Chapter 4 section 1 notes
advertisement

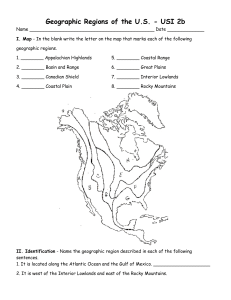
Chapter 4 section 1 Contiguous – joined together inside a common boundary Coastal Plains – broad lowlands along the eastern & southeastern coast Atlantic Coastal Plain – poor soil & many port cities Megalopolis – a number of cities & suburbs that form a continuous line of settlement; New York City, Boston, Philadelphia, Baltimore & Washington D.C. Gulf Coastal Plain – better soils than Atlantic Coastal Plain The Appalachian Mountains – run from eastern Canada to Alabama The oldest mountains on the continent – they have been worn down over time by erosion Interior Plains – 2 parts Central Plains – east of Mississippi River – rolling hills and flatlands – fertile & productive land. Great Lakes are found here. Many ports located in the Great Lakes because of St. Lawrence Seaway. Great Plains – west of Mississippi River to Rocky Mountains; northern border into Canada south to the Mexican border. Contain vast grain fields. Mountains & Plateaus – Rocky Mountains stretch from Alaska to Mexico. Continental divide – the ridge that separates the rivers of the continent Plateaus, canyons & deserts exist between the Rockies & the Pacific Ocean Pacific Coast – 2 mountain ranges near the coast Cascade Range – Washington to Northern California Sierra Nevada – run along California’s eastern side Fertile valleys along the coast Alaska – Mountain ranges cover much of Alaska. The people mostly live along the southern coast & central river valley Hawaii – 8 large islands; 120 other islands; formed from volcanoes A variety of climates in The United States. Mostly mid-latitude climates. Humid continental; humid subtropical; marine west coast; steppe; high latitude; tropical