Classification, Immune System, Bacteria, Viruses & Fungi
advertisement

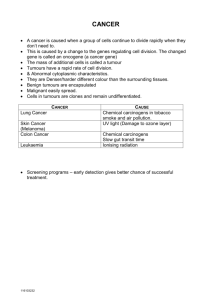
preAP/GT S12 Ch. 19 Bacteria and Viruses Review Name ___KEY_____________ Period______________ 1. Why is it important to sterilize the Petri dishes and agar before growing bacteria? prevent contamination 2. Which of the following is the smallest in size? Circle one: bacterium animal cell virus 3. What is the difference between passive and active immunity? Active = “earned immunity”, had disease or vaccine, build up own antibodies; Passive = “borrowed immunity”, get antibodies from someone else 4. Draw and name the 3 shapes of bacteria. Coccus Bacillus Spirillum 5. How can HIV be spread? Body fluids – sexual transmission, contact with blood or other fluids How can you avoid HIV? Avoid contact 6. What does an antibiotic do? Kill bacteria 7. Where can bacteria be found? everywhere 8. List examples of uses for helpful bacteria. nitrogen fixers (in plants), decomposers, break down waste, produce Vitamin K in intestines 9. What does a vaccine do? Makes your body produce antibodies against a specific disease-causing agent so that you build a “memory” to it and can fight the disease if you’re ever exposed 10. Which kingdom(s) contain prokaryotes? Eubacteria, Archaebacteria 11. What are the bacterial kingdoms? Same as above 12. What are the two ways in which bacteria cause disease? Destroying cells, producing toxins 13. List the major groups of pathogens to humans. Bacterial, viral, fungal, animal (worm parasites) 14. What is a virus? Non-living; only contains nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) and protein coat (capsid); obligate parasite 15. What is a viroid? Only contains nucleic acid; infects plants What is a prion? Only contains protein; infects animals 16. List and describe the various methods of reproduction in bacteria. binary fission – asexual splitting; conjugation – sharing of nucleic acid with other bacteria; similar to “sexual” reproduction 17. Why are viruses not considered to be truly “living” organisms? Don’t have all characteristics of life – such as: use of energy 18. Overuse of antibiotics has caused bacteria to become resistant to our best arsenal of antibiotics. This is due to natural selection of the bacteria in which only those with the resistant genes survive. Matching. 19. d 19. dormant cycle of viral infection a. prokaryote 20. a 20. organism without a nucleus b. antibiotics 21. g 21. organism with a nucleus c. HIV 22. f 22. destructive cycle of viral infection d. Lysogenic 23. b 23. kills bacteria e. capsid 24. j 24. causes infectious diseases f. Lytic 25. i 25. instrument used to see bacteria g. eukaryote 26. h 26. instrument used to see viruses 27. e h. electron microscope 28. c 27. protein coat of a virus i. compound/light microscope 29. k 28. virus that causes AIDS j. pathogen 30. n 29. virus that attacks bacteria k. bacteriophage 31. l 30. visible group of bacteria l. agar 32. m 31. growth medium for bacteria m. virus 32. all are obligate parasites n. colony Matching. Which type of pathogen causes the following 33. smallpox a. virus 34. tooth decay b. bacteria 35. HIV/AIDS c. prion 36. tuberculosis 37. Lyme disease 38. herpes 39. flu 40. diphtheria 41. Mad Cow Disease 42. strep throat *Study chapter 19 review on pages 493-494. diseases? 33. a 34. b 35. a 36. b 37. b 38. a 39. a 40. b 41. c 42. b 43. What is the germ theory of disease? Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms that can be identified and produce a similar set of symptoms in any infected individual 44. List the five agents of disease. Fungus, bacteria, virus, animal (such as parasitic worms) 45. How are diseases spread? Contact, fluids, inhalation 46. How are bacterial infections treated? Antibiotics Prevented? Avoid contact, sanitation/ other health prevention strategies, some have vaccines 47. How are viral infections treated? Usually just the job of the immune system; some antivirals Prevented? Many have vaccines – otherwise, avoid contact preAP/GT S12 48. Differentiate between specific and non-specific defense. Non-specific – keep everything out!; specific – targets specific antigens on specific pathogens (ex. measles antibodies can only measles, not chicken pox) 49. Differentiate between first line, second line and third line of defense. First – skin, mucus, antimicrobial proteins, sweat, tears, etc – keep all out; Second – WBC’s, inflammatory response; Third – Humoral (B-cells, antibodies) & Cell-mediated defense (T-cells) 50. What is interferon? Substance body produces that interferes with viral reproduction 51. Differentiate between humoral immunity and cell-mediated immunity. See #49 52. What is active immunity and how is it different from passive immunity? See #3 53. An overreaction of the immune system to an antigen is referred to as allergy. 54. What is the function of histamines? Increase inflammation in response to injury – swelling, dilation of blood vessels – brings in more WBC’s, increase heat 55. What is an autoimmune disease? List a few examples. Body immune system destroys itself (arthritis, Lupus) 56. How does the environment affect your immune system? Some factors can stress immune system and therefore not allow you to fight off diseases as easily; some environmental factors can cause disease (ex. cancer) 57. List four behaviors important in maintaining health. Healthy diet, abstination from unhealthy activities, regular check-ups (Hygiene, vaccinations), exercise *Study chapter 40 review on pages 1057-1058 __B_ 58.The first time your body encounters a foreign organism, your immune system fights the organism by using __?_; also called the body’s first line of defense. A. specific immunity B. non-specific immunity C. antihistamines D. T-cells __A___ 59. White blood cells that recognize and destroy specific foreign organisms are called A. B- cells B. histamines C. macrophages D. lysosomes __B___ 60. Which is NOT part of your body’s first line of defense against disease? A. macrophages B. T-cells C. stomach acid D. mucous membranes __B___ 61. Which is NOT true about specific immunity? A. The body had already been exposed to the antigen. B. Macrophages ingest the antigen. C. T-cells attach to the antigen. D. Suppressor B-cells stop the attack on the antigen. __D___ 62. Which is NOT true about T-cells? A. They mature in the thymus. B. They form in the bone marrow. C. They are deficient in people with HIV. D. They ingest disease-causing organisms, using pseudopods. True or False: On the lines provided write T for true statements and F for any false statements. __F___ 63. Phagocytosis occurs when mast cells eat antigens. __T___ 64. Some lymphocytes destroy antigens the first time the two meet. __F___ 65. Most antigens break the immune system’s first line of defense and are destroyed by lymphocytes. __T___ 66. Vaccines introduce antigens into the body; as a result, the immune system learns to recognize and destroy the antigen the next time it enters the body. Matching: Write the letter of the term that matches the description on the lines provided. A. allergen B. histamine C. phagocyte D. specific immunity E. vaccination __C___ 67. Cell that ingest antigens. (pathogens) __D___ 68. Cell Mediated response to specific antigens that occurs after first exposure to the disease organism. __B___ 69. A chemical released by mast cells that causes swelling, increased mucus and allergy symptoms. __E___ 70. The introduction of dead or weakened antigens into the body that results in lasting immunity. preAP/GT S12 Label the parts of the bacteriophage below. 71. capsid (protein coat) 72. tail sheath 73. DNA/nucleic acid 74. tail fibers Label the bacterium below. A. cell wall B. cell membrane C. flagellum D. DNA E. pili 71 . 72 73 74