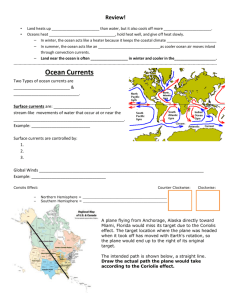
Ag Earth Science – Chapter 16.1 – Oceanic Circulation 16.1
advertisement
Ag Earth Science – Chapter 16.1 – Oceanic Circulation 16.1 Vocabulary Word Ocean current Surface current gyre Coriolis effect upwelling 1|Page Definition Paraphrase Picture Density current I. Surface Circulation A. Ocean Currents – B. Surface Currents – 1. C. Gyres – 1. Coriolis Effect – a. Because of the Earth’s rotation, currents are deflected to ________ in the Northern Hemisphere and to the _________ in the Southern Hemisphere. D. E. F. Upwelling – 1. II. Upwelling brings greater concentrations of dissolved nutrients, such as nitrates and phosphates, to the ocean surface. Deep-Ocean Circulation A. 2|Page Density Currents – 1. Cold, salty water is more dense than warmer water, so it drops down vertically into the depths of the ocean and is replaced by less dense water. 2. Evaporation of ocean water in warm surface areas also can increase salinity (density) and causes the denser water to drop and be replaced by less dense water. III. Conveyor Belt Model A. Simplified Model of Ocean Circulation a. Travels from Atlantic Ocean through Indian and Pacific Oceans and back again. 1. 2. 3. 3|Page