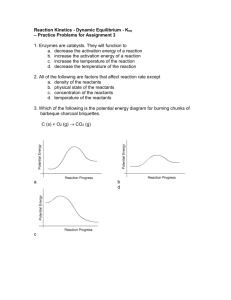
Two types of chemical reactions:
advertisement

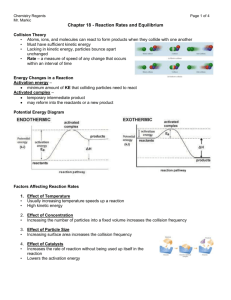
18.1- Equilibrium: A state of dynamic balance 1) When a reaction results in almost complete conversion of reactants to products, chemists say that the reaction goes to completion. A+BC 2) But most reactions do not go to completion. They appear to stop. This is because the reactions are reversible. The reaction can occur in both the forward and the reverse direction. Forward: A + B C Reverse: C A + B Reaction: A + B C Example: Forward: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Reverse: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Reaction: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Chemical equilibrium = a dynamic state in which the forward and reverse reactions balance each other because they take place at equal rates Rateforward reaction = Ratereverse reaction Law of chemical equilibrium = at a given temperature, a chemical system may reach a state in which a particular ratio of reactant and product concentrations has a constant value. The equilibrium constant, Keq, is the numerical value of the ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations. Reactants aA + bB Products cC + dD Keq = [C]c[D]d [A]a[B]b If [products] > [reactants], then Keq > 1. If [reactants] > [products], then Keq < 1. The state of matter of the reactants and products is significant. Only gases and aqueous solutions are included in the Keq expression. Solids and liquids are pure substances and have a concentration of 1, so they are not included in the Keq expression. If all the reactants and products are in the same physical state, the reaction is a homogeneous equilibrium. If there is more than one physical state, the reaction is a heterogeneous equilibrium. 18.2- Le Chatelier’s principle: If a stress, or change, is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress (change). The 3 sources of stress are: 1) Changes in concentration of a reactant or product. 2) Changes in temperature to an endothermic or exothermic reaction. a) Endothermic reaction: heat is added as a reactant and the overall change in energy is positive (ΔH= +). Heat + A + B C + D b) Exothermic reaction: heat is released as a product and the overall change in energy is negative (ΔH= -). A + B C + D + heat 3) Changes in pressure due to a change in volume. (If V increases, P decreases. If V decreases, P increases.) The equilibrium system will shift as follows in response to: 1) changes in concentration, [ ] a) if [ ] increases on one side, favor the opposite side b) if [ ] decreases on one side, favor the same side 2) changes in temperature (heat) a) if heat increases on one side, favor the opposite side b) if heat decreases on one side, favor the same side 3) changes in pressure (volume) a) if pressure increases (volume decreases), then favor side with less moles b) if pressure decreases (volume increases), then favor side with more moles