Chapter 13/14: Kinetic Theory
advertisement

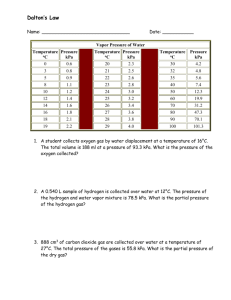
Winkle 2/8/16 ACCELERATED CHEMISTRY SEMESTER TWO STUDY GUIDE Chapter 12: Stoichiometry Moles to moles Moles to mass Mass to moles Mass to mass Limiting Reagents (reactants)- this is the big part but you need to know the above to solve them Percent yield Chapter 13/14: Kinetic Theory A. Know the principles of the kinetic theory B. Definition of Pressure - units for measuring pressure - know conversions from all units C. Kinetic Energy and Temperature - definition of absolute zero - Celsius/Kelvin conversions D. States of matter: know the characteristic of solids, liquids, and gases E. How does the balloon in a flask work F. Understand differences in pressure at high and low elevations Chapter 13/14: Gases A. STP – standard temperature and pressure B. Boyle’s Law: Know the definition and pressure EX: At constant temperature, 338 ml of a gas has a pressure of 86.1 kPa. What is the volume as the pressure is increased to 104 kPa? C. Gay-Lussac’s law D. Charles Law EX: Assuming constant pressure, what volume would 123 ml of a gas occupy as the temperature goes from 25oC to 67oC? E. Combined Gas Law: know the equation and how to use it EX: p. 463 #14 Chapter 14.4: Gases and the Mole A. Molar Volume/ Avagadro’s number Winkle 2/8/16 B. Ideal Gas Law: know defintion and equation EX: What pressure is exerted by 0.622 mol of a gas contained in a 9.22 L vessel at 16oC? EX: How many moles of gas occupy a 486 ml at 11oC and 66.7 kPa? EX: At what temperature is a gas if 0.0851 moles of it is contained in a 604 ml vessel at 100.4 kPa? C. Ideal Gas Law to calculate molecular mass EX: What is the molecular mass of a gas if 150.0 ml has a mass of 0.922 g at 99oC and 107.0 kPa? EX: What is the molecular mass of a gas if 0.858g of it occupies 150.0 mL at 106.3 kPa and 2oC? D. Gas Stoichiometry- you may have to do a limiting reactant problem here!!! Make sure you study it!!! Rules: mass/gas volume Rules: gas volume/mass 1. balance equation 1. balance equation 2. find # of moles given 2. change volume of gas to moles of gas 3. mole ratio 3. mole ratio 4. express moles of gas in volume of gas 4. Express moles of substance in grams EX: An excess of hydrogen reacts with 14.0g of nitrogen. How many mL of ammonia are produced at STP? EX: What volume of hydrogen of STP can be produced when 6.54g of zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid? E. Gas Stoiciometry: Limiting reactants (remember how much you hated these??) Nuclear A. Know about half-life and what it means B. Know how to balance nuclear equations- be sure to know the symbols for the particles used Solutions A. Vocab that goes along with this B. Solubility curves C. Molarity- how to calculate it or create solutions from other solutions M1V1=M2V2 Chapter 18: Chemical Equilibrium A. Equilibrium Constants: Writing Keq expressions and solving for concentrations Winkle 2/8/16 EX: At a given temperature the Keq for the gas phase reaction, 2HI H2 + I2 is 1.4 x 10-2. If the concentrations of both H2 and I2 at equilibrium are 2 x 10-4 M, find [HI]. B. Le Chatelier’s Principle: know how changing variables (like concentration, etc.) effect an equilibrium. Chapter 19: Acids and Bases A. Know how to identify: acid, base, conjugate acid, conjugate base B. Identifying Strong and Weak Acids C. Neutralization reaction: Acid + Base D. Ionization Constants (Ka and Kb) E. pH scale F. Calculating pH and pOH Salt + Water