Earth`s Materials Study Guide – Rocks, Minerals, and Fossils

Earth’s Materials Study Guide – Rocks, Minerals, and Fossils
3 Types of Rocks
Igneous
Igneous rock was once ________ but it has cooled and ____________.
The melted material is called _______ or _______ .
Igneous rocks may be glassy or grainy with crystals of different types of minerals in them.
_________ is an example of an igneous rock.
Sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are made at the bottom of ______________, when
_____________ settles and gets pressed and cemented together.
Some may contain pieces of animal shells or skeletons or other remains of plants or animals (___________________).
_________________ and limestone are examples of sedimentary rocks.
Metamorphic
Metamorphic rock was once another type of rock deep inside Earth, but _______and
____________ caused the minerals to change.
Rocks may have wavy _____________________.
Sometimes the rocks are formed by only intense ______________.
________________ and slate are examples of metamorphic rocks.
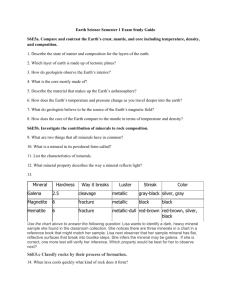
Mineral Properties
A mineral is non-living, solid, and natural. It has properties that can be identified.
Luster – Whether a mineral is ___________ or ______________.
Hardness - Hardness refers to whether the mineral can be __________or can _________ something else.
The harder a mineral, the fewer things can scratch it.
The hardness is numbered 1-10 with 1 being the softest and 10 being the hardest.
Diamond is the hardest mineral.
Streak – The ____________ of the powder left behind when a mineral is rubbed on a rough surface.
Color – The color of a mineral can be used to help identify it, but it can _________ be used as the only method. Many minerals come in a variety of colors and many minerals are the same color.
How to find a mineral, using a mineral identification key
Fossils
A fossil is the remains of a living thing that lived long ago that has turned to rock.
Mold – An ___________ left by a plant or animal that hardens into rock.
Cast – Sediment fills a mold and hardens into _____, taking the shape of the once living thing
Preserved Parts – Preserved plants and animals turned to rock or have been trapped in something
Soil
Number the following soil types in order from the soil with the smallest grains
(1) to the soil with the largest grains (3).
____Silt ____Clay ____Sand