Supplemental Information
advertisement

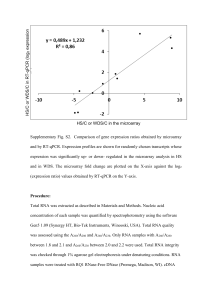
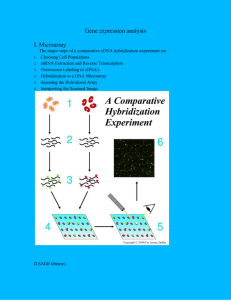
Supplemental Information (Methods) Serum starvation: Cells were seeded at 70-80% confluence and incubated overnight. The following day cells were washed once with PBS then incubated overnight in media containing 0.5% FBS for 18 hours. The cells were restimulated with media containing 10% FBS for various lengths of time. RNA labeling and array hybridization: Construction of the ARE-cDNA microarray and derivation of its content was previously described (Khabar et al., 2004b). Total RNA (15ug) was reverse transcribed using SuperScript II (Invitrogen) using primers from the Genisphere kit (Genisphere, Hatfield, PA). cDNA from control (vector) or experiment (TTP or mutTTP vector)-transfected samples were labeled with either Cy3 or Cy5, combined, and then hybridized to the cDNA array as per the manufacturer's instructions. Following hybridization at 50˚C in a sealed humidified chamber overnight, the slides were washed with SSC buffer (3M NaCl and 0.3M sodium citrate, pH 7.0) followed by ethanol fixation step, and then centrifuged to remove unbound cDNA before dendrimer hybridization. Hybridization mixes contained 3DNA dendrimer capture reagent labeled with Cy3 (control) and Cy5 (experiment). The hybridization mixes were then added to pre-warmed microarray slides and incubated for three hours in a dark humidified chamber at 50˚C followed by SSC washes to remove unbound dendrimer molecules. Scanning of the cDNA microarray was performed with ScanArray 5000 scanner (GSI Lumonics). The intensities of green and red fluorescent signals from each spotted cDNA sequence on the microarray were calculated using adaptive circle algorithm and mean intensity of the pixels (QuantArray Software, GSI Lumonics). The background corrected intensities were then normalized to total signal intensities to account for variations in overall RNA concentrations and labeling efficiencies. Signal thresholds were set using 80th percentile of empty controls. Intensity ratios were calculated as follows: background subtracted normalized Cy5 intensity/background subtracted normalized Cy3 intensity (experiment/control). At least three independent microarray experiments were performed in addition to dye-swapping where dye assignment is reversed and each gene is represented by n=2-4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR: RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using SuperScript II reverse transcriptase. For mRNA decay studies, Actinomycin D (5ug/ml) was added 1hour after restimulation with 10% FBS for various lengths of time after which cells were harvested for total RNA extraction using Trizol reagent (Sigma) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. An amount of 50-60ng of cDNA was used in qPCR reactions. Quantitation of mRNA was performed using Taqman expression assays (Applied Biosystems) designed for the following: ZFP36 (TTP), PLAU, PLAUR, MMP1 and human RPLPO and mouse -actin as endogenous controls. Real-time PCR reactions were performed in multiplex using TaqMan Universal Master Mix according to manufacturer’s instructions in a 96-well Chromo 4 thermocycler (BioRad). The primers span introns to control DNA contamination and the 6carboxyfluorescein (6FAM)-labeled TaqMan probe is targeted to intron-exon junctions for further control of DNA contamination and specificity. Relative mRNA expression was calculated using the standard curve method using a 4-point standard curve prepared from pooled samples. The mRNA expression in each sample was normalized to that of the endogenous control in which its TaqMan probe is labeled with a 5 reporter VIC dye (human RPLPO for human samples and mouse B-actin for murine samples). Reactions were set up in triplicate and R2 of the standard curves were 0.999 or greater.