Terms - kjpederson
advertisement

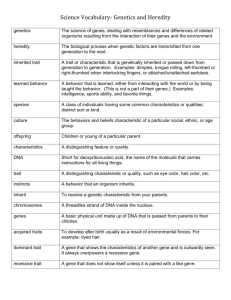
Biology I Genetics Unit Terms Chapter 9 (p. 178) 1. allele (p. 169): an alternative form of a gene 2. codominance (p. 176): an inheritance relationship in which neither of two alleles of the same gene totally masks the other 3. complete dominance (p. 176): an inheritance relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over the other; both Bb and BB have the same phenotype 4. dominant (p. 168): referring to an allele that masks the presence of another allele for the same characteristic 5. F1 generation (p. 166): the offspring of cross-pollinated P1 generation of plants 6. F2 generation (p. 166): the offspring of self-pollinated F1 generation plants 7. genetics (p. 165): the field of biology devoted to understanding how traits are passed from parents to offspring 8. genotype (p. 172): the genetic makeup of an organism 9. heredity (p. 165): the transmission of traits from parents to their offspring 10. heterozygous (p. 173): referring to a gene pair in which the two alleles do not code for the same trait 11. homozygous (p. 173): referring to a gene pair in which the two alleles code for the same trait 12. Law of independent assortment (p. 169): law stating that pairs of genes separate independently of one another in meiosis 13. Law of segregation (p. 168): law stating that pairs of genes separate in meiosis and each gamete receives one gene of a pair 14. P1 generation (p. 166): a strain obtained through self-pollination 15. phenotype (p. 172): the external appearance of an organism that is determined by the individual’s genotype 16. phenotypic ratio (p. 175): the ratio of the offsprings’ phenotypes 17. probability (p. 173): the number of times an event is expected to happen divided by the number of opportunities for an event to happen 18. Punnett square (p. 174): a model used to establish the probabilities of the results of a genetic cross 19. pure (p. 166): Plants that are pure for a trait always produce offspring with that trait 20. recessive (p. 168): referring to an allele that is masked by the presence of another allele for the same characteristic 21. strain (p. 166): denotes plants that are pure for a specific trait 22. testcross (p. 175): the crossing of an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype 23. trait (p. 165): in genetics, a category within which alternate characteristics, such as height and eye color, can be observed. Chapter 10 page 197 1. codon (p 193): a group of three sequential nitrogen bases of an mRNA molecule 2. genetic code (p 193): triplets of nucleotides in mRNA that determine the sequence of amino acids in protein 3. messenger RNA (p 191): called mRNA, the type of RNA that carries genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes 4. mutation (p 189): a change in DNA 1 Biology I Genetics Unit Terms 5. protein synthesis (p 193): the formation of proteins using information coded on DNA and carried by RNA 6. replication (p 188): the process by which DNA copies itself during interphase 7. ribosomal RNA (p 191): called rRNA, the type of RNA found in a ribosome 8. transcription (p 191): the process in which RNA is made from DNA 9. transfer RNA (p 191): called tRNA, the type of RNA that carries amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes 10. translation (p 194): the process of converting the genetic code in RNA into the amino acid sequence that makes up a protein Chapter 11 page 215 1. activation (p 205): the initiation of transcription by the removal of a repressor protein 2. benign tumor (p 211): an abnormal but non-threatening cell mass 3. cancer (p 211): the uncontrolled growth of cells 4. carcinogen (p 212): a cancer-causing substance 5. carcinoma (p 211): a malignant tumor that grows in body tissues 6. enhancer (p 208): a region adjacent to a eukaryotic gene that must be activated if the gene is to be expressed 7. gene expression (p 203): the transcription of DNA into RNA and then into proteins 8. genome (p 203): the complete genetic material contained in an individual 9. growth factor (p 212): protein that regulates the rate and sequence of the events of cell division 10. inducer (p 205): in the lac operon, the molecule that binds to repressor molecules and induces gene expression 11. leukemia (p 211): a progressive, malignant disease of the blood-forming organs 12. lymphoma (p 211): a tumor in the tissues that form blood cells 13. malignant tumor (p 211): a cancerous mass of cells 14. metastasis (p 211): the spread of cancer cells beyond their original site 15. mutagen (p 212): an environmental factor that damages DNA 16. oncogene (p 214): a gene that induces cancer or other uncontrolled cell proliferation; a mutated or activated proto-oncogene that is associated with the development of tumor cells 17. operator (p 204): a sequence of DNA to which a repressor binds to prevent mRNA synthesis from the adjacent gene; characteristically composed of one or more palindromic sequences 18. pre-mRNA (p 207): a form of mRNA that contains introns and exons 19. regulator gene (p 205): a genetic unit that regulates or suppresses the activity of one or more structural genes 20. repression (p 205): the blockage of transcription by the action of a repressor protein 21. repressor protein (p 205): a protein that inhibits a specific gene from being expressed 22. sarcoma (p 211): a tumor growing in bone or muscle tissue 23. structural gene (p 204): a gene that codes for a product, such as an enzyme, protein, or RNA, rather than serving as a regulator 24. transcription factor (p 208): one of the additional proteins bound to enhancers and RNA polymerase that regulate transcription 25. tumor (p 211): an abnormal mass of cells 2 Biology I Genetics Unit Terms 26. tumor-suppressor gene (p 214): a gene that suppresses tumor formation but when mutated causes a loss in cell function, resulting in tumor formation Chapter 12 page 233 1. amniocentesis (p 232): a procedure used in fetal diagnosis in which fetal cells are removed from the amniotic fluid 2. carrier (p 228): individuals who have one copy of a recessive autosomal allele 3. chromosome map (p 224): a diagram of allele positions on a chromosome 4. colorblindness (229): a recessive X-linked disorder in which an individual cannot distinguish between certain colors 5. deletion (p 225): a mutation in which a segment of DNA breaks off of a chromosome 6. Down syndrome (p 231): a disorder caused by an extra twenty-first chromosome and characterized by a number of physical and mental abnormalities 7. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (p 229): a form of muscular dystrophy that weakens and progressively destroys muscle tissue 8. frame shift mutation (p 226): a mutation that results in the misreading of the code during translation because of a change in the reading frame 9. germ-cell mutation (p 224): a change in the DNA of a sex cell 10. lethal mutation (p 224): a mutation that causes death, often before birth 11. linkage group (p 222): the group of genes, located on the same chromosome, that are usually inherited together 12. multiple-allele traits (p 229): controlled by three or more alleles of the same gene that code for a single trait 13. nondisjunction (p 225): the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis or the failure of sister chromatids to separate during mitosis 14. pattern of inheritance (p 228): certain phenotypes that are usually repeated in predictable patterns from one generation to the next 15. pedigree (p 227): a diagram of the genetic history of an individual; can show how a trait is inherited over several generations 16. phenylketonuria (PKU) (p 232): a genetic disorder in which the body cannot metabolize phenylalanine 17. point mutation (p 225): the change of a single nitrogen-containing base within a codon 18. polygenic trait (p 229): a trait controlled by multiple genes 19. sex linkage (p 222): the presence of a gene on a sex chromosome 20. sex-influenced trait (p 229): a trait that is influenced by the presence of male or female sex hormones 21. sickle cell anemia (p 226): a genetic disorder caused by a point mutation that substitutes adenine for thymine in a single DNA codon. This substitution results in a defective form of the protein hemoglobin. 22. single-allele trait (p 228): a trait controlled by a single allele 23. somatic mutation (p 224): a mutation that occurs in a body cell 24. translocation (p 225): a mutation in which a broken piece of chromosome attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome; movement or organic molecules in plant tissues 25. trisomy (p 231): a chromosomal anomaly in which an individual has an extra chromosome in any of the chromosome pairs 3 Biology I Genetics Unit Terms 26. trisomy-21 (p 231): a human congenital disorder caused by trisomy of chromosome 21 due to the failure of the sister chromatids to separate during mitosis or the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis (see Down syndrome) 27. X-linked gene (p 222): a gene found on the X chromosome 28. Y-linked gene (p 222): a gene found on the Y chromsome Chapter 13 page 253 1. cloning vector (p 240): a carrier used to clone a gene and transfer it from one organism to another 2. DNA fingerprint (p 243): a pattern of bands made up of specific fragments from and individual’s DNA 3. DNA technology (p 239): the technology involved in genetic engineering 4. gel electrophoresis (p 244): technique used to separate nucleic acids or proteins b size and charge 5. gene clone (p 240): an exact copy of a gene 6. gene therapy (p 246): treatment of a genetic disorder by introducing a healthy gene into a cell 7. genetic engineering (p 239): a form of applied genetics in which scientists directly manipulate genes 8. herbicide (p 251): weed-controlling chemicals 9. Human Genome Project (p 246): worldwide scientific collaboration to determine the nucleotide sequence of the entire human genome 10. insulin (p 241): a hormone that lowers the blood glucose level 11. pathogen (p 250): an organism that causes disease 12. recombinant DNA (p 241): a DNA segment from at least two different organisms 13. restriction enzyme (p 239): a protein that recognizes specific sequences in a DNA molecule and cuts it into pieces 14. transgenic organism (p 242): a host organism that has received recombinant DNA 15. vaccine (p 250): a solution containing a harmless version of a virus, bacterium, or toxin that causes an immune response when introduced to the body 4