Warm Up #10
advertisement

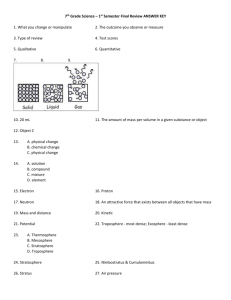
Warm Up #1 (Set II Fourth Quarter) 1. What is the moon phase after the first quarter moon? A. full moon B. last quarter C. waxing gibbous D. waning gibbous 2. What is the moon phase after the full moon? A. full moon B. last quarter C. waning gibbous D. waxing gibbous 3. How many degrees is the Earth tilted? A. 24° B. 23.5° C. 24.5° D. 25° Warm Up #2 1. What are the next three moon phases after Waxing Crescent moon? First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon 2. Draw a Last Quarter or 3rd. Quarter Moon. 3. What is the difference between Waning and Waxing? Waning shows the light on the left and waxing shows the light on the right. Warm Up #3 1. The asteroid belt is located between? Mars and Jupiter 2. What causes most meteors to burn up before landing on Earth? A. the friction between the meteor and atmosphere B. the meteor is traveling very slowly C. the meteor is really, really small D. the heat from the sun melts it 3. Why does the moon go through different phases? A. the moon is in Earth's shadow B. the moon reflects sunlight at different angles C. the earth reflects sunlight to the moon D. the moon rotates on its axis Warm Up #4 (see handout) 1. What two countries were involved with the Space Race? USSR, United States 2. What was the name of the Soviet Union's first satellite? Sputnik 3. How is the space shuttle different from the rockets used with John Glenn and the Apollo Mission? Apollo was not re-useable and landed in the water. The space shuttle launched like a rocket, maneuvers like a spaceship, and lands like a jet. Warm Up #5 1. A major first step in the exploration of space was A. the Apollo Program B. the Sputnik Satellite C. the Hubble Telescope D. The International Space Station 2. Draw a picture of the sun, moon, and Earth to show Neap Tides. 3. Draw a picture of the sun, moon, and Earth to show Spring Tides. Spring Tide Warm Up #6 (Use Energy handout) 1. What is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work. 2. What are the two categories for energy? Kinetic and Potential Energy 3. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? Kinetic energy = energy in motion and Potential energy = stored energy Warm Up #7 1. What is the difference between a renewable and nonrenewable resource? Nonrenewable means their supplies are limited and take a long time to replace. Renewable energy sources are replenished in a short time. 2. What does the law of conservation of energy state? Energy can never be lost. It can only change from one form to another. 3. Name all the energy forms under potential energy and under kinetic energy. Potential= Chemical, Nuclear, Stored Mechanical, Gravitational Kinetic= Radiant, Thermal, Motion, Sound, Electrical Warm Up #8 1. Can energy be transferred from one object to another? Why? (See handout or page 321) Yes, energy can be transferred because of the law of energy states: Energy is neither created nor destroyed. 2. Name the five examples of energy transfer? page 321 or handout Turning on a lamp = Electrical to mechanical, to light to thermal Turning on a gas stove = Chemical to Heat Starting a car = Chemical to Electrical to Mechanical Lighting fireworks = Heat to Chemical to Light to Sound Turning on a fan = Electrical to Mechanical 3. Fossil fuels is a nonrenewable resource. Name three types of fossil fuels. Coal, Natural Gas, Oil Warm Up #9 1. A student who jumps up and down in a room for 60 seconds is demonstrating what change in energy? Chemical → Motion → Thermal 2. Under normal circumstances, energy in a system cannot be increased or decreased, it can only be A. magnified B. ended C. grown D. transformed (changed) 3. After the Sun's energy has been absorbed by the land, atmosphere, and oceans on Earth, what happens to the energy? A. it disappears completely B. it changes to heat energy and stays completely on Earth C. the energy for the Sun changes to heat energy, some of which goes to space D. it changes to kinetic energy and keeps the Earth in its orbit Warm Up #10 1. The energy transformations (change of form) of a gasoline car are A. chemical-->thermal-->mechanical B. nuclear--> thermal-->mechanical C. sunlight-->potential-->mechanical D. potential-->mechanical-->magnetic 2. What sequence of items below best demonstrates the energy transformation from the Sun to a plant? (Show at least 3 changes) Solar Chemical Motion 3. A rock sitting on top of a cliff has potential energy?