Biology - Class Notes
advertisement

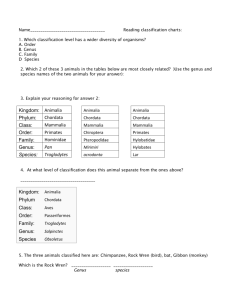
Classification and Kingdoms Phylogeny Is the study of the evolutionary history of a species... how it developed over time. Phylogenetic Tree Example How are living organisms organized? • They are grouped into categories according to their similarities Taxonomy The science of classifying organisms according to their natural relationships. Carolus Linnaeus ( 1707 - 1778 ) Swedish naturalist, devised the system we still use today. It uses two names to identify each species All Organisms were classified and given a Scientific Name He placed structurally similar animals into groups he called species Linnaeus grouped similar species into a larger category called a genus ( plural: genera ) He grouped similar genera into a stilllarger category called a family Families make up larger groups called orders. Orders make up larger groups called classes. Classes make up larger groups called phyla. (singular: phylum) Phyla make up the largest group called a Kingdom. In Kingdoms Plantae and Fungi .... the second-largest group is called a Division instead of a Phylum. 8 Level System of Classification of Living Things (In order from Largest to Smallest) • • • • • • • • Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species How can anyone ever remember all of these names -AND in the correct order ??? How can anyone ever remember all of these names -AND in the correct order ??? There’s a secret to it! If you can remember the following sentence, you can remember all of these groups too! Dashing King Phillip Came Over For Great Spaghetti Domains • Today Scientists have added a new group called Domains. There are 3 domains: Eukarya Archaea Eubacteria • Domains are larger than Kingdoms so we now can add DASHING King Philip Came Over For Great Spaghetti ! Members of a species can reproduce and create offspring which are also capable of reproducing. A horse and a donkey can mate and produce offspring. However, the offspring (called a mule) is sterile and cannot reproduce. Therefore, horses and donkeys belong to different species. System of Scientific Naming = Binomial Nomenclature Binomial means “two names.” Nomenclature means “a system of naming.” Scientific Name =Genus species • Written in LATIN • Always Written in Italics or underlined • Genus is always written with a CAPITAL letter • species is always written with a LOWER CASE letter You are a member of : Homo sapiens. Your genus is Homo and your species is sapiens; therefore, your scientific name is Homo sapiens. Your COMMON NAME is Human Classification of Man: Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia You are a multicellular mobile heterotroph Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primata Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens We named ourselves after our ability to think Examples of Scientific Names and their Common Names Alligator mississippiensis Alligator mississippiensis American Alligator Dichotomous Key A written set of opposite choices that is used to identify a species Dichotomous Key Example Does the organism have spines? If “Yes” continue, if “No” skip to question 114. Does the organism have five appendages (legs)? If “Yes” continue, if “No” skip to question 21. There are: 6 Kingdoms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. - Archaebacteria Eubacteria - Protista - Fungi - Plantae - Animalia EXAMPLES and CHARACTERISTICS EuBacteria = Bacteria (Domain) Eubacteria Unicellular Prokaryote Cell walls are made of peptidoglycan. (sugar) Archaebacteria Domain Archaea • Prokaryotes • Unicellular • Live in extreme environments like hot springs, the dead sea and places with no oxygen. ( Thermophiles, Halophiles, methanogens) • Cell walls DO NOT contain peptidoglycan. Protista = Protozoans and Algaes Protista = Unicellular Eukaryote Mobile and Non-Mobile Autotrophs and Heterotrophs Fungi = Mushrooms Molds and Yeasts Fungi = Multicellular Eukaryote Non-Mobile Heterotroph Plantae = Oak Trees and Roses etc... Plantae = Multicellular Eukaryote Non-Mobile Autotroph Animalia = Sponges, Humans Grasshoppers, Cats etc... Animalia = Multicellular Eukaryote Mobile Heterotroph