31.12B Behavior Treatment Review Committee Procedures
advertisement

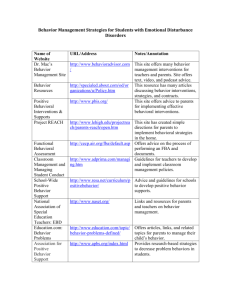
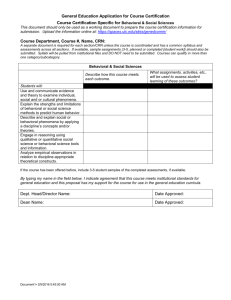
GUIDELINES FOR BEHAVIOR TREATMENT REVIEW COMMITTEE TREATMENT PLANS 1. Behavior Treatment Plan Standards a. The Person Centered Planning process will identify when a Behavior Treatment Plan needs to be developed. b. Behavior Treatment Plans containing intrusive and/or restrictive interventions shall only be developed when assessments have been completed to rule out physical, medical or environmental causes of the behavior. c. Behavior Treatment plans containing intrusive and/or restrictive techniques shall only be developed when the use of positive behavioral supports and interventions have failed to change the behavior. d. Behavior Treatment Plans must have written consent by the individual, guardian, or parent of minor child prior to implementation of the plan. 2. Essential Elements of a Behavior Treatment Plan a. Background/Introduction Person served Age Diagnoses Residence Current services Relevant history b. Assessment tools Clinical review of records Clinical interview(s) Observations Identify functional assessment tool Preference assessment (to identify a number of preferred activities or items that can be included as either non-function based reinforcers or simply to make a more enriched living environment) c. Analysis/Assessment Results of assessments performed to rule out relevant physical, medical and environmental causes of the problem behavior Functional assessment. Frequency, intensity and duration of target behaviors. Condition under which target behaviors occur, do not occur, including possible antecedents, maintaining consequences, and evocative events Evidence of the kinds of positive behavioral supports or interventions, including their amount, scope and duration that have 116104853 Guidelines Effective Date: 1/1/14 Page 1 of 3 GUIDELINES FOR BEHAVIOR TREATMENT REVIEW COMMITTEE d. e. f. g. h. i. been attempted to ameliorate the behavior and have been previously used and/or proved to be unsuccessful. Please include data on treatment fidelity, including effectiveness of staff implementation and concerns with staff ability to implement Medication (List medication prescribed to address an Axis I or II diagnosis, or medication prescribed that is not a standard treatment or dosage for the individual’s condition.) Dosage Purpose Protocol for Urgent Administration of Medication (if prescribed to control or manage behavior, not for symptom management of a diagnosed condition.) Target Behavior(s) Operational definition(s) Goal of Plan As related to target behaviors Procedure Description of procedure and plan for implementation, including: Positive approaches/proactive strategies to increase replacement behavior. Staff reaction strategy to occurrence of target behavior. Negative consequences, if any. If proposing an intrusive or restrictive technique: Risks (medical, psychological, etc.) and benefits of the intervention, to the individual and others; the plan for minimizing and monitoring the risks and consequences of the intervention. Evidence of continued efforts to find other options. Peer reviewed literature or practice guidelines that support the proposed restrictive or intrusive intervention as a treatment. References to the literature should be included, and where the intervention has limited or no support in the literature, why the plan is the best option available. Data Collection Procedure to collect data. Monitoring and Training Plan for monitoring and staff training to assure consistent implementation and documentation of the intervention(s) Plan for monitoring effectiveness of intervention Plan for reducing restrictive and/or intrusive components 116104853 Guidelines Effective Date: 1/1/14 Page 2 of 3 GUIDELINES FOR BEHAVIOR TREATMENT REVIEW COMMITTEE Recommended qualifications and competencies for authors of behavior treatment plans including intrusive and/or restrictive techniques. 1. Recommended competencies: a. Ability to perform a functional assessment b. Ability to clinically interpret functional assessment data c. Ability to develop behavioral treatment plan that improves positive functioning d. Ability to utilize positive behavioral supports as behavioral interventions. 2. Training/experience suggestive of above competencies a. Masters’ level clinician, trained in Behavioral Analysis. b. Bachelor’s level clinician who has acquired competencies through training and experience, in consultation with and final approval by Master’s level clinician trained in Behavioral Analysis. c. Experience with Positive Behavioral Supports and Gentle Teaching is additionally preferred. 116104853 Guidelines Effective Date: 1/1/14 Page 3 of 3