Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
advertisement

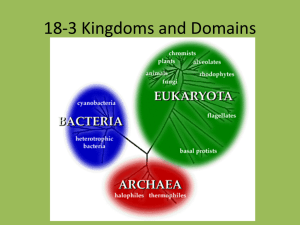
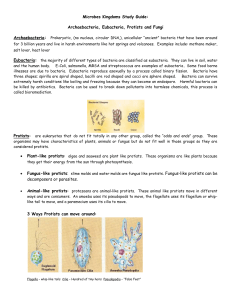
1. What language is used for classification? Latin 2. What is the name of the classification system? binomial nomenclature 3. Which scientist developed the naming system? Linnaeus 4. Why do we need to classify? To organize all living things 5. List the 8 taxonomic levels (broad to specific). Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species 6. Which 2 taxonomic levels make up a scientific name? Genus & species 7. What are the 3 rules for writing a scientific name? (1) The Genus is written 1st and species is written 2nd. (2) Genus is capitalized and species is lower case. (3) It must be underlined or italicized. 8. What is the difference between the five kingdom system and the previous six kingdom system? 5 Kingdom—Monera & 6 Kingdom— Archaebacteria and Eubacteria 9. List 2 differences between bacteria & viruses. 1) bacteria are living & viruses are not; 2) bacteria are bigger than viruses 10. List one difference between Archaebacteria & Eubacteria. Archaebacteria live in extreme habitats and Eubacteria live everywhere else 11. List the 3 types of Archaebacteria, describe their environments, and give an example of where they can be found specifically. 1) METHANOGEN-IN SWAMPS/MARSHES 2) HALOPHILE-SALTY ENVIRONMENTS-Dead Sea 3) THERMOPHILES-ACIDIC & HOT WATER-Hot sulphur springs 12. Draw and label a prokaryote. 13. Draw and label a virus. Nucleic Acid: DNA or RNA Capsid: a protein coat 14. Describe and draw the 3 shapes of bacterial cells. Cocci (spherical) Bacilli (rods) Spiralla (spiral) 15. What are the two prefixes that explain how bacterial cells are arranged and what do they mean? STAPHYLO- ARE CLUSTERS OF BACTERIA AND STREPTO- ARE CHAINS OF BACTERIA 16. What type of cell does the influenza virus want to attack? THROAT CELL 17.Define antibodies. Proteins made by B-cells 18.Give two examples of how bacteria are used in everyday life. CHEMICALS, SEWAGE TREATMENT, NITROGEN FIXATION, FOOD PROCESSING 19. Give an example of how viruses are used in the medical field. They are used to treat bacterial infections 20. How are protists classified? Animal-like, plantlike, fungus-like 21. A) pseudpodia, B) cilia, C) flagella 22. What are plant-like protists called? Algae 23. What are animal-like protists called? protozoa 24. What is the role of fungus-like protists in the environment? To decompose dead organisms 25. What is the function of a contractile vacuole? to get rid of excess water in a cell 26.What is the function of an eyespot? To help an organism detect light Protists # of cells Nutrition Cell type Both Unicellular & Multicellular Autotrophic Heterotrophic Eukaryotic Fungi 28. What complex carbohydrate is found in the wall of fungi? chitin 29. List three ways in which fungi can be useful to us. 1) decompose dead organisms, 2) food, 3) antibiotics 30.List three ways fungi obtain food. 1)saprophyte, 2) parasite, 3) mutualism 3rd 9 Weeks Study Guide Add these 3 statements to your study guide: 31. The father of evolution is Charles Darwin. 32. Evolution is when organisms make gradual genetic changes over time. 33. Natural selection is having good traits that help organisms survive, reproduce, and pass the trait along