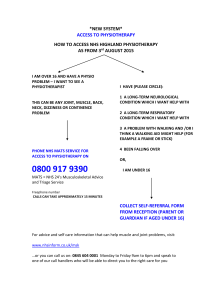
DUfisterKZ
advertisement

1 Evaluation of the Daugavpils University (DU) Curriculum and Programmes for speciality Physiotherapy (4 study years) Accreditation Commission: prof. Lembit Allikmets (Faculty of Medicine, University of Tartu), prof. Aleksandras Kisčiunas (Kaunas University of Medicine), Dr. Güntis Osis (Director LFA, Riga) has made side visits to the DU during two days, June 13 and 14’ 2002, has had meetings with Rector, Vice-Rectors, Dean, Faculty members, Librarians and students and also the Clinical Chiefs and teachers. All needed info was presented to the Commission members: info about the aims, organization, management, immatriculation, structure of curriculum, annotations and essentials of programmes. The people we met in DU and hospitals were very enthuziastic about their mission, friendly and helpful. We are particularly indepted to Dr. Juris Dzelme, Director of HEQEC, Ministry of Education of Latvia, who took care of the organization of our visit, and also to the government of DU. I thank especially the eminent Baltic colleagues of this commission, A. Kisčiunas and G. Osis, who helped me to understand specific problems of this country. 1. Goals and aims of the Curriculum The aims are: to master basic knowledge and minimum necessary skills for practical actions on the level of professional Bachelor degree of higher education in the field of Physiotherapy, to educate specialists with a level-5 professional qualification in physiotherapy. The graduates have rights to continue their education in Master studies. 2. Structure and Division of the Curriculum The Curriculum for 4 years is divided into 4 main (A, B, C, D) blocks: (A) basic disciplines in medicine (anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology, microbiology, genetics, biochemistry, biometrics); also Latin terminology and computer sciences are included. (B) obligatory disciplines for professional specialization in physiotherapy (fundamentals of physiotherapy, physical medicine, physiotherapy in pediatrics, in neurology, in traumatology and orthopaedy, internal diseases, massage, manual therapy, ergotherapy, speech therapy), 14 CP-s are devoted to medical pathology, 2 CP-s to medical psychology, 2 CP-s to first aid. (C) optional courses in humanities 2 and social sciences, which include 14 disciplines (56 CP-s), among which students have elect at least 20 CP-s. The large scale of optional courses is possible because of University level education, where there are many faculties and departments. (D) optional (free choice) courses include 10 disciplines (17 CP-s) among which students have to get at minimum 6 CP-s. This part D is added to master profesisonal field in medicine. The professional study programme for Bachelor’s degree includes in total 171 CP-s. Out of these 129 CP-s include basic, medical, professional and practical courses in A, B, C and D parts, 30 CP-s to clinical practice. Each year the students are obligued to write a course paper and in the end Bachelor’s paper. The clinical practice is performed in Daugavpils City Central Hospital, National Rehabilitation Centre ”Vaivari” (incl. Latgale regional branch), Rehabilitation hospital “Baltezers”, P. Stradina Clinical Hospital and in the Institute of Orthopaedy and Traumatology in Riga, Rehabilitation Centre “Ligatne”. 3. Educational process and assessment The Curriculum has all disciplines needed for contemporary education of physiotherapists. The load of teaching is divided quite equally during 6 semesters of the first three study years. The number of exams and tests are satisfactory divided by semesters. 4th year is devoted mostly to clinical practice, plus 3-4 months for wrighting Bachelor’s dissertation. Programmes in special disciplines are mastered in cooperation with Rigas Stradins University professors. It is very valuable that in DU is an active Multimedia Center where several teaching aids, including videos have been made. Most of the teaching faculty is qualified because there have been earlier tradition in teaching basic medical and health disciplines to the physical culture students and also for other faculties of the DU. There are enough good lecture rooms both in the University and in hospitals. The library has very necessary for speciality literature and few journals. DU has supplied the division with the number of computers and there is a good cooperation between DU and General Hospital in Daugavpils. 8 highly qualified clinical specialists are among teachers. 4. Research, involvement of students Research in medicine in DU is increasing, the Department of Physiology is collaborating with the Departments of physics. The students get special tasks every 3 year to work through and to present the course paper. Also the topics for Bachelor’s dissertations are planned. The division of Physiotherapy has been started only 3 years ago and first students will graduate 2003. Among teaching faculty there are two professors, 12 docents and quite a member of lectors and teaching assistants. Some assistance is given by RSU in few disciplines. The overview was given to us by Dean of RSU and Director of “Vaivari”, professor Aivars Vetra. Also research is assisted by RSU. 5. Feedback, quality assurance All students fill out a teacher and course evaluation form in the end for each course. The questionnaires are anonymous and give possibility to use the information to improve the class. 6. Financial Resources The study programme is chiefly financed by the state budget, but students of the second and third year had to pay tuition Ls 300 per years. The class which entered 2001, has 10 students according to state plan and others (8 students) have to pay 300 Ls. 7. Conclusions The strong points of the Curriculum and programmes are: - the structure of University gives comparatively good technical provision and teaching staff, and good cooperation with other DU departments, - clear aim and strategy of the programme, - strong ties and cooperation with RSU School of Physiotherapy, Daugavpils city Central Hospital and National rehabilitation Centers, - possibilities for students to use through Internet the electronic data-bases, - good cooperation between faculty members and students, regular evaluations for the development of Curriculum, - European level of prgrammes, good equilibrium between credit points and practical training. The weak points are: - the teaching staff has very high load of auditorial work (700-1000 hrs annually), - insufficient research activities in physiotherapy by part of the academic staff, 4 - insuffisiently employed possibilities of lecturers exchange with foreign Universities, - insufficient financing of the study programme, specially for supplying modern technical equipment for research and clinical practice, - too much time is devoted to teach foreign languages. Recommendations - The number of hours (CP-s) for teaching biomechanics and orthopaedics should be increased. - To increase financing of the faculty for developing possibilities for research. - The Government of Latvia should think about increasing medical profile in the DU, there could be possibilities to open there also school for public health or school for nursing sciences. It seems to be important both to strenghten regional measures to develop Latgale and to use medical teaching staff more effectively. General conclusion The Curriculum and programmes are well designed and well comparable to the programmes of physiotherapy in the European Union. Recommendation: to accredit the Curriculum and programmes of Physiotherapy in the Daugavpils University for 6 years. Professor Lembit Allikmets University of Tartu Chairman of Accreditation Commission 5 Individual report About study program Daugavpils University Professional Study Curriculum in Physiotherapy with Bachelor's Degree in Health Care Goals and aims of the study program After graduation students acquire professional degree of Physiotherapist, which allows to work within profession of Physiotherapy and Bachelor's Degree in Health Sciences. That allows to continue academic career in different branches of Health Sciences. Structure and division of the study program Course is full — time and last four years. Physiotherapy curriculum functionally is divided in to four main subject groups: 1. Foundation subject - total amount of credit points is 51, 2. Clinical sciences - total amount of credit points is 14, 3. Sciences and Techniques of Physiotherapy - total amount of credit points is 80, 4. Other subjects - total amount of credit points is 26. There is large common field of activity practical by physiotherapists. In the physiotherapy curriculum not separate included rehabilitology, ergonomics. More hours should be for biomechanics, orthopaedics. The education process and assessment. Education is provided by qualified physiotherapy teachers or clinical physiotherapists. Clinical experience is supervised by Latvia Physiotherapists association. For student's education used: lectures, practical classes, seminars, students independent work, individual research project, clinical practise. Each subject has its own assessment requirements - test, colloquiums, exams. At the end of each Physiotherapy subject there is combined exam. Research, involvement of students in research. Every student has individual research projects. The total amount of credit points for research is enough. Strong and week points Main strength of the programme is good background and comparable with curricula of PT programmes with European country's. Weakness - some technical instruments are required. Conclusion The program is well designed and is similar to the other programmes of physiotherapy in the European union. Recommendation: accreditation for 6 years. 2002.06.14. 6 Dr.habil, professor Aleksandras Kriščiūnas Head clinical of Rehabilitation Kaunas University of Medicine Individuālais studiju programmas novērtējums. Daugavpils Universitātes Profesionālo studiju programmas “Fizioterapija” ar bakalaura grādu veselības aprūpē. Fizioterapijas programma ir 4 gadīgā universitātes līmeņa izglītības programma, kas sastāv no 4 galvenajām priekšmetu grupām. Programma ietver visas galvenās mācību priekšmetu grupas, kuras saskan ar Eiropā akceptētiem fizioterapijas izglītības standartiem. Izglītības programmas nodrošināšanai augstskolā ir nepieciešamais akadēmiskā personāla sastāvs. Labā līmenī ir nodrošināta A. grupas priekšmetu materiāli tehniskā bāze. Augstskola ir organizējusi nodarbību bāzi (Daugavpils Universitātē, Daugavpils pilsētas centrālajā slimnīcā) un klīnisko prakšu norises vietas (Daugavpils pilsētas centrālā slimnīca, Nacionālais rehabilitācijas centrs “Vaivari” un tā Latgales reģionālās filiāles, Rehabilitācijas centrs “Baltezers”, Stradiņa klīniskā slimnīca, Traumatoloģijas un ortopēdijas institūts, Rehabilitācijas centrs “Līgatne”, Universitātes bērnu klīniskā slimnīca). Klīniskās prakses vada medicīniskais personāls ar nepieciešamo izglītību un pieredzi. Programmas vājie punkti: 1. Nepieciešams papildināt tehnisko aprīkojumu, kas nepieciešams “Fizioterapijas pamatu” apgūšanai un zinātniski- pētnieciskā darba veikšanai; 2. Jāpapildina programmu ar Ergonomijas priekšmetu. Programmas pozitīvie aspekti: 1. Ir nodrošinātas klīnisko prakšu iziešanas vietas, klīnisko prakšu kredītpunktu apjoms sakrīt ar Eiropas valstu fizioterapijas izglītības standartiem. 2. Tiek veikts regulārs programmas salīdzinošs novērtējums ar citu (Latvijas un Ārvalstu) augstskolu programmām. 7 Slēdziens. Novērtējot Daugavpils universitātes studiju programmu “Fizioterapija” ar bakalaura grādu veselības aprūpē secinu, ka ir izveidota laba bāze kvalitatīvai turpmākai programmas attīstīšanai ar sekojošam speciālistu studijām maģistratūrā. Studiju programma ir veiksmīgi integrēta Daugavpils Universitātes struktūrā. Rekomendēju akreditēt programmu 6 gadiem. 2002.06.14. Guntis Osis LFA priekšsēdētājs