Reading and Interpreting Seismographs
advertisement

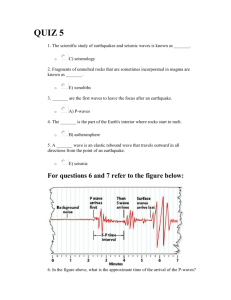
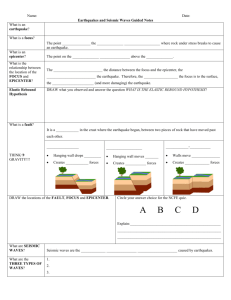
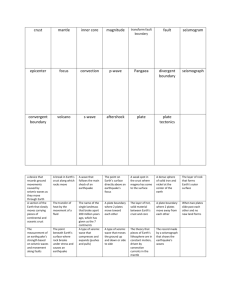
Name _____________________ Lab # _________ Date __________ SEISMOGRAPH LAB Objective: To learn how to read seismogram printouts from a seismograph. To learn how to read the ESRT's Earthquake P-Wave and S-Wave Travel Time chart. Introduction: Earthquakes occur when there is movement along a _________ in the earth's crust. The movement along this line produces shock waves (seismic waves) that are sent out in all directions through the earth. ________________ are scientific instruments which record the shaking of the earth's crust. There are 3 types of waves that are sent out when an earthquake occurs. Compressional waves or ___-waves vibrate in the direction they travel. This wave travels fastest or slowest and is the first or last wave to reach a seismic station. These waves can travel through all substances and layers of the earth. Shear waves or ___-waves vibrate perpendicular to their direction of travel. These waves travel fastest or slowest and are the first or last wave to reach a seismic station. Secondary waves can only travel through solids therefore they can not travel through the _____________ of the earth because it is a liquid. Scientists have created both P and S waves in the laboratory and have seen that S-waves do not travel through liquids, therefore they assume the outer core must be liquid. Longitudinal Waves or L-Waves are very slow waves which move in many directions. They are responsible for the destruction on land caused by earthquakes. Vocabulary Words to Define (3 pts each) Seismograph Time lag Fault Origin Time Earthquake - Procedure: Use the ESRT and your brain to answer the questions that follow, make sure you put all your answers on the answer page at the back of the lab. Practice Problems as a group: A) How long does it take a P-Wave to travel 2000 km? _________ B) How long does it take a S-Wave to travel 2000 km? _________ C) How far will an S-Wave travel in 15 minutes? ___________ D) What is the time lag (in minutes and seconds) if you are 4000 km away? ________ E) What is the time lag if you are 2000 km away? _________________ F) A seismologist is reading a seismogram which was recorded on his seismograph, she calculates the difference in arrival time between P and S waves is 5 minutes and 40 seconds, how far away is the earthquake from the seismic station? __________ km Write down the procedure that is necessary to perform this calculation. Now try one more, the lag time is 3 minutes, how far away is the earthquake? __________km What is the time lag for these seismic locations? Answer these questions on the answer page! 1. How many minutes for an S wave to travel 3000 km? 2. How far does an S wave travel in 19 minutes? 3. How many minutes for an S wave to travel 1000 km? 4. How many minutes for a P wave to travel 2000 km? 5. How far does a P wave travel in 8 minutes? 6. How far does a P wave travel in 4 minutes? 7. If a P wave arrives in 7 minutes, then when will an S wave arrive? 8. If the S wave arrived in 4 minutes, when did the P wave arrive? 9. If the P and S wave arrived 4 minutes apart, how far away is the epicenter? 10. If the P and S wave arrived 10 minutes apart, how far away is the epicenter? 11. If the S wave arrived 6 minutes after the P wave, how far is the epicenter? 12. An earthquake occurred 4600 km away, what is the time lag? 13. An earthquake occurred 7000 km away, what is the time lag? 14. An earthquake occurred 2000 km away, what is the difference in arrival time between waves? 15. An earthquake is 9000 km away, when will the P wave arrive? 16. An earthquake occurred at 10:00 am today and is 4200 km away, at what time the did the P wave arrive? 17. Same question as 16, at what time did the S wave arrive? 18. An earthquake occurred at 7:14 pm and is located 2000 km from the seismic station. At what time will the S-wave arrive at the station? 19. A seismic station is 5800 km from an earthquake. It recorded the arrival of the P-wave at 8:12 am. At what time did the earthquake occur? (think about it!) 20. The time lag for an earthquake is 3 minutes and 40 seconds. If the earthquake occurred at 1:37 am, when did the P wave arrive? 21. Extra Credit - Try if you dare!!!! Don't ask me for help, cause I won't help you. A seismic station in New York records the P and S waves times for an earthquake that occurred in Los Angeles California. The P wave arrived exactly when the 5th period bell rang and students left their classrooms. When did the earthquake occur local time in Los Angeles? Read the following Seismograms and determine the distance each station is from the epicenter. Discussion Questions - You must answer in complete sentences or its minus 10 points. What information can you gather regarding an earthquake, if you have P and S wave readings from one seismic station? Describe the motion of a P wave and an S wave as it travels through the earth. Include a diagram of how each wave travels. How does the lag time for a seismic station close to an earthquake compare with the lag time from a seismic station that is further away? Graph the relationship between time lag (y-axis) and distance from an earthquake (x-axis). Why do scientist think the outer core of the earth is liquid? Why do scientist think the outer core and inner core are made of iron and nickel? What happens to the velocity of an earthquake wave as it move through denser material? Conclusion : Describe the events that cause an earthquake, then describe the order of event that happen after an earthquake which lets seismologist determine the distance to the earthquake. Seismic Lab Answer Sheet 1_________________ 2_________________ 3_________________ 4_________________ 5_________________ 6_________________ 7_________________ 8_________________ 9_________________ 10________________ 11_________________ 12_________________ 13_________________ 14_________________ 15_________________ 16_________________ 17_________________ 18_________________ 19_________________ 20________________ 21 Extra Credit ______________ 22_________________ 23_________________ 24_________________ 25_________________