The Building Block of Business The Economics of
advertisement

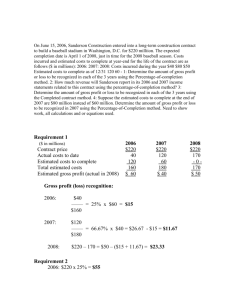
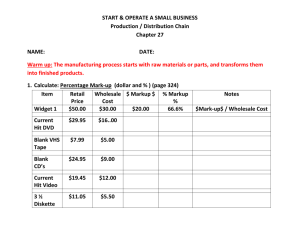
The Building Block of Business The Economics of One Unit of Sale Economics of One Unit of Sale Entrepreneurs use profits: 1) 2) 3) To pay themselves To expand their businesses To start other businesses Retail: one unit or item (i.e., one watch) Manufacturing: one order (any quality) Service: one hour of service time or a standard block of time devoted to a task (i.e., one hour of lawn-mowing service) Wholesale: a dozen of an item (i.e., 12 watches) Cost of Goods Sold for One Unit Selling Price per Unit - COGS per Unit Revenue -COGS Gross Profit per Unit Gross Profit Total Revenue – Total Cost of Goods Sold = Total Gross Profit Selling Multiple Units Average sale per customer - Average cost of sale per customer Average gross profit per customer Your Business and the Economics of One Unit “Later, you will learn about the principles of competitive advantage, unique selling proposition, and marketing and advertising.” -How to start and operate a small business The Four Types of Business Manufacturing: makes a tangible product (you can literally touch it). A sneakers manufacturer makes sneakers but does not necessarily sell them to individual consumers. Wholesale: wholesalers buy the sneakers in large quantities from the manufacturer and then sell smaller quantities (typically in dozens) to shoe stores. Retail: retail shoe stores sell the sneakers one pair at a time to consumers. Service: a service business sells intangible products (you can’t actually touch them). A personal trainer, for example, sells his or her expertise to help people exercise. The Cost of Labor in the EOU Manufacturing Business: unit = 1 card Selling Price per Unit: Materials: Labors: Cost of Goods Sold per Unit: Gross Profit per Unit: $4.50 $1.00 1.50 $2.50 Hiring Others to Make the Unit of Sale When Janet was creating the cards herself, she was getting paid to do so. But, now that she has friends helping her and pays them a $6 rate, Janet’s income is based on the gross profit. Going for Volume Manufacturing Business: unit = 1 card Selling Price per Unit: $4.50 Materials: $1.00 Labor: 1.50 Cost of Goods Sold per Unit: $2.50 Gross Profit per Unit: 2.50 $2.00 Janet's Total Gross Profit Revenue ($ 3.50 X 2,000 Cards ): Materials ($1 X 2,000): Labor ($1.50 X 2,000): Cost of Goods Sold: Gross Profit: $7,000.00 $2,000.00 3,000.00 $5,000.00 5,000.00 $2,000.00 Lessons to Be Learned Five breakthrough steps entrepreneurs can take are: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Calculating the unit of sale. Determining the economics of one unit of sale. Substituting someone else’s labor. Trying to sell in volume. Creating jobs and operating at a profit. Becoming a Business Leader When becoming a leader, the entrepreneur has to promote him or herself. Vocabulary Cost of goods sold The cost of selling “one additional unit” for a product-based business. Economics of one unit of sale [EOU] The figuring of markup and profit around a business’s unit of sale. Gross profit Total sales revenue minus total cost of goods sold. Unit of sale The amount of product (or time, in a service business) from which a business figures its operations and profit; considered the “building block” of a business.