Diuretics
advertisement

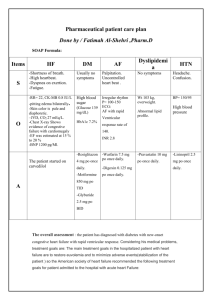
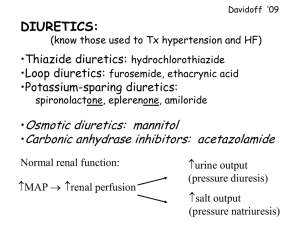
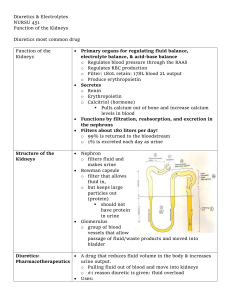
DOWNRIVER CARDIOLOGY CONSULTANTS PATIENT EDUCATION INFORMATION REGARDING: DIURETICS Diuretics are utilized to increase the elimination of fluid and salt from the body through your urine. There are different categories of diuretics. Generally, the thiazide type diuretics such as Hydrochlorothiazide are utilized in the treatment of hypertension or high blood pressure. Loop diuretics such as Lasix or Bumex are much more potent and are frequently used in the treatment of congestive heart failure. Both of these types of diuretics have a tendency to lose other salts in the body such as potassium and magnesium. A separate category of drugs are the potassium-saving drugs such as Aldactone, Dyridium (as combined in Dyazide or Maxzide) and Midamor. Diuretics should be utilized in the lowest dose possible to create a beneficial effect. In the treatment of hypertension, the dose of Hydrochlorothiazide may be as low as 6.25 mg daily. This is present in combination with some pills for hypertension. Otherwise the only way to take a dose this low is to split in quarters a 25 mg pill. The other option is to take half of pill at 12.5 mg. It may be necessary to increase the dose to 50 mg for the greatest effect. Usually though in the treatment of hypertension it is better to use several medications at lower doses in an attempt to reduce side effects and at the same time have a good effect on the blood pressure. In fact, sometimes adding another low dose medication provides a greater effect than doubling the original prescription. In the treatment of congestive heart failure the dosage of diuretic can be reduced once fluid loss is achieved. In some instances, the medication can be taken on an every other day regime or only when needed based on weight gain or the observance of fluid retention. Spironolactone is a diuretic that effects many of the hormone abnormalities that are found in congestive heart failure. Because of its effect both in this fashion and in saving potassium, it is recommended that everyone with a weakened heart muscle be placed on Aldactone. A low dose of 25 mg a day seems to be sufficient for this therapy. Higher doses may be required if correction of a low potassium is necessary. Generally, diuretics have a low side effect profile. The most frequent adverse effects relate to the loss of other salts in the body. In particular, a low potassium can be dangerous in relationship to heart rhythm problems. Magnesium may also play a role in heart rhythm disturbances. The higher dose of diuretic utilized may cause a higher incidence of salt abnormalities. However, this is not always true and is also related to the amount of salt ingested and lost through other mechanisms. Many patients will require a potassium supplement. In addition, potassium can be obtained through food sources such as bananas. However, bananas are not the highest source of potassium and dried fruits have considerably more potassium. Excessive use of diuretics may cause low levels of sodium and low blood volume leading to weakness and lightheadedness. LAB Sodium Potassium Chloride CO2 Magnesium 1st week 2nd week 3rd week 4th week 6th week 8th week 3 months If already on a diuretic: LAB Electrolytes Magnesium 3 months 6 months 9 months 12 months