biochemistry lesson
advertisement

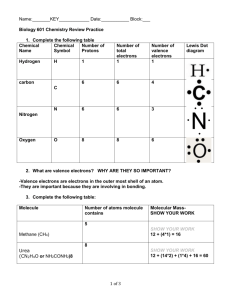
Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Aims Compare hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds Relate properties of water to polarity Distinguish adhesion, cohesion and density Agenda Slide Show/Notes Demos Notes Practice Motivation Show video of Jesus lizard…How is that possible? Elicit that not only is the lizard special, but water has special properties too, which is why it makes up 70% of any living thing and is necessary for life to exist on earth. If the water was squeezed out of each person… Explain that today we will observe some properties of water in order to understand what makes it so unique and why it is so important to living things. Development Slide Show Explain these properties are possible because of the the chemistry of water Review electronegativity Review polarity – demo with molecule or students Illustrate hydrogen bonds Complete notes and label diagram Demo Stations Water/Alcohol/Salt (Solvent), Ice/Water (Density), Water/Alcohol/Nickel (Cohesion), Boat/Alcohol/Water (Surface Tension), Water/Towel (Adhesion) Teacher leads demo or assigns each group to perform and explain a station Have students complete table with observations as each demo is presented Show slides as each demo is presented Students complete explanation of property and its importance Complete notes Practice Matching Labeling Identifying property described Table Students complete table in pairs Use knowledge of properties of water to explain each phenomenon, some may repeat Exit Slip: Table Homework: Read and take notes over 2-2 or CCC 3.3-3.7 Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Do Now 1. Identify the state of matter and describe the arrangement of molecules and energy level for each. 2. Use the picture to define electronegativity. 3. Look at the picture of HCl and answer the questions below. a. Is HCl an element or a compound? b. Are hydrogen and chlorine held together by ionic or covalent bonds? c. Is HCl polar or non-polar? 4. Identify the top three elements found in living things. Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Polarity Atoms become stable when their _____________ shells are filled with electrons • A covalent bond occurs when two atoms ________ a pair of valence electrons. • The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons is __________________________. • The more __________________ the atom, the more strongly it pulls electrons toward itself. • Electronegativity increases toward _____________. • A _________ covalent bond occurs when electrons are shared unequally by atoms with different _____________________. • Water is a ________ molecule because ____________ has a greater appetite for electrons than ___________ does. This gives the oxygen atoms a slight __________ charge and the hydrogen atoms a slight __________ charge. • The _____________ end of oxygen in a water molecule is attracted to the _______________ end of hydrogen in another water molecule, creating ________________ bonds. • Hydrogen bonds are ________________ than covalent bonds, but give water many special properties Diagram Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Water Demos You will observe five demonstrations of the properties of water. As each demo is presented, write your observations in the table below. Then explain what each property means in your own words. Property Observations Your explanation of property Why its important Solvent Density Cohesion Surface Tension Adhesion Important Properties of Water due to Hydrogen Bonds • _______________ is the attraction between molecules of the same substance. An example is _____________ ________________ on water. • _______________ is the attraction between molecules of different substances. An example is when ____________ sticks to the sides of a glass cylinder. • ________________ water has less density than _______________ water, so ice floats. • Water can dissolve any _______________ substance, making it a good ______________ . Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Practice 1. Label each image with oxygen, hydrogen, +, - , covalent bond, hydrogen bond. 2. Match the term to the description. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Cohesion Adhesion Density Hydrogen bond Polar covalent bond Water Electronegativity ___ Bond where electrons are shared unequally ___ Attraction between same type of molecules ___ Attraction between different type of molecules ___ Appetite for shared electrons ___ Amount of molecules in a given space ___ More dense as liquid than as solid ___ Bond between oxygen and hydrogen of different molecules 3. Identify the property that explains each phenomena (density, adhesion, cohesion) a. An ice cube floats in water b. A paper clip floats on water c. Shallow water freezes but deeper water does not d. A t-shirt wicks sweat from skin e. Insects walk on surface of pond f. g. h. Solid vs. Liquid Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Exit Slip In the table below, explain each phenomenon using your knowledge of the special properties of water. The following terms may be useful: polar, covalent, hydrogen bond, cohesion, adhesion, density, solid, liquid. Phenomenon Lizard walks on water Ice cube floats on water Foil boat floats on water Water climbs sides of graduated cylinder Property of Water Explanation Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Complete the Venn Diagram: NON-POLAR COVALENT BOND POLAR COVALENT BOND IONIC BOND Complete the table below comparing bond types: Bond Type Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Type of Atoms involved Strength Example Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Do Now 1. Label the atoms, charges and bonds in the diagram below. 2. Identify two differences between covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds. 3. What makes water a polar molecule? 4. Identify the characteristic of life described: a. A seed becomes a tree b. A lizard sits in the sun to keep warm c. A volleyball player eats a power bar before a game for energy d. Identical twins have the same DNA e. Pigs share a common ancestor with cows Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 1: Water is the solvent of Life 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Mix a spoonful of salt with water. What happens? Mix a spoonful of salt with alcohol. What happens? What does it mean to say water is the solvent of life? What chemical property of water allows it to be the solvent of life? What kinds of things would water dissolve? Why is this important to living things? Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 2: Density of Water 1. Place an ice cube in water. What happens? 2. Place an ice cube in alcohol. What happens? 3. Looking at the pictures below, which is more dense: liquid water or ice water? 4. How does this explain what happened to the ice cube in water? 5. What chemical property of water allows this to happen? 6. Why might this be important to living things? Gaseous water Liquid Water Ice Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 3: Cohesion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Drop as many drops of water on the penny as you can. Drop as many drops of alcohol on the penny as you can. Which could hold more drops? How does cohesion explain what happened? What chemical property of water allows cohesion to occur? Why is this important to living things? Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 4: Surface Tension 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Place the foil boat in the water and try to keep it from sinking. Place the foil boat on alcohol and try to keep it from sinking. Which boat stayed on top of the water? How can you explain this? (hint: the boat is not actually floating) What chemical property of water allows this to happen? Why might this be important to living things? Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 5: Adhesion 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Place a 5 drops of water on a paper towel. What happens? Place 5 drops of alcohol on a paper towel. What happens? Looking at the pictures below, how can you explain this? What do you think adhesion is? What chemical property of water allows this to happen? Why might this be important to living things? Biochemistry THE MIRACLE MOLECULE Station 6: Moderation of Heat 1. Heat 50 ml of water for two minutes and record change in temperature. What happens? 2. Heat 50 ml of alcohol for two minutes and record change in temperature. What happens? 3. What does it mean to say that water moderates heat? 4. What chemical property of water allows this to happen? 5. Why might this be important to living things?