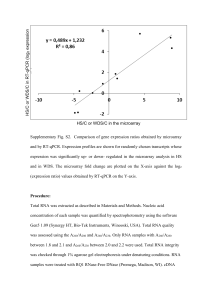
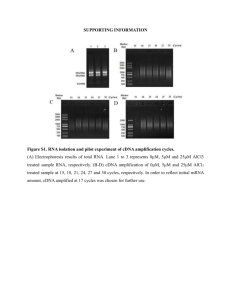
NPH_3432_sm_NotesS1
advertisement

Supporting Information Notes S1 Microarray design and production EST sequence production and analysis Five cDNA libraries were constructed from primary or secondary stem tissues, or from leaf tissues of young trees (80–120 cm tall) grown under greenhouse conditions (see Supporting Information Table S4). Four of the libraries (GQ009–GQ012) used healthy plants of Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray) x P. deltoides hybrid (clone H11-11) subjected to conditions that altered plant N status, and one library (GQ014) was made from leaves of naturally occurring Populus deltoides x P. balsamifera (jackii) inoculated with the rust-causing fungal pathogen Melampsora medusae Thüm. (1878). A complete description of the tissues and methods used for these libraries, together with other Populus libraries developed by the Arborea project (Université Laval), has been made available at www.arborea.ulaval.ca. For each library, cDNA was prepared from 500 ng poly A+ selected RNA, directionally ligated into the pBluescript II SK (+) vector (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA), and transformed by electroporation into Escherichia coli DH10B cells (Invitrogen) for propagation. The high-throughput sequencing procedures, which included colony selection, plasmid isolation, sequencing reactions and capillary analysis, were conducted as previously described by Pavy et al. (2005). Sequencing of 7,680 random cDNA inserts was performed from the 5’ end by using purified plasmid as templates. The sequence data from the 7680 cDNAs were trimmed to remove vector and low quality portions of the reads. In total, 5851 quality reads with at least 100 contiguous nucleotides that had Phred20 quality scores were obtained. Cluster analysis was carried out using as described by Pavy et al. (2005) and produced 4628 unique sequences, comprising 956 contigs (alignment of sequences from two or more cDNAs) and 3052 singleton ESTs. Functional annotations of the resulting unique consensus sequences (from contigs and singletons) were performed by sequence similarity searches using BLAST and HMM against several databases (nr, pfam, PopGI) as well as gene ontology assignment and classification into multigene families. The similarity searches were updated in March 2009. Selection of cDNA clones, amplicon production and microarray printing We selected 3444 unique cDNA clones to use in microarray production, based on the following criteria and procedures. We counter-selected against redundant sequences by forming clusters of sequences sharing greater than 95% identity over 100 bp and selecting a single cDNA per cluster to create a target, as described in Pavy et al. (2008). We also selected cDNAs to restrict the insert length to between 400 bp and 2000 bp for efficient PCR amplification and to ensure relative uniformity of amplicon concentrations (Pavy et al., 2008). Finally, to avoid including putative Melampsora cDNAs from library GQ014, we removed the sequences unique to that specific library and which did not match sequences from the first (unassembled) release of reads from the poplar genome sequence. The cDNA clones selected for inclusion on the microarray were robotically rearrayed from daughter glycerol stock and PCR amplified as described in Pavy et al. (2008). All of the rearrayed clones were sequenced from the 5’ end to enable validation of the identity of each cDNA spotted on the microarray. A sequence was obtained for 3120 (90%) of the original clones. Among the quality sequences (Phred 20 over 100 nt), 95% gave an exact match with the original sequence of the cDNA clone. Plasmid inserts were PCR-amplified in a GeneAmp PCR System 9700 (Applied Biosystems) by using 2.5 µl of lysed culture, 0.2 µM M13 reverse, 0.2 µM -21M13 forward, 15 mM MgCl2, 100 mM Tris-HCl, 500 mM KCl, 250 µM dNTPs, 9U AmpliTaq, and nuclease-free H2O to bring the final volume to 100 µl. PCR conditions were as follows: 5 min at 94°C denaturation; 31 cycles of 30 s at 94°C, 30 s at 50°C, and 2 min at 72°C; and 7 min at 72°C. Three microliters of each PCR product were run on a 1.2% agarose gel (E-Gel® Pre-cast Agarose Electrophoresis System, Invitrogen) to assess quality and yield was determined at 260 nm with a SpectraMax plus (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Of the 3444 clones, more than 94% of the amplicons consisted of a single product, which had sufficient intensity and the expected size. PCR products were robotically purified on Multiscreen PCR filter plates (Millipore, Etobicoke, ON), consolidated into 384-well plates, lyophilized by speed-Vac, and resuspended in 20 µl 50% DMSO. The cDNAs were printed on Corning UltraGaps slides with the Chipwriter Pro microarray printer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). SMP3 Microspot quill pins (TeleChem International, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) in a 48-pin tool were used to deposit ~7 nl (~0.2 ng cDNA) per spot onto the slide. The PCR products were randomized prior to spotting to avoid a biased distribution of cDNA from libraries or tissues. The resulting microarrays have a 4 × 6 subgrid layout with 160 spots per subgrid, with each spot having an approximate diameter and pitch of 100 µM and 200 µM, respectively.