W-Ocean Currents[1]
advertisement
![W-Ocean Currents[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007397237_1-710c5ffe595c133e309d957ef64211fd-768x994.png)
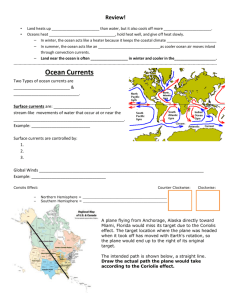
Name: _____________________________________________________ Pd.: ________ Date: ______________________ Ocean Currents Section I – Short Answer: Complete the following sentences using the word bank below. Antarctica Circulating winds climate Word Bank counter clockwise Gulf Stream currents Humboldt equator Large land masses North Atlantic Current Northern Hemisphere West Wind Drift 1. The phrase “rivers within an ocean” refers to the ocean’s _______________________. 2. Two ocean currents that affect the coasts of North America are the ______________________________ and ________________________________. 3. The currents below the ______________________ flow in a ________________________________ direction. 4. The ___________________________ current, in the Southern Hemisphere, completely circles the cold continent of _______________________. 5. Currents affect the _____________________________ of neighboring land masses. 6. The _______________________________ is a cost South American coastal current. 7. The _______________________________ is a warm ocean current that affects England’s climate. 8. _______________________________ cause currents to change directions. 9. _______________________________ push surface water in different directions. 10. Currents in the _____________________________ are eastward flowing ‘rivers’. Section II – Multiple Choice: Select the best answer to complete or answer the questions below. 11. Which type of current results from underwater landslides? a. rip current b. turbidity current c. longshore current d. tidal current 12. Which of the following best describes the water found in the deep currents of the Atlantic Ocean? a. cold with high salinity b. cold with low salinity c. warm with high salinity d. warm with low salinity 13. The currents in the northern Indian Ocean are governed by winds called: a. monsoons b. tsunamis c. trade winds d. tombolos 14. Deep Atlantic currents are formed largely as a result of the: a. erosion by surface winds. b. heating of surface water. c. rotation of the Earth. d. sinking of denser water. 15. The deflection of the Earth’s winds and ocean currents is caused by the Earth’s rotation called ____. a. Doldrums b. Coriolis Effect c. Gulf Stream d. Density current Section III – Completion: Complete the table below using the choices listed for each column to identify the characteristics of the currents listed below. The table can be completed using the “Global Ocean Currents” map on page 532 of the McDougal-Littell textbook (blue and tan class set). Answer the questions below the table. Answer choices Current Ocean Basin Location of Basin General Temperature Atlantic Pacific Indian East West Warm Cold Flow direction relative to the Equator Toward Away from Gulf Stream California Canary Peru Brazil Kurishio W. Australia E. Australia Beneguela Agulhas 16. What is the general relationship between a current’s temperature and the side of the ocean on which that current flows? 17. In what direction, clockwise or counterclockwise, do the major circulation patterns rotate in the Northern Hemisphere? 18. In what direction, clockwise or counterclockwise, do the major circulation patterns rotate in the Southern Hemisphere? 19. Why does each hemisphere have a different pattern? 20. An ocean fog will occur when moist air blowing from a warm ocean current meets warm air over a cold ocean current. Which Australian coast (N, S, E, or W) is most likely to experience such fogs?