consumer: (primary consumer), is an animal or fish that feeds on the lowest level of a community's food web, mainly plants Second Level Consumer: consumers eat 1st order consumers (gecko, wolf) Producer: serves as a source of food for other organisms in a food chain. They include green plants, which produce food through photosynthesis, and certain bacteria that are capable of converting inorganic substances into food through chemosynthesis serves as a source of food for other organisms in a food chain. Producers include green plants, which produce food through photosynthesis, and certain bacteria that are capable of converting inorganic substances into food through chemosynthesis Decomposers: Decomposers and scavengers break down dead plants and animals. They also break down the waste of other organisms. If they weren't in the ecosystem, the plants would not get essential nutrients, and dead matter and waste would pile up Food Web: a graphical description of feeding relationships among species in an ecological community (of who eats who), shows how energy and materials flow through a community of species as a result of these feeding relationships. Energy Pyramid: the graphical representation of the trophic levels (nutritional) by which the incoming solar energy is transferred into an ecosystem. The source of energy for living beings on Earth is the Sun. Third-Level Consumer: eat 2nd order consumers (dog, bear, etc) Water Cycle: (hydrologic cycle) is the journey water takes as it circulates from the land to the sky and back again. Evaporation: the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas or vapor. It is the primary pathway that water moves from the liquid state back into the water cycle as atmospheric water vapor Condensation: It is the process in which water vapor in the air is changed into liquid water. Condensation is crucial to the water cycle because it is responsible for the formation of clouds Precipitation: It is water released from clouds in the form of rain, freezing rain, sleet, snow, or hail. It is the primary connection in the water cycle that provides for the delivery of atmospheric water to the Earth. (rain) Nitrogen Fixation: The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into compounds, such as ammonia, by natural agencies or various industrial processes Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Cycle: The oxygen produced during photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration. The carbon dioxide produced in cellular respiration is used in photosynthesis. Succession: is the slow, regular sequence of changes in the development of communities of plants and animals