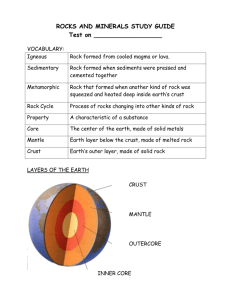
Topic 2 - Gouverneur Central School District
advertisement

Topic 2 – Quizzes Minerals Minerals luster hardness Streak cleavage Crystal fracture inorganic specific gravity color 1. color of the mineral in the powdered form 2. resistance to scratching 3. least reliable method to identify 4. regular breakage 5. once living is not it 6. irregular breakage 7. the way light reflects 8. density ratio of mineral to water 9. regular shaped solid 10. naturally occurring inorganic crystalline solid Bonus: Define Excelsior. Rocks Rock cycle streak igneous Fossil fuels felsic sedimentary metamorphic Hardness foliation mafic fossils 1. light colored, low density, Al-rich 2. rocks changed by heat and pressure 3. resistance to scratching 4. re-alignment of crystals into light and dark bands (banding) 5. dark colored, high density, Fe-rich 6. diagram of continuous life of a rock 7. formed millions of years ago from remains of ancient organisms, coal, oil, gas 8. rocks formed from a melt 9. color of powder of a mineral 10. can form from evaporation of seawater Bonus: What direction is the Sun at noon? Topic 2 Rock Formation Name Date Vocabulary Quiz Matching: Place the letter of the correct vocabulary word in the space provided, next to the corresponding definition. a. texture f. crystal k. igneous rock b. sedimentary rock g. organic l. solidification c. cementation h. beds/strata m. crystalline d. compaction i. Nonsedimentary rock n. crystallization e. precipitation j. monomineralic o. chemical sedimentary rock 1. The layers of sedimentary rock. 2. A type of solidification in which molten rock cools to form nonsedimentary igneous rocks composed of minerals that have a definite arrangement of their atoms. 3. The process by which deposited sediment is pressed down by overlying sediments, water, and/or Earth movements, resulting in the formation of sedimentary or metamorphic rocks. 4. A rock composed of just one mineral. 5. Size, shape, and arrangement of mineral crystals or sediments in a rock. 6. This type of rock forms by the evaporation and/or precipitation of dissolved minerals. 7. An Earth material that is composed of and/or was formed by life forms. 8. A type of deposition in which dissolved substances come out of solution to form solids. 9. A solid with a definite internal structure because of its constituent atoms are arranged in a characteristic, regular, repeating pattern. 10. Rocks that form the processes of cementation, precipitation of minerals, dewatering and compression. 11. Rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molted material above or below the Earth’s surface. 12. Rocks that do not form directly from sediments. Regents Earth Science Objective Quiz: Minerals Name Date 1. List the difference between rocks and minerals. Rocks Minerals 2. What are the two most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust by mass? and 3. List five possible Physical properties of minerals. 4. The hardest most common mineral is . 5. Define hardness: 6. The most abundant mineral is . . 7. The structural unit of the most abundant mineral class is called the and has the formula . 8. The differing crystal structure of different minerals is best explained by the . .