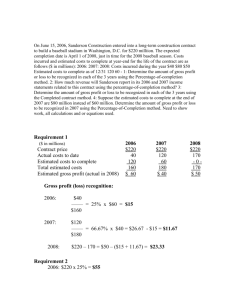
Building Area Definitions Summary: ASHRAE, ASTM, BOMA
advertisement

Summary of Building Area Definitions
Michael Deru
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
November 8, 2004
Summary
Eleven documents were reviewed with building area definitions. Most of them use a gross
building area definition from the exterior walls or from the centerline of walls separating
buildings for energy intensity calculations. Some include parking areas and other unconditioned
spaces. Some of the documents provide vague definitions of the area with no guidance on what
to include or not to include.
Summary of Area Metrics
Document and Area Metrics
ASHRAE 90.1-2001
Gross floor area
Gross building envelope floor area
Gross lighted floor area
Gross semiheated floor area
ASHRAE 100-1995
Area Factor
Area of the space
Conditioned floor area
Gross lighted area
Building area
ASHRAE 105-1984 (RA 99)
Floor area
ASTM E1836 – 01
Building Exterior gross area
Facility interior gross area
ANSI-BOMA Z65.1-1996
Gross building area
Gross measured area
Floor rentable area
EPA – Energy Star®
Gross area
EIA - CBECS
Floorspace
Gross floorspace
Square footage
FEMP E.O.13123 Guidance
Gross square footage
2003 International Building Code
Building Area
D:\106730394.doc
Clear
Def.
Include
Ext.
Walls
Include
uncond.
Spaces
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Some
Some
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
N/A
No
Yes
No
?
No
N/A
No
No
?
Yes
Yes
?
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No?
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No?
No?
No?
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
?
Yes
No clear metric name or definition
given
No
Yes
Yes
Both definitions include areas
with a roof but no exterior walls.
2/12/2016
1
Comments
general def. for other metrics
excludes slab-on-grade floors
1989 – inside of walls
Complicated formula
General definition
Used for EUI and CI
Ref “gross floor area” with no def.
Does not mention parking areas
Includes a diagram relating all the
area metrics
Generally used for EUI
Difficult to measure
Gross meas. area – vertical pen.
No clear metric name or definition
given
Gross Floor Area
2003 International Energy
Conservation Code
Conditioned Floor Area
Gross Floor Area
No
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
Protocol for Commercial Buildings
Total floor area
Floor area and volume
Ground-coupled floor area
No
No
No
?
?
?
Yes
Yes
Yes
ASHRAE 90.1-2001
Floor area, gross: The sum of the floor areas of the spaces within the building including
basements, mezzanine and intermediate-floored tiers, and penthouses with headroom height of
7.5 ft or greater. It is measured from the exterior faces of exterior walls or from the centerline of
walls separating buildings, but excluding covered walkways, open roofed-over areas, porches
and similar spaces, pipe trenches, exterior terraces or steps, chimneys, roof overhangs, and
similar features.
a. Gross building envelope floor area: the gross floor area of the building envelope, but
excluding slab-on-grade floors.
b. Gross conditioned floor area: the gross floor area of conditioned spaces.
c. Gross lighted floor area: the gross floor area of lighted spaces.
d. Gross semi-heated floor area: the gross floor area of semi-heated spaces.
Space: an enclosed space within a building. The classifications of spaces are as follows for the
purpose of determining building envelope requirements.
a. Conditioned space: a cooled space, heated space, or indirectly conditioned space defined
as follows:
(1) Cooled space: an enclosed space within a building that is cooled by a cooling
system whose sensible output exceeds 5 Btu/hft2 of floor area.
(2) Heated space: an enclosed space within a building that is heated by a heating
system whose output capacity relative to the floor area is greater than or equal to
the criteria in Table 3-2.
(3) Indirectly conditioned space: an enclosed space within a building that is not a
heated space or a cooled space, which is heated or cooled indirectly by being
connected to adjacent space(s) provided (a) the product of the U-factor(s) and
surface area(s) of the space adjacent to connected spaces(s) exceeds the combined
sum of the product of the U-factors(s) and surface area(s) of the space adjoining
the outdoors, unconditioned spaces, and to or from semiheated spaces (e.g.
corridors) or (b) that air from heated or cooled spaces is intentionally transferred
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
2
(naturally or mechanically) into the space at a rate exceeding 3 air changes per
hour (ACH) (e.g., atria).
b. Semi-heated space: an enclosed space within a building that is heated by a heating
system whose output capacity is greater than or equal to 3.4 Btu/hft2 of floor area but is
not a conditioned space.
c. Unconditioned space: an enclosed space within a building that is not a conditioned
space or a semi-heated space. Crawl spaces, attics, and parking garages with natural or
mechanical ventilation are not considered enclosed spaces.
Table 3.2: Heated Space Criteria
Heating Output
Climate
(Btu/hft2)
(HDD65)
5
10
15
20
25
30
0-1800
1801-3600
3601-7200
7201-10,800
10,801-16,200
16,201+
ASHRAE 100-1995
Area Factor (AF): a multiplying factor that adjusts the unit power density (UPD) for spaces of
various sizes to account for the impact of room configuration on lighting power utilization.
{Complicated term that takes into account the floor area and ceiling height}
Area of the space (A): the horizontal lighted area of a given space measured from the inside of
the perimeter walls or partitions, at the height of the working surface.
Conditioned area: that area provided with positive supply of heating and cooling to maintain
temperature between 50F (10C) and 86F (30C).
Conditioned floor area: the sum of the conditioned floor areas of the several floors of the
building, including basements, mezzanine and intermediate floored tiers, and penthouses of
headroom height, measured from the exterior faces of exterior walls or from the centerline of
walls separating buildings. {Used for calculation of the EUI and CI}
Gross lighted area: the sum of the total lighted areas of a building measured from the inside of
the perimeter walls for each floor of the building.
Section 5.2 Building area: The conditioned floor area of each building or complex claiming
compliance shall be determined in square feet (square meters). The gross floor area of a complex
shall consist of the sum of the floor areas of all buildings within that complex.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
3
ASHRAE 105-1984 (RA 99)
Floor area: the sum of the areas of several floors of the building, including basements
mezzanine and intermediate floored tiers, and penthouses of headroom height measured from the
exterior faces of exterior walls or from the centerline of walls separating buildings, but excluding
Covered walkways, open roofed-over areas, porches, and similar spaces;
Pipe trenches, exterior terraces or steps, chimneys, roof overhangs, and similar features.
ASTM: E 1836 – 01
A.1.2.4.1 Building exterior gross area measures all floor areas on all levels of a building. The
measurement indicates total constructed space and is useful for building efficiency and
construction cost comparisons.
A1.4 Floor Area Measurement Guidelines
A1.4.1.1 Measurements—All measurements shall be made along the plane of the floor to the
points where floors and walls intersect.
A1.4.1.2 Clear Headroom—Floor area that does not have sufficient clear, unobstructed
headroom to conform to local building codes or that has headroom less than that required for
occupancy (typically 2.0 to 2.3 m (6.5 to 7.5 ft)) shall not be included in any floor area
measurement.
A1.4.1.3 Floor Area—This standard includes only areas that are totally enclosed within the
building. Climate conditions and construction practices will dictate the degree of weather
tightness typical for exterior walls in a local area. Basements, enclosed porches, penthouses,
mechanical equipment rooms, lobbies, mezzanines, corridors, interior parking, and enclosed
loading docks are included. Spaces outside the exterior walls or without a roof covering are not
included in the floor area measurement. Interstitial areas and excluded areas are not included in
floor area measurement.
A1.4.1.4 Void Areas—The floor areas of rooms more than one story in height and having void
areas on upper floors, such as atria, light wells, or lobbies, are included in the area measurement.
Major vertical penetrations are not considered void areas.
A1.5 Building Exterior Gross Area
A1.5.1 Building exterior gross area is the sum of the floor areas on all levels of a building that
are totally enclosed within the building (see Fig. A1.4). Measure building exterior gross area to
the outside face of exterior walls, disregarding canopies, cornices, pilasters, buttresses, balconies
that extend beyond the wall face, and courtyards that are enclosed by walls but have no roof. The
building gross area of basement space includes the area measured to the outside face of basement
or foundation walls.
A1.5.2 If the property line lies within a building wall that is common with an adjoining building,
measure the building exterior gross area to the property line. If the property line does not lie
within a building wall but the wall is structurally common with an adjoining building, measure
building exterior gross area to the center of the structural portion of the common wall.
A1.5.3 Exterior bridges and tunnels that are totally enclosed, constructed areas connecting two or
more buildings are included in building exterior gross area.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
4
A1.9 Major Vertical Penetrations
A1.9.1 Major vertical penetrations shall include stairs, elevator shafts, flues, pipe shafts, vertical
ducts and their enclosing walls. Stairs and elevator shafts shall be considered major vertical
penetrations for all affected floors, even the lowest level at which they originate. Not included in
this category are stairs, dumbwaiters, and lifts that do not serve a general building circulation
function but exclusively serve a specific tenant. In calculating the area of vertical penetrations,
disregard areas less than 0.1 m2 (1 ft2).
A1.9.2 This definition of major vertical penetrations is consistent with that given in ANSI Z65.1.
Figure A1.1: Floor Area Measurement Relationships
ANSI-BOMA Z65.1-1996
DOMINANT PORTION shall mean the portion of the inside FINISHED SURFACE of the
permanent outer building wall that is 50% or more of the vertical floor-to-ceiling dimension, at
the given point being measured as one moves horizontally along the wall. DOMINANT
PORTION itself is a vertical measurement between FINISHED SURFACEs (or a series of
vertical measurements), with the number of measurements needed based upon the conditions
found along the wall. If, for instance, a window system is 4’-6” (1.372 m) high and the floor to
ceiling dimension is 9’-0” (2.743 m), the DOMINANT PORTION is the inside surface of the
glass for the full width of the window system. If, however, the window system is 4’-5” (1.346
m), the DOMINANT PORTION is the inside surface of the wall. In designs of alternating
window systems and wall sections, the DOMINANT PORTION will move in and out as often as
conditions dictate. If no FINISHED SURFACE of the permanent outer building wall is 50% or
more of the vertical floor-to-ceiling dimension, or if the permanent outer building wall is not
vertical, the DOMINANT PORTION shall be the inside finished surface of the wall where it
intersects the finished floor. In the case of STORE AREA with street level frontage, the
DOMINANT PORTION shall be the building line.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
5
GROSS BUILDING AREA shall mean the total constructed area of a building. It is generally
not used for leasing purposes.
GROSS MEASURED AREA shall mean the total area of a building enclosed by the
DOMINANT PORTION, excluding parking areas and loading docks (or portions of same) outside
the building line. It is generally not used for leasing purposes and is calculated on a floor by floor
basis.
MAJOR VERTICAL PENETRATIONs shall mean stairs, elevator shafts, flues, pipe shafts,
vertical ducts, and the like, and their enclosing walls. Atria, lightwells and similar penetrations
above the finished floor are included in this definition. Not included, however, are vertical
penetrations built for the private use of a tenant occupying OFFICE AREAs on more than one
floor. Structural columns, openings for vertical electric cable or telephone distribution, and
openings for plumbing are not considered to be MAJOR VERTICAL PENETRATIONs.
FLOOR RENTABLE AREA shall mean the result of subtracting from the GROSS MEASURED
AREA of a floor the MAJOR VERTICAL PENETRATIONs on that same floor. It is generally
fixed for the life of the building and is rarely affected by changes in corridor size or
configuration.
Definitions also exist for USABLE AREA, OFFICE AREA, STORE AREA, BUILDING
COMMON AREA, FLOOR USABLE AREA, FLOOR COMMON AREA, BASIC RENTABLE
AREA, and RENTABLE AREA.
EPA – Energy Star
The Energy Star documentation uses the terms gross floor area, floor area, gross building area,
and lists the a definition of area as the “gross building square footage.” The documentation is not
consistent and does not list a clear definition for area measurements. The following FAQs are
included in the PE’s guide for clarification.
Are common areas to be included when determining the floor area of the building or a
given space (for example, office space)?
Yes, the user-entered value for area must be the gross interior area of the building, or in the case
of a user-specified office block, the gross interior area of the office block. This includes all area
enclosed by the exterior walls of the building, including hallways, lobbies, stairways, elevator
shafts, and electrical/mechanical/janitorial closets.
Should the floor area of a parking garage or surface parking be entered into Portfolio
Manager?
Yes, if the energy consumption for a parking garage or surface parking is included in the utility
data. Portfolio Manager will compensate for the energy use of the garage based on the floor area,
but will report the gross floor area of the building less the floor area of the garage or parking lot.
Can parking garage or surface parking be excluded from the analysis?
Yes, if the energy consumption of the garage or surface parking is separately metered and is not
included in the utility bill data provided in Portfolio Manager.
How is the area (that is, square footage) and energy use for an unattached parking garage
treated when the electricity and/or fossil fuels are NOT separately metered?
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
6
Unattached garage space on the same meter is treated as if the structure were physically attached
to the primary building and is subject to the eligibility requirements for the ENERGY STAR
label.
EIA – CBECS
The following definitions were taken from the CBECS glossary at
http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/cbecs/background.html.
Conditional Energy Intensity: Total consumption of a particular energy source(s) or fuel(s)
divided by the total floorspace of buildings that use the energy source(s) or fuel(s), i.e., the ratio
of consumption to energy source-specific floorspace. This measure is used in the fuel-specific
detailed tables.
Floorspace: All the area enclosed by the exterior walls of a building, including indoor parking
facilities, basements, hallways, lobbies, stairways, and elevator shafts. For aggregate floorspace
statistics, floorspace was summed or aggregated over all buildings in a category (such as all
office buildings in the United States).
Gross Energy Intensity: Total consumption of a particular energy source(s) or fuel(s) by a group
of buildings, divided by the total floorspace of those buildings, including buildings and
floorspace where the energy source or fuel is not used, i.e., the ratio of consumption to gross
floorspace. (See Conditional Energy Intensity.)
Gross Floorspace: Total floorspace of a group of buildings, regardless of which end uses are
present or which energy sources or fuels are used within the buildings. (See Energy SourceSpecific Floorspace and Gross Energy Intensity.)
Square Footage: Floorspace, in units of square feet. One square foot is approximately equal to
0.0929 square meters. (See Floorspace.)
Federal Agency Energy Scorecard for Compliance with E.O. 13123
Energy intensity is reported on a per gross square foot basis. The only area guidance is the
following: “Report the gross square footage of the buildings and facilities in your agency’s inventory
for each reporting category. Enter this number in thousands of square feet, rounded to the nearest tenth of
an integer.”
2003 International Building Code
Area, Building (Section 502.1): The area included within surrounding exterior walls (or exterior
walls and fire walls) exclusive of vent shafts and courts. Areas of the building not provided with
surrounding walls shall be included in the building area if such areas are included within the
horizontal projection of the roof or floor above.
Floor Area, Gross (Section 1002.1): The floor area within the inside perimeter of the exterior
walls of the building under consideration, exclusive of vent shafts and courts, without deduction
for corridors, stairways, closets, the thickness of interior walls, columns or other features. The
floor area of a building, or portion thereof, not provided with surrounding exterior walls shall be
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
7
the usable area under the horizontal projection of the roof or floor above. The gross floor area
shall not include shafts with no opening or interior courts.
2003 International Energy Conservation Code
Conditioned Floor Area: The horizontal projection of that portion of interior space which is
contained within exterior walls and which is conditioned directly or indirectly by an energyusing system.
Conditioned Space: A heated or cooled space, or both, within a building and, where required,
provided with humidification or dehumidification means so as to be capable of maintaining a
space condition falling within the comfort envelope set forth in ASHRAE 55.
Cooled Space: Space within a building which is provided with a positive cooling supply(see
“Positive cool supply”).
Gross Floor Area: The sum of the areas of several floors of the building, including basements,
cellars, mezzanine and intermediate floored tiers and penthouses of headroom height, measured
from the exterior faces of exterior walls or from centerline of walls separating buildings, but
excluding:
1. Covered walkways, open roofed-over areas, porches and similar spaces.
2. Pipe trenches, exterior terraces or steps, chimneys, roof overhangs and similar features.
Heated Space: Space within a building which is provided with a positive heat supply (see
“Positive heat supply”). Finished living space within a basement with registers or heating
devices designed to supply heat to a basement space shall automatically define that space as
heated space.
Positive Cool Supply: Mechanical cooling deliberately supplied to a space, such as through a
supply register. Also, mechanical cooling indirectly supplied to a space through uninsulated
surfaces of space-cooling components, such as evaporator coil cases and cooling distribution
systems which continually maintain air temperatures within the space of 85F (29C) or lower
during normal operation. To be considered exempt from inclusion in this definition, such
surfaces shall comply with the insulation requirements of this code.
Positive Heat Supply: Heat deliberately supplied to a space by design, such a supply register,
radiator or heating element. Also, heat indirectly supplied to a space through uninsulated
surfaces of service water heaters and space-heating components, such as furnaces, boilers and
heating and cooling distribution systems which continually maintain air temperature within the
space of 50F (10C) or higher during normal operation. To be considered exempt from
inclusion in this definition, such surfaces shall comply with the insulation requirements of this
code.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
8
Protocol for Monitoring Energy Efficiency Improvements in Commercial and
Related Buildings
Total floor area: Floor area of all spaces, conditioned and unconditioned, considered as part of
the building surveyed. Include the areas of all additions completed at the time of the survey.
Consider all stories, not simply the “footprint” area.
Number of stories: General indication of the height of the building. Include all levels, both
above and below grade, considered as part of the building surveyed. Fractional entries should be
explained.
Floor area and volume: Enter the total area and volume of space that is heated, cooled, and
unconditioned for above and below grade levels. Atria are entered separately and should not be
included in the totals entered previously. Area both heated and cooled will be recorded twice.
Ground-coupled floor area: Floor area having thermal contact with the ground primarily by
conduction (e.g. a concrete slab). The ground-coupled floor area would be zero for a floor
separated from the ground by a crawl space.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
9
References
ASHRAE (1995). Energy Conservation in Existing Buildings. ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA Standard
100-1995. Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating and Refrigerating Engineers.
ASHRAE (1999). Standard Methods of Measuring and Expressing Building Energy
Performance. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 105-1984. Atlanta, GA: American Society of
Heating and Refrigerating Engineers.
ASHRAE (2001). Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings.
ANSI/ASHRAE/IESNA Standard 90.1-2001. Atlanta, GA: American Society of Heating
and Refrigerating Engineers.
ASTM (2001). Standard Classification for Building Floor Area Measurements for Facility
Management. E 1836-01. West Conshohocken, PA: American Society for Testing and
Materials.
BOMA (1996). Standard Method for Measuring Floor Area in Office Buildings. ANSI/BOMA
Z65.1-1996. Washington, D.C.: Building Owners and Managers Association
International.
DOE (2002). “Report Guidance for FY 2002 Annual Report on Federal Government Energy
Management and Conservation Programs.” Memorandum. Federal Energy Management
Program. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy.
http://www.eere.energy.gov/femp/aboutfemp/doc/02guide.doc. Accessed May 13, 2003.
EIA (2003). Energy Information Administration, Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy.
http://www.eia.doe.gov/ Accessed May 13, 2003.
EPA (2001). Professional Engineer’s Guide to the Energy Star® Label for Buildings. Draft EPA
430-F-01-xxx. Nov. 2001. Washington, D.C: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
ICC (2002). 2003 International Building Code. Country Club Hills, IL: International Code
Council.
ICC (2003). 2003 International Energy Conservation Code. Country Club Hills, IL: International
Code Council.
MacDonald, J. M.; Sharp, T.R.; Gettings, M.B. (September 1989). A Protocol for Monitoring
Energy Efficiency Improvements in Commercial and Related Buildings. ORNL/CON291. DE89 012800. Oakridge, TN: Oakridge National Laboratory.
D:\106730394.doc
2/12/2016
10