CH 15 Notessheet
advertisement

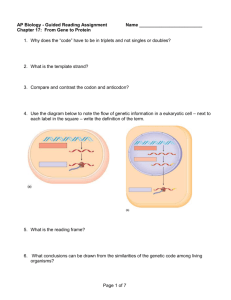
Genes Expression or Genes and How They Work: Transcription, Translation, & More • • Central Dogma – _________________________________ During polypeptide synthesis, ______________________ is the site of polypeptide assembly. – _____________________________________ transports and positions amino acids. – ________________________ directs which amino acids are assembled into polypeptides Proposed by _________________________ in 1958 to describe the flow of information in a cell. Information stored in DNA is transferred residue-by-residue to RNA which in turn transfers the information residue-by-residue to protein. The Central Dogma was proposed by Crick to help scientists think about molecular biology. It has undergone numerous revisions in the past 45 years. Transcription Overview Def: DNA sequence is _________________________ into RNA sequence – initiated when ________________________ binds to promoter binding site – moves along DNA strand and adds ________________________________ nucleotide disengages at _______________ Translation Overview Def: nucleotide sequence of ___________________ is translated into _______________________ sequence in the polypeptide – rRNA recognizes and binds to start sequence – moves three nucleotides at a time disengages at stop signal – Gene expression - ___________________________________________ Genetic Code • How does the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule encode the information that specifies the order of amino acids in a polypeptide? • The answer came in 1961 through an experiment lead by ______________________. • Crick and colleagues reasoned that there must be _________________ or block of info that coded for an amino acid • They hypothesized that it was most likely _____________________ – Why 3? – 2 nucleotides did not have enough combinations (____________________________) – 3 nucleotides (___________) which is enough to cover the roughly 20 known amino acids • Now known • Genetic code consists of a series of information blocks called __________________. – reading frame (__________________) • each codes for one amino acid • highly redundant • Could be _________________________ • Punctuated code would have a ________________________ that separates codons • Non-punctuated code would _____________ • In the following example, O is not a base pair but the “______________________” • Crick concluded that it is not punctuated as _____________________________________ _______________________________. • Code is practically ______________ • ex: AGA codes for arginine in ___________________________________________ • great evidence that all life has ____________________________ • Genes coded in one organism can be ____________________________ – SWEET biotechnology • Code is practically universal…____________________ • In 1979 mammalian mitochondria found to have a ___________________________ – In mitochondrial DNA, UGA is not a stop codon as it is in “universal code” – Other codons are different – Chloroplasts and ciliates (protists) have ______________________________ • It is thought that the changes to _____________________________________________ __________________________________ More on RNA • • – Central Dogma shows ___________________________________________________ RNA’s structure is different from DNA _________________ • _________________ • _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ RNA Structure – – – – – __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Both DNA and RNA contain four nitrogenous bases, but rather than thymine, RNA contains a similar base called uracil (U). Transcription • RNA polymerase – only one of two DNA strands (template or antisense strand) is transcribed – non-transcribed strand is termed coding strand or sense strand – In both bacteria and eukaryotes, the polymerase adds ribonucleotides to the growing 3’ end of an RNA chain. synthesis proceeds in 5’3’ direction Transcription Bubble • • • • Promoter – Transcription starts at ____________________binding sites called __________________ on DNA template strand. Initiation – Other eukaryotic factors bind, assembling a ___________________________. RNA polymerase begins to ___________________________. Elongation – Transcription bubble moves ___________________ at constant rate leaving ___________ strands protruding from the bubble. Termination – Stop sequences at the end of the gene cause ___________________________ formation to cease, ______________________ to dissociate, and RNA polymerase to ___________. Transcription Process Video (we will watch this twice!!) – For RNA polymerase to successfully bind to a eukaryotic _______________ and initiate – – – – – – – transcription, a set of proteins called ___________________ must first assemble on the promoter. The assembly process begins _________________ from the transcription start site, where proteins called ____________________ bind to a short TATA sequence in the promoter. Other basal factor proteins then bind, eventually forming a full ________________________ able to capture the RNA polymerase. Basal factors are essential for transcription but cannot by themselves increase or decrease its rate. A second set of transcription factors called coactivators link the basal factor proteins called activators. Activators are ________________________ that bind to sequences on DNA called enhancers. Enhancers are located at sites that are ________________________________________. The interaction of activator proteins with transcription factor subunits ___________________ of transcription. Many enhancers, scattered around the chromosome, can bind different activators, which provide a variety of responses to various signals. When a second kind of regulatory protein called a repressor binds to a “silencer” sequence located adjacent to or overlapping an enhancer sequence, the corresponding activator is not longer able to bind to the DNA. Eukaryotic Transcription • Eukaryotic transcription differs from ______________________ transcription: What is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes again? – ________________________ enzymes – ___________________________ at promoter – RNAs are _________________ after transcription Translation: From mRNA to Protein • The process of converting the _________________ in a sequence of _______________________ into a sequence of ________________________________ is known as ____________________. • Translation takes place at the ________________________________________________. The role of transfer RNA • For proteins to be built, the ________________________ dissolved in the cytoplasm must be brought to the __________________. • This is the role of ___________________ • Each ____________________ attaches to only one type of ______________. • The first codon on _______________________, which codes for the amino acid methionine • _____________ signals the start of ______________________. • When this signal is given, the ___________________ along the ___________ to the next _______. • A new ___________________ carrying an amino acid ______________ with the second ________________ • • The amino acids are joined when a ____________________________ is formed between them. A chain of amino acids is formed until the _______________ is reached on the ______________. Translation (in more detail) • • • Begins when initial portion of ____________________ binds to _______________________ – __________________ molecule with complimentary _____________________ binds to exposed codon ________________ some _________ molecules recognize more than ________________ Activating enzymes – tRNA molecules attach to ____________________ through the action of ______________ ___________ (aminoacyl-tRNA syntheases). must correspond to specific anticodon ________________________ molecule as well as particular __________________Start and stop signals – start signal coded by ____________________ – stop signal coded by one of three ___________________: _____________________ What do you think “nonsense codons” means here? • Initiation – ______________________________ begins with the formation of an initiation complex. initiation factors • Elongation – After initiation complex forms, _______________ subunit binds, exposing ____________ adjacent to the initiating codon, positioning it for interaction with another amino acid-bearing ____________________. • Translocation – ________________ moves nucleotides along __________________ A bit about the peptide bond formation • A peptide bond (amide bond) is a ___________________ chemical bond formed between two molecules when the ______________________ of one molecule reacts with the __________________ of the other molecule, thereby releasing a __________. • This is a ______________________ reaction (also known as a _________________________), and usually occurs between ___________________. • The resulting C(O)NH bond is called a _________________, and the resulting molecule is ______. • The four-atom functional group -C(=O)NH- is called a ___________________ • Termination – ___________________ are recognized by release factors that release the newly made _________________________________. – There is _____________ with complimentary antidcodon to (UAA, UAG, UGA) Spliced Gene Transcripts • • DNA sequence specifying a protein is broken into segments _______________ scattered among longer noncoding segments _________________. Initially, ___________________ is produced for the _________________. – Small nuclear ribonuclearproteins (_______) associate with proteins to form ___________. Lariat forms, _________________ and _______________ to form _____________. ________________________ How Spliceosomes Process RNA (we will watch this twice!!) – Most eukaryotic genes are composed of numerous ______________________ called exons, – – – – – – embedded within stretches of __________________________ called introns. The initial messenger RNA molecule or _________________________ copied from a gene by RNA polymerase, is a faithful copy of ________________, including _______________________. Before the primary transcript is ________________, the introns are removed by a process called __________________________________. Particles composed of proteins and a special types of RNA called small nuclear RNA, or _______, play a role in RNA splicing. One kind of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) contains snRNA that can bind to the ______ of an intron by forming base-pairs with complementary sequences on the ________. A different snRNP binds to the _____________________. Additional introns interact, causing the intron to _______________, thereby bringing the two ends of the intron together. The large complex of snRNPs, called a ___________________, then _______________ and the exons are joined together. The snRNPs are then released. • During RNA processing, intron sequences are _________________________ before it is used in polypeptide synthesis. – remaining sequences are ____________________ remaining exon sequences are _________________ to form final ______________________ An Overview of Eukaryotic Gene Expression ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Gene Expression • Most ______________ genes possess introns (prokaryotic genes do not.) • Individual ________________ molecules often contain transcripts of ____________________. • Eukaryotic mRNA molecules must be __________________ and must pass across the _________ ___________ before translation. • In prokaryotes, translation begins at the AUG codon preceded by a special nucleotide sequence. • Eukaryotic mRNA molecules have introns cut out and exons joined together before ____________. • Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger than prokaryotic ribosomes. How do mutation effect proteins • • Any change in DNA sequence is called a ___________________. Mutations can be caused by errors in ____________________________________________ _______________________ The effects of point mutations • A point mutation is a change in a ________________________ in DNA • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the _______________________________ Frameshift mutations • A mutation in which a single base is __________________ from DNA is called a frameshift mutation because it _______________ the reading of codons by one base. • Structural changes in chromosomes are called __________________________ Causes of Mutations • Any agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen. • Mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and even high temperatures • Forms of radiation, such as X rays, cosmic rays, ultraviolet light, and nuclear radiation, are dangerous mutagens because the energy they contain can damage or break apart Chromosomal Alterations • When a part of a chromosome is _______________, a deletion occurs. A B C D E F G H A B C E F G H Deletion • When part of a chromatid ________________ to its sister chromatid, an insertion occurs. • The result is a duplication of ______________________________ chromosome A B C D E F G H A B C B C D E F G H Insertion • When part of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches backwards, an ______________________. A B C D E F G H A B C B C D E F G H Insertion • When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, a ___________ _____________. AB C D E F GH WX Y Z W X AB C DE F GH Translocatio Y Z