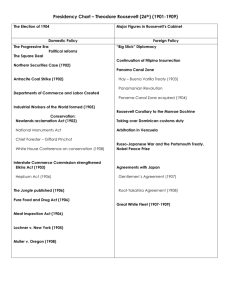
Presidency Chart – Theodore Roosevelt (26th) (1901
advertisement
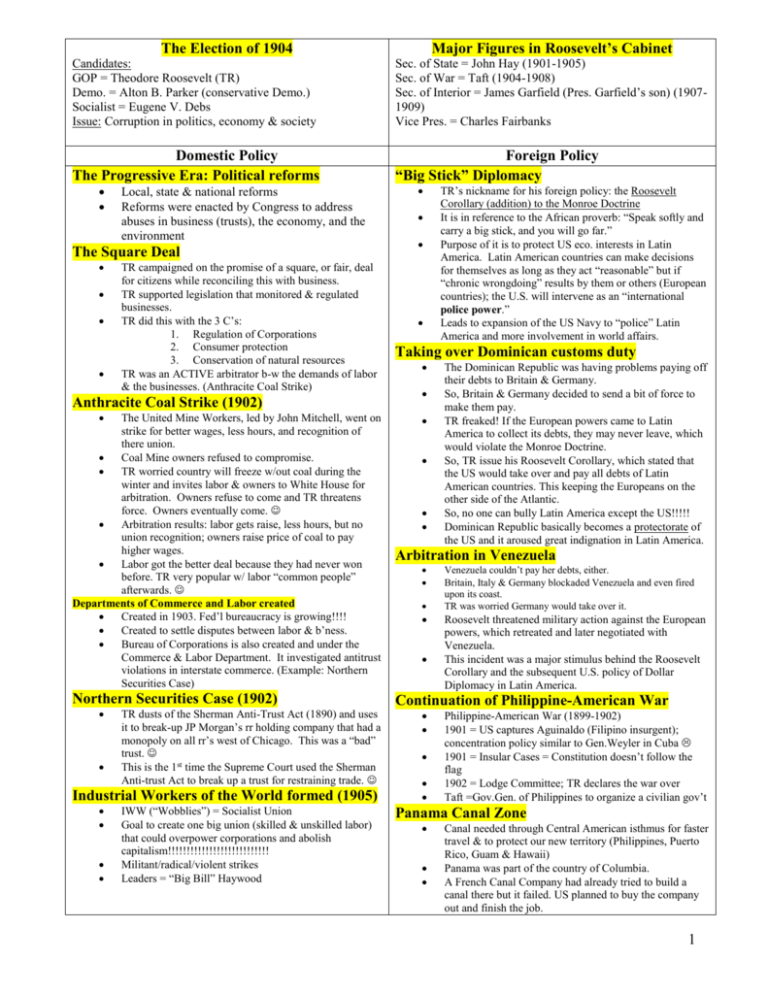
Major Figures in Roosevelt’s Cabinet The Election of 1904 Candidates: GOP = Theodore Roosevelt (TR) Demo. = Alton B. Parker (conservative Demo.) Socialist = Eugene V. Debs Issue: Corruption in politics, economy & society Sec. of State = John Hay (1901-1905) Sec. of War = Taft (1904-1908) Sec. of Interior = James Garfield (Pres. Garfield’s son) (19071909) Vice Pres. = Charles Fairbanks Domestic Policy The Progressive Era: Political reforms Foreign Policy “Big Stick” Diplomacy Local, state & national reforms Reforms were enacted by Congress to address abuses in business (trusts), the economy, and the environment The Square Deal TR campaigned on the promise of a square, or fair, deal for citizens while reconciling this with business. TR supported legislation that monitored & regulated businesses. TR did this with the 3 C’s: 1. Regulation of Corporations 2. Consumer protection 3. Conservation of natural resources TR was an ACTIVE arbitrator b-w the demands of labor & the businesses. (Anthracite Coal Strike) Anthracite Coal Strike (1902) TR’s nickname for his foreign policy: the Roosevelt Corollary (addition) to the Monroe Doctrine It is in reference to the African proverb: “Speak softly and carry a big stick, and you will go far.” Purpose of it is to protect US eco. interests in Latin America. Latin American countries can make decisions for themselves as long as they act “reasonable” but if “chronic wrongdoing” results by them or others (European countries); the U.S. will intervene as an “international police power.” Leads to expansion of the US Navy to “police” Latin America and more involvement in world affairs. Taking over Dominican customs duty The Dominican Republic was having problems paying off their debts to Britain & Germany. So, Britain & Germany decided to send a bit of force to make them pay. TR freaked! If the European powers came to Latin America to collect its debts, they may never leave, which would violate the Monroe Doctrine. So, TR issue his Roosevelt Corollary, which stated that the US would take over and pay all debts of Latin American countries. This keeping the Europeans on the other side of the Atlantic. So, no one can bully Latin America except the US!!!!! Dominican Republic basically becomes a protectorate of the US and it aroused great indignation in Latin America. The United Mine Workers, led by John Mitchell, went on strike for better wages, less hours, and recognition of there union. Coal Mine owners refused to compromise. TR worried country will freeze w/out coal during the winter and invites labor & owners to White House for arbitration. Owners refuse to come and TR threatens force. Owners eventually come. Arbitration results: labor gets raise, less hours, but no union recognition; owners raise price of coal to pay higher wages. Labor got the better deal because they had never won before. TR very popular w/ labor “common people” afterwards. Departments of Commerce and Labor created Created in 1903. Fed’l bureaucracy is growing!!!! Created to settle disputes between labor & b’ness. Bureau of Corporations is also created and under the Commerce & Labor Department. It investigated antitrust violations in interstate commerce. (Example: Northern Securities Case) Arbitration in Venezuela Northern Securities Case (1902) Continuation of Philippine-American War TR dusts of the Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890) and uses it to break-up JP Morgan’s rr holding company that had a monopoly on all rr’s west of Chicago. This was a “bad” trust. This is the 1st time the Supreme Court used the Sherman Anti-trust Act to break up a trust for restraining trade. Industrial Workers of the World formed (1905) IWW (“Wobblies”) = Socialist Union Goal to create one big union (skilled & unskilled labor) that could overpower corporations and abolish capitalism!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Militant/radical/violent strikes Leaders = “Big Bill” Haywood Venezuela couldn’t pay her debts, either. Britain, Italy & Germany blockaded Venezuela and even fired upon its coast. TR was worried Germany would take over it. Roosevelt threatened military action against the European powers, which retreated and later negotiated with Venezuela. This incident was a major stimulus behind the Roosevelt Corollary and the subsequent U.S. policy of Dollar Diplomacy in Latin America. Philippine-American War (1899-1902) 1901 = US captures Aguinaldo (Filipino insurgent); concentration policy similar to Gen.Weyler in Cuba 1901 = Insular Cases = Constitution doesn’t follow the flag 1902 = Lodge Committee; TR declares the war over Taft =Gov.Gen. of Philippines to organize a civilian gov’t Panama Canal Zone Canal needed through Central American isthmus for faster travel & to protect our new territory (Philippines, Puerto Rico, Guam & Hawaii) Panama was part of the country of Columbia. A French Canal Company had already tried to build a canal there but it failed. US planned to buy the company out and finish the job. 1 Conservation: 1. Newlands Reclamation Act (1902) 150 million acres were added to the national forest reserve Fed’l gov’t sold semi-arid land in the West & used the $ from the sales to build dams for rivers, canal systems & irrigation to make the land better, so people from urban areas would move there. 2. National Monuments Act (1906) Also called the Antiquities Act Original purpose to protect Native American ruins & artifacts on fed’l lands in the West It gave the Pres. The power to create National monuments, even for scientific interests. TR used it to make the Petrified Forest (AZ) and the Grand Canyon National Monuments. 190 million acres of forest federalized & protected; Pinchot insisted trees be planted when cut down; millions of acres of land set aside to protect resources. Panamanian Revolution (1903) TR tried to negotiate a deal with Columbia to buy the Panama Canal Zone but Columbia wouldn’t bargain in good faith. Roosevelt ultimately decided, with the encouragement of Panamanian business interests, to help Panama declare independence from Colombia in 1903. The US blocked the sea borders of Panama, so that Columbia couldn’t help. A brief revolution, of only a few hours, followed the declaration, and Colombian soldiers were bribed $50 each to lay down their arms. On November 3, 1903, the Republic of Panama was created, with its constitution written in advance by the United States. Hay – Buena Varilla Treaty (1904) 3. Gifford Pinchot Head of the U.S. Forest Service (conservationist) He is famous for reforming the management and development of forests in the United States and advocated the scientific conservation for the planned use & renewal of the nation’s forest reserves. Later will be fired by Pres. Taft in the Pinchot-Ballinger Controversy, which upsets TR. Panama Canal (1904-1914) 4. White House Conference on conservation (1908) Governors for most of the states came together to work on conservation and to implement it. National conservation policy created. Interstate Commerce Commission strengthened -Elkins Act (1903) = rr regulation strengthened the ICC (created ay the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887) by imposing heavy fines on rr offering rebates and on the shippers accepting them. The railroad companies were not permitted to deviate from published rates. -Hepburn Act (1906) = rr regulation Scholars consider it the most important piece of legislation regarding rr in the first half of the century. Gave the ICC power to set max. rr rates ICC orders binding; that is, the railroads must either obey or contest the ICC orders in federal court. Anti-rebate provisions were toughened, free passes were outlawed, and the penalties for violation were increased. ICC gained the power to prescribe a uniform system of accounting, require standardized reports, and inspect railroad accounts. Shortly after the Panamanian revolution, this treaty was signed which gave the US the Panama Canal. The U.S. paid $10 million to secure rights to build on and control the Canal Zone to extend ten miles on either side of the canal route in perpetuity; Panama was to receive a payment of $10 million and annual rental payments of $250,000. B/c of U.S. support for Panamanian secession, relations with Colombia remained fragile until Washington paid that country $25 million in restitution, or "canalimony," under the Thomson-Urrutia Treaty of 1921. Engineering achievement; its completion shortened the route of freighters between San Francisco, California and New York City by 8,000 miles 1906 = TR visited it (1st pres. To leave country) Col. Wm. Gorgas exterminated yellow fever Cost $400 million Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905) Japan attacks Russia, since Russia had been in Manchuria, and proceeded to administer a series of humiliating victories until the Japanese began to run short on men. Japan has defeated a world power!!!!!! AWWWhhh. Portsmouth Treaty (1905) Japan & Russia ask TR to negotiate the treaty to end the Russo-Japanese War At Portsmouth, New Hampshire, both sides met, and though both were stubborn (Japan wanted all of the strategic island of Sakhalin while the Russians disagreed), in the end, TR negotiated a deal in which Japan got half of Sakhalin but no indemnity for its losses. Neither Russia nor Japan felt like they received a “square deal” and b/c of this America lost two allies. Now, TR is worried about Japan!!! Nobel Peace Prize (1906) TR wins the Nobel Peace Prize for his mediations in the Russo-Japanese War and in his mediations in some North African disputes as well. 2 Consumer Protection: The Jungle published (1906) Written by muckraker, Upton Sinclair Exposed the corruption of the meatpacking industry Socialist novel = message is that socialism is the only effective tool to fight capitalism & the only tru remedy available to the poor masses of U.S. Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) All food & drugs (medicine) must have label with ingredients. forbade the manufacture, sale, or transportation of adulterated food products or poisonous patent medicines Agreements with Japan: 1. Gentlemen’s Agreement (1907) Meat Inspection Act (1906) TR read The Jungle was suspicious of Sinclair's socialist attitude and its conclusions, and so sent labor commissioner Charles P. Neill and social worker James Bronson Reynolds, men whose honesty and reliability he trusted, to Chicago to make surprise visits to meat packing facilities. Despite betrayal of the secret to the meat packers, who worked three shifts a day for three weeks to clean the factories prior to the inspection, Neill and Reynolds were still revolted by the conditions at the factories, and at the lack of concern by plant managers. Following their report, the Neill-Reynolds Report, President TR became a supporter of regulation of the meat packing industry. USAD will inspect meat processing plants that conduct business in interstate commerce. 3 requirements: (1) mandatory inspections of livestock before & after slaughtering (2) sanitary standards for slaughterhouses & meatpacking plants (3) USAD has authority to do this all the time. After the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, the city decreed that due to lack of space, Japanese children would have to attend a special school. The Japanese parents wrote Japan’s foreign minister and it became an international issue. TR settled this with a series of informal agreements between the US and Japan. Japan agreed not to issue passports to citizens for travel to the United States, thus eliminating immigration. In exchange, schools in San Francisco, California, agreed not to discriminate against students of Japanese descent. 2. Root-Takahira Agreement (1908) Agreement made after TR’s Russo- Japanese settlement in order to prevent TR’s conciliatory moves from being interpreted as signs of weakness. This is a contract b-w the US & Japan. Both countries pledged to respect each other’s territorial possessions in the Pacific and to uphold Hay’s Open Note Policy in China. Great White Fleet (1907-1909) 16 US battleships of the Atlantic fleet went on a 14 month voyage around the world. The battleships were freshly painted white. TR sent them to show the world how strong the US was. The ships stopped by Japan to show them we were strong NOT weak and they should respect us. Voyage for PEACE, so we wouldn’t have war. Lochner v. New York (1905) Set back for labor & unions Conservative Supreme Court loves laissez-faire eco. & it does NOT believe in gov’ts power to regulate the eco. (NOT progressive) The court says that a state can NOT make a law limiting the hours a (male) baker can work in a week b/c it violates the 14th Amend. “right to free contract” of the due process clause. Muller v. Oregon (1908) Oregon passed a law limiting the hours women & children could work in a week. The law is challenged. Brandeis (Progressive) was hired by Florence Kelley to be the defense attorney and he won. He become famous because of this case & is later appointed to the Supreme Court under Wilson. He is the 1st Jewish SC justice. Brandeis created the “Brandeis brief” for this case. The brief was filled with scientific & social science data backing up his reasoning that women were the weaker sex and that it was the state’s duty to protect them. The Supreme Court agreed with Brandeis and said the law did NOT violate the 14th Amend. b/c women were inherently weaker & the law was necessary & proper to protect their health and the health of their unborn children. 3