Study Guide Part 2 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
advertisement

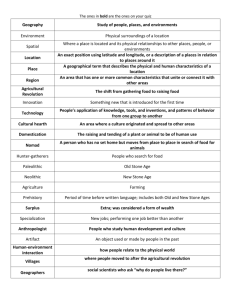
16. Some dates are given with a c. in front of them. This stands for what Latin word? Circa What does it mean? About or approximately 17. What is a historian? A person who studies and writes about the people and events of the past. 18. In addition to studying important events, what else do historians want to know about these events? What caused the events, and what were the effects of the events. 19. What is the difference between a primary source and a secondary source? A primary source is a firsthand piece of evident from people who saw or witnessed an event. A secondary source was created after an event by someone who was not there. 20. Give 2 examples of primary sources. Letters, photographs, clothing 21. Give 2 examples of secondary sources history books, encyclopedias 22. How do we know about people and events from prehistoric times, if they could not write down their history? From the artifacts they left behind 23. Why is the Stone Age called the Stone Age? During this time period, early humans used stone to make tools and weapons 24. What does Paleolithic mean? Old Stone Age 25. How did early humans get food during the Paleolithic Period? Hunting and gathering 26. Why didn’t early humans settle down and live in one place? They had to keep moving to find food 27. What kinds of shelters did early humans use as they adapted to their environment? Caves or shelters made out of wooden poles and animal hides 28. How did the ability to control fire improve the lives of early humans? Give at least 4 examples. Provide warmth and light; allowed people to cook their meals; scared away animals; smoked meat lasted longer 29. During the Ice Age, did ice cover all the continents? NO 30. What adaptations did early humans make to adapt and survive during the Ice Ages? Give at least 3 examples. Used fire to stay warm; changes in diet; built stronger shelters; used animal furs to make warmer clothes 31. Historians believe language, religion, and art were developed by early humans during the Old Stone Age. These are all elements of culture a. During the Old Stone Age, which developed spoken or written language? spoken b. What type of Paleolithic (Stone Age) art has been discovered? Describe what is shown in this artwork. Cave paintings; usually of animals 32. What stone was especially good for making tools with sharp edges? flint 33. What is the major change made during the Neolithic Revolution? People domesticated plants and animals so farming replaced hunting and gathering 34. What does the word Neolithic mean? New Stone Age 35. Give 2 other names for the Neolithic Revolution. Farming Revolution; Agricultural Revolution 36. Why do historians call this period a revolution? Because it caused such huge changes in how people lived. 37. Why did the Neolithic Revolution lead to the development of small town and villages? Farmers stayed in 1 place to tend their crops & store their harvest. So, people built permanent homes close to their neighbors in villages 40. Explain how farming surpluses lead to specialization. If farmers produce more food than their families need, some people can do different jobs (that’s specialization) 41. What did many farmers do with the surplus food they produced? Trade! 42. More big changes – describe the changes in Neolithic culture: a. shelters/housing permanent houses made of mud brick b. art decorations painted on the inside of walls of homes c. religion special buildings just for worship d. jobs people made pottery, wove cloth, made tools from stone – then metal e. technology (think materials, products) used clay to make pottery, plant fibers to make cloth, mud to make bricks, copper then bronze to make tools and weapons f. clothing woven cloth from plant fibers 43. How is bronze made? Mixing copper and tin 44. Why use bronze instead of copper or tin? It was harder and lasted longer 45. Why was the period between 3,000 B.C. and 1,200 B.C. called the Bronze Age? During this period many tools and weapons were made of bronze