QUIZ 5
advertisement

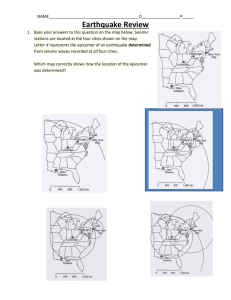
QUIZ 5 1. The scientific study of earthquakes and seismic waves is known as _______. o C) seismology 2. Fragments of unmelted rocks that are sometimes incorporated in magma are known as _______. o E) xenoliths 3. _______ are the first waves to leave the focus after an earthquake. o A) P-waves 4. The _______ is the part of the Earth's interior where rocks start to melt. o B) asthenosphere 5. A _______ wave is an elastic rebound wave that travels outward in all directions from the point of an earthquake. o E) seismic For questions 6 and 7 refer to the figure below: 6. In the figure above, what is the approximate time of the arrival of the P-waves? o B) 2 minutes, 15 seconds 7. According to the figure above, what is the approximate S-P travel time? o A) 1 minute, 45 seconds 8. Using data from three locations to find the epicenter of the earthquake, is called the method of ___________________ o c) triangulation 9. The _________ interval is the time difference between the arrival of the primary and secondary waves, this is then used to calculate the distance from the seismograph to the earthquake. o S-P 10. On the circle that is drawn using the distance calculated from the difference of the arrival of primary and secondary waves, gives you the _____________ of the circle. o radius 11. In the figure above, the largest earthquakes correlate with which type of plate boundaries? o Subduction zones (continental - oceanic) 12. In the figure above, what is the approximate speed of S-waves and the Pwaves as the earthquake starts? o B) 3km/sec and 6km/sec True/False 13. The Earth's density as a whole is approximately 2.8 g/cm3. o True 14. P-waves travel by compression-expansion. o True 15. The mantle makes up roughly 80% of the Earth's volume. o True Fill in the blank 16. A large, destructive wave sometimes caused by am earthquake is called a _______. TSUNAMI 17. _______ is the bouncing back of a wave from an interface between two mediums. REFLECTION 18. S waves cannot travel through ____________ LIQUIDS 19. ______________ happens when a wave increases or decreases its speed when it changes of medium. REFRACTION 20. The theory that stress is continually built up along a fault and released when earthquake occurs is known as the _______ rebound theory. ELASTIC 21. The method of using data from three seismic stations to locate an earthquake is known as _______. TRIANGULATION 22. _______ are fragments of unmelted rock that are sometimes incorporated in magma. XENOLITHS 23. The area inside the Earth where rocks start to turn plastic is known as the _______. ASTHENOSPHERE