Denotation- the meaning of the word that is strictly literal, as found in
advertisement

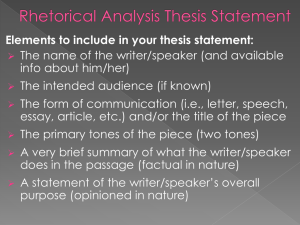
Nonfiction Terms Four Types of NONFICTION: 1. monologue- a speech by one person with out interruption by other voices. A dramatic monologue reveals the personality and experience of a person through a long speech. 2. autobiography- is a form of nonfiction in which a person relates his or her own life story 3. biography- is a form of nonfiction in which a writer tells the life story of another person. 4. information text- is writing that provides the knowledge to guide and educate you. (examples magazines and newspaper articles on current topics, as well as instructional manuals and textbooks) 5. audience- a writer’s readers or listeners 6. allusion- a reference to a historical or literary person, place, event, or aspect of culture 7. argument- speaking or writing that expresses a position or states an opinion with supporting evidence. An argument often takes into account other points of view. 8. analysis- a way of thinking that involves taking apart, examining, and explaining a subject or idea 9. anecdote- a brief story told as an example to illustrate a point 10. diction- is word choice, including the vocabulary used, the appropriateness of the words, and the vividness of the language 11. denotation- the meaning of the word that is strictly literal, as found in the dictionary, as opposed to the ideas and feelings the words carries 12. connotation- the meaning of a word that carries ideas and feelings, as opposed to the word’s strictly literal definition 13. context- the setting or situation in which something happens; the parts of a statement that occur just before and just after a specific word and help determine its meaning 14. dialogue- spoken conversation of fictional characters or actual persons. It is used to reveal character and to advance action. In a story or novel, quotation marks are generally used to indicate a speaker’s exact words. A new paragraph usually indicates a change in speaker. 15. tone- the writer’s or speaker’s attitude toward the subject----ex. Include detached, ironic, serious, angry, and so on. 16. mood- the feeling about a scene or a subject created by the writer. The mood of a piece of writing may be suspenseful, mysterious, peaceful, fearful, and so on. 17. summary- a brief restatement of the main idea of the passage 18. topic sentence- a sentence that expresses the main idea of a paragraph 19. metaphor- a figure of speech that is a comparison without using the word like or as. Ex. “All the worlds a stage” 20. author’s purpose- the reason an author writes; what the author wants the reader to take with him/her from the text. 21. anaphora- repetition of beginning phrases of sentences to create a dramatic effect. Anaphora often will appear in speeches or in dramatic dialogues. 22. commentary- series of notes explaining or interpreting a written text 23. appeals- are how a writer/speaker tries to convince his or her intended audience 24. ethos- an ethical appeal is based on the nature of the person making the appeal. Think: is the source credible? 25. pathos- an appeal to emotion. Think- is the writer simply “playing” me? 26. logos- an appeal to reason. Think- does the logic follow? Are the statistics skewed or unrepresentative? Nonfiction Terms 1. audience (Gram) 15. topic sentence (Gram) 2. allusion (both) 16. tone (both) 3. argument (both) 17. autobiography (both) 4. analysis (Gram) 18. biography (Lit) 5. anecdote (both) 19. information text (not in either text) 6. connotation (both) 20. purpose (not in either text) 7. context (Gram) 21. anaphora (not in either text) 8. diction (Lit) 22. appeals (not in either text) 9. dialogue (both) 23. ethos (not in either text) 10. denotation (both) 24. pathos (not in either text) 11. mood (both) 25. logos (not in either text) 12. monologue (both) 26. commentary (not in either text) 13. metaphor (both) 14. summary (Gram)