3 - Coastalzone
advertisement

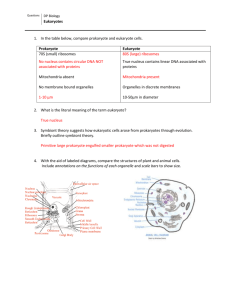
Week Three Chapter 5 Cell structure and function Cell Theory (the study of cells is cytology) All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary information 3 basic structures of all cell types: 1. plasma membrane - a physical boundary that separates the cell from the outside environment 2. organelles- internal structures that are suspended I the cytoplasm 3. cytoplasm – sort of jelly-like substance, mostly water. Prokaryotes v. eukaryotes Prokaryotes: the term means “before the nucleus”, they lack a distinct nucleus, though some have a nuclear area where DNA is found they lack a membrane to contain the DNA. Smaller than eukaryotes, grow faster. Bacteria and cyanobacteria, all are members of the kingdom Prokaryotae or Moneran Characteristics: lack most membrane bound organelles, have DNA in a concentrated region, tend to grow rapidly and divide often. Eukaryotes: protists, fungus, plants and animals. Characteristics: possess specialized membrane-bound organelles, Nuclear membrane, other specialized membranes Cell Size: Prokaryotes .2 –5 micrometers, eukaryotes 10-100 micrometers Surface to volume ratio limits cell size (OVERHEAD) Volume increases with the cube of the diameter (V=d3) Surface area increases with the square of the diameter As a cell grows its volume (cytoplasm) increases at a faster rate than its surface area (plasma membrane) Cell Shape Related to function – epithial cells are plate like, roughly square or spherical, nerve or muscle cells are elongated Micrsoscope invented in the 1600’s Cell Structure: Eukaryotes see drawing on page 89, figure 5-8) Cytoplasm: material outside of nucleus, consists of fluid and particles and membranes Nucleoplasm: material inside nucleus Nucleus – largest organelle) Nuclear envelope Double Membrane Has many nuclear pores Nucleolus (nuceioli plural) Site of ribosome assembly Ribosomes leave through pores and are found free in the cytoplasm or associated with Endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes are organelles that are part of the protien synthesis machinery Genetic Material: DNA Chromatin Seen in cells that are not dividing Decondensed DNA associated with RNA and proteins Chromosomes Seen in cells that are dividing Condensed DNA in a highly organized and compact form Endoplasmic reticulum sets of membranes continuous with the nuclear and plasma membranes Membranes act to divide up the cytoplasm into compartments and channels Two types: 1. rough ER: have ribosomes, mat be free or attached to the rough ER, ribosomal function: development of the primary structure of proteins 2. smooth ER: lack ribosomes, function: phosolipid, steroid synthesis Golgi Complex) stacks of flattened membranes (look like a stack of pita bread) sets of smooth membranes derived from the ER Functions: sorting and modifying proteins, ultimately transports products to the plasma membrane or are stored in the cytoplasm, also produces the lysosomes Lyosomes (in animals) Contain powerful digestive enzymes Function as the cell’s recycling center by digesting worn-out organelles or materials ingested by cell Rheumatoid arthritis is due to damage in joints due to leaky white blood cell lysosomes Microbodies Various organelles which regulate different metabolic reactions such as peroxisomes break down hydrogen peroxide, glyoxysomes are important in germiniating seeds Organelles involved with Energy Production and Utilization Mitochondria The power plants of the cell Site of cellular respiration, which converts organic molecules to ATP Double membrane bound; specialized membranes for energy production Have a small amount of their own molecules of DNA, ribosomes Chloroplasts Site of photosynthesis Also double membrane bound Inner structure Stacked membrane system (thylakoids) (3rd system of membranes) Pigments:chorophyl and others Also have their own DNA molecules Other plastids include leukoplasts which store starch and are colorless, and chromoplasts which store colored pigments READY FOR THE EXAM?