Plate Tectonics and Volcanoes
advertisement

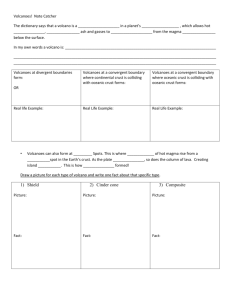
Plate Tectonics and Volcanoes Lesson Plan DIAGNOSTIC PHASE: Analytic Description of Pupil(s): Identify the NY Learning Standards: This Lesson Addresses: Standard 1: Analysis, Inquiry, and Design Standard 2: Students will access, generate, process, and transfer information, using appropriate technologies. Standard 4: Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical development of ideas in science. 4.2.1l The lithosphere consists of separate plates that ride on the more fluid asthenosphere and move slowly in relationship to one another, creating convergent, divergent, and trans-form plate boundaries. These motions indicate Earth is a dynamic geologic system. •These plate boundaries are the sites of most earthquakes, volcanoes, and young mountain ranges. •Compared to continental crust, ocean crust is thinner and denser. New ocean crust continues to form at midocean ridges. •Earthquakes and volcanoes present geologic hazards to humans. Loss of property, personal injury, and loss of life can be reduced by effective emergency preparedness. 4.2.1n Many of Earth’s surface features such as mid-ocean ridges/rifts, trenches/subduction zones/island arcs, mountain ranges (folded, faulted, and volcanic), hot spots, and the magnetic and age patterns in surface bedrock are a consequence of forces associated with plate motion and interaction. Goal: To understand how plate tectonics accounts for the features and processes (sea-floor spreading, mid-ocean ridge, volcanoes, subduction zones, mountain ranges) that occur on or near Earth’s surface. Objective(s): Students will be able to explain the Theory of Plate Tectonics. Students will be able to explain the relationship between plate tectonics and the location of volcanoes. Students will use world maps to explore the relationship between locations of plate boundaries and areas of high volcanic occurrences. Students will be able to describe movement of plates along convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. Students will be able to compare and contrast three types of volcanoes. Students will discover natural hazards and the risks and benefits of volcanic activity. Students will research a volcano and share findings on a class wiki page. Entry Skills: Students should know convection currents in the mantle cause movement of the Earth’s plates. Students should know the structure and layers of the Earth. Students should have map skills. Model/Strategy: Students will use digital resources to engage in an inquiry-based exploration of volcanic activity to form a hypothesis about the relationship between plate boundaries and areas of volcanic occurrences. Students will discover the distribution patterns of volcanoes by plotting locations of volcanoes on a world map. Students will explore the movement of plates along boundaries using digital simulations. Students will work with partners to research a volcano and create a wiki page over a two to three week period during volcano unit. See Project Requirements. Materials: Computers with Internet access or computer lab; printer; Smart Board/Proxima; Interactive Science Notebooks, chart paper and markers, colored pencils, Wiki Space, world map worksheets, Plate Boundary Diagrams (Figures 1 -4), Plate Tectonics: The Big Picture diagram, Classroom Organization: Some components of the lesson will be whole group direct instruction using the Smart Board. Students will complete some tasks independently and also work in cooperative groups to complete other tasks. Culminating wiki project will be with partners in a collaborative effort to contribute to the class wiki. IMPLEMENTATION PHASE Anticipatory Set: Show you tube video, “Volcanoes erupting on the Big Island of Hawaii” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hec9yK-QQ4o Prior to the video, ask students, “What they think of when they hear the word volcano?” (Accept all responses at this time. Typical responses include explosions, fiery eruptions, lava, death, destruction) As significant as those aspect are, challenge students previous conceptions by asking students to also consider other aspects of volcanoes that influence the arts, history, and literature of people living near them. Tell the students they will be researching a volcano over the next few weeks and creating a wiki page that includes how the volcano has affected the people living nearby. Procedures for achieving objective(s) Sequence of Objectives Assessment Background Information for the Teacher Most volcanoes occur along diverging plate boundaries, such as the mid-ocean ridge, or in subduction zones around the edges of oceans. Exceptions to this pattern are volcanoes that form at “hot spots”. Volcanoes at Diverging Plate Boundaries – form along the mid-ocean ridge. Along the ridge, lava pours out of cracks in the ocean floor. Volcanoes at Converging Plate Boundaries – Many volcanoes form near the plate boundaries where oceanic returns to the mantle. Subduction causes slabs of oceanic crust to sink through a deep-ocean trench into the mantle. The crust melts and forms magma, which then rises back toward the surface. When the magma from the melted crust erupts as lava, volcanoes are formed. Converging plates often form volcanoes when two oceanic plates collide (Island Arc) or when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. In both situations, oceanic crust sinks through a deep ocean trench, melts to form magma, and then erupts to the surface as lava. Hot Spot Volcanoes - A hot spot is an area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust like a blow torch. Hot spots often lie in the middle of continental or oceanic plates far from any plate boundaries. Unlike volcanoes in an island arc, volcanoes at hot spots do not result from subduction. Essential Questions: How do features on the Earth’s surface change? How are the locations of geographic features related to the locations of plate boundaries? What causes the Earth’s plates to move? What are the benefits to a region of volcanic activity? Begin the Lesson (2 days) Day 1 1. Prior Knowledge: Create a K-W-L Chart and record student responses on chart paper. What do you know about volcanoes? 2. Provide definitions for key vocabulary (Preview Vocabulary) Plate Tectonics–Theory that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle divergent boundary – A plate boundary where two plates move away Student Responses Interactive Science Notebook from each other convergent boundary – A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other transform boundary – A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions Ring of Fire – A major belt of volcanoes that rims the Pacific Ocean Subduction – The process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deepocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary . 3. Investigate It: Where are Volcanoes Found on Earth’s Surface Students will work in small groups to study the interactive map of Earth’s volcanoes around the globe by Houghton Mifflin Company at http://www.uky.edu/AS/Geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module04swf.s wf and include information below on World Map Worksheet. Interactive Science Notebook Critical Thinking Do the locations of volcanoes form a pattern? Develop a hypothesis to explain where Earth’s volcanoes are located. Are there any volcanoes on the map whose location cannot be explained by your hypothesis? How can you explain the pattern of volcanoes? (Volcanoes form along the boundaries of Earth’s plates. The Ring of Fire is a belt of volcanoes that circles the Pacific Ocean. Most volcanoes occur along diverging plate boundaries such as the mid-ocean ridge or in subduction zones around the edges of oceans. Some volcanoes form at “hot spots” far from the boundaries of continental or oceanic plates.) Expected Outcome: Yes, there is a pattern. Volcanoes seem to be related to plate boundaries. Printable world map – Provide students with world map. Students will indicate the location of volcanoes around the world, type of boundaries, and the movement of plates along those boundaries and include a map legend. a. b. c. d. e. 4. Map Activity Plot volcanic activity Mark plate boundaries Indicate movement at plate boundaries using arrows Plot hot spots Include a map legend Class Discussion – Lead a discussion based on the following questions? Questions & Answers Where are the majority of volcanoes located? Ring of Fire What is the relationship between plate boundaries and location of volcanoes? Volcanoes form along the boundaries of Earth’s plates 5. Follow-up Lesson: Movement of plates at boundaries Day 2 1. Review concepts 2. Direct Instruction – Teach how volcanoes form at convergent and divergent boundaries and at Hot Spots. Display Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, and Figure 4 on the Smart Board. Questions and Answers Questions and Answers 3. Use hand movements to show how plates move. (Kinesthetic) Observation 4. Plate Tectonic Activity: Students will use digital media to discover how the movement of plates at convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries change Earth’s surface by visiting websites below. Observation PBS, A Science Odyssey: Mountain Maker, Earth Shaker http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectonics/ Animation of volcanic islands forming over a hot spot http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0904 /es0904page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization Animation of Volcanism at a subduction zone http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0902 /es0902page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization Animation of Process that occur along plate boundaries http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/visualizations/es0804 /es0804page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization 4. Interactive Notebook –Summarize the movement of convergent and divergent boundaries (Right-side entry). Draw a diagram of convergent and divergent boundaries. (Left-side entry) 5. Class Discussion – Lead a discussion based on the following questions? Interactive Notebook Entries Questions & Answers What type of boundary is located at the mid-ocean ridge? Divergent boundary Where are hot spots located in relationship to earth’s plates? Some volcanoes form at “hot spots” far from the boundaries of continental or oceanic plates What happens when continental crust and oceanic crust meet? Oceanic crust plunges back into the mantle at a subduction zone Continental crust and continental crust? Mountains, volcanoes form Oceanic crust and oceanic crust? Island Arcs form Guided Practice Activities: Students will use digital media to discover how the movement of plates at convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries change Earth’s surface. Bloom’s Taxonomy Questions: Knowledge: Label plate boundaries Comprehension: Explain the formation of volcanoes at convergent and divergent boundaries, and hot spots. Application: Construct a volcano that incorporates features of the surrounding town or city. Analysis: Students will analyze different types of plate boundaries. Evaluation: Assess the effect of volcanic activity on people living near a volcano. Synthesis: Develop a hypothesis to explain where Earth’s volcanoes are located. Closure: Ticket to Leave - Students will write down something knew they learned and share with the class in Interactive Science Notebook. Independent Practice: Students will label diagram: Plate Tectonics: The Big Picture Evaluation of Learning: Interactive Notebook –Summarize the movement of convergent and divergent boundaries (Right-side entry). Draw a diagram of convergent and divergent boundaries. (Left-side entry) Volcano Wiki Project (Culminating Project) Volcano Jeopardy (End of Unit Review) Differentiated Instruction: Flexible grouping, Modify assignments to instructional level, Visual Learner: Visualizations/Simulations for abstract concepts, Kinesthetic Learner: Use hand movements to show direction of plate movements. Follow-up Lesson: Volcanic Activity –Students will be able to describe what happens when a volcano erupts and explain how the two types of volcanic eruptions differ. Connections: Language Arts: Explore how myths help to explain nature and science. Students may read, discuss, and respond in writing to a variety of myths. Vulcan “Roman God of Fire” Hephaestus “Greek God of Fire and Forge” Pele “Hawaiian Goddess of Volcanoes” USGS, Volcanoes in Legends and Mythology, http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/LivingWith/PopCulture/mythology.html Figure 1 Converging plates often form volcanoes when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate. Oceanic crust sinks through a deep-ocean trench, melts to form magma, and then erupts to the surface. Figure 2 Converging plates build up Earth’s surface when continental plates collide with another continental plates. Figure 3 Converging plates often form volcanoes when two oceanic plates collide. The older, denser plate dives under the other plate creating a deep-ocean trench. The plate sinks into the asthenosphere. It begins to melt forming magma. The magma seeps upward through cracks in the crust eventually breaking through the oceanic floor creating volcanoes. The resulting volcanoes create a string of islands called an island arc. Figure 4 Some volcanoes form from “hot spots” in Earth’s mantle. A hot spot is an area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust like a blowtorch. Hot spots usually occur in the middle of continental or oceanic plates far from any plate boundaries. Unlike volcanoes in an island arc, the volcanoes at a hot spot do not result from subduction. Figures found on U.S. Geological Survey http://pubs.usgs.gov/publications/text/understanding.html Plate Tectonics: The Big Picture Volcano Wiki Project Project Description: You will be researching a volcano. Using this information, you will build a model of your volcano and create a Wiki page for your volcano. Volcano Model: 1. Construct a model of volcano including any defining features of the volcano including craters and lakes. 2. Incorporate features of the surrounding area such as cities, oceans, forests, etc. into the model. - Possible materials may include clay, Styrofoam, paint, plaster, paper, etc. 3. Attach a picture of the volcano to your model. 4. Attach a note card to your volcano following the model below: Name of Volcano Elevation (Height) Age of Volcano: Country: Date of Last Eruption: Nearest City: Type of Volcano: (Cinder, Composite, Shield, Lava Plateau, Caldera, etc) Three Interesting Facts: (complete sentences) Student(s) Name(s): Science Period: Date: Volcano Wiki Project (Documentary) 1. Include the following information in your Wiki - Volcano name, country - Type of Volcano (Cinder, Composite, Shield, Lava Plateau, Caldera, etc) - Include an image or video of this volcano - Include a picture of your model volcano - Research the history of the volcano’s eruptions - Describe the most famous eruption from this volcano and its effects - Research the risks and benefits of this volcano to the surrounding town/area - Include aspects of how the volcano has influenced the arts, history, and literature of the people living in the region. - Include the effect of volcanic activity on soil and agriculture for the region. - Investigate environmental concerns of the volcanic eruptions. 2. References – You must use at least two on-line sources. You must cite sources correctly. Online Bibliography Formatting Sources: http://www.easybib.com http://www.noodletools.com Revisit the You Tube video: “Volcanoes erupting on the Big Island of Hawaii” http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hec9yK-QQ4o Volcano Wiki Project Rubric CATEGORY Content Organization Attractiveness Contribution to the Group Accuracy Model 4 Excellent Achievement All report requirements are included. Covers topic in depth with very strong understanding of the volcano researched. Strong creativity. Clear organization. Makes excellent use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. to enhance the presentation. 3 Adequate Achievement Most report requirements are included. Covers topic with strong understanding of the volcano researched. 2 Limited Achievement Some report requirements are included. Shows limited understanding of the volcano researched. 1 Minimal Achievement Missing many report requirements. Shows minimal understanding of the volcano researched. Some creativity. Definite organization. Makes good use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. to enhance the presentation No creativity. Lacks organization. Makes use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. but often these detract from the presentation content. Contributes greatly to the development of the class wiki. Free of mechanical errors. No HTML errors in wiki (e.g., broken links, missing images) Contributes adequately to the development of the class wiki. Few mechanical errors. Few HTML errors in wiki (e.g., broken links, missing images) Limited creativity. Some organization. Makes use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. but occasionally these detract from the presentation content. Contributes moderately to the development of the class wiki. Some mechanical errors. Some HTML errors (e.g., broken links, missing images) Model strongly resembles volcano. Features of surrounding area included. Model resembles volcano. Most features of surrounding area included. Model somewhat resembles volcano. Some features of surrounding area included. Contributes minimally to the development of the class wiki. Overwhelming mechanical errors. Overwhelming HTML errors (e.g., broken links, missing images) Model does not resemble volcano. Features of surrounding are not included.