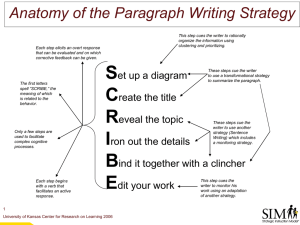
Nonfiction Terms: Definitions & Examples
advertisement

Nonfiction Term Definitions 1. Nonfiction- Prose writing that deals with real people, things, events, and places. True writing. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Fiction- Writing that deals with imaginary people, places, and events. Fake Writing Autobiography- An account of the writer’s own life written from the author’s perspective Biography-An account of a person’s life written or told by another person. Memoir- A narrative composed from personal experience. Often shorter than autobiographies Bias-Prejudice or inclination to one side regarding a topic, person, event,etc. Objective- not influenced by personal feelings, interpretations, or prejudice; based on facts; unbiased 8. Subjective- Placing excessive emphasis on one's own moods, attitudes, opinions, etc 9. Speech-A form of communication in spoken language made by a speaker before an audience for a given purpose. 10. Thesis- One or more sentences that state the central idea or purpose of an essay or other work of nonfiction 11. Tone- Attitude a writer takes toward a subject, a character, or the audience. 12. Main Idea- The central message, insight, or opinion in a work 13. Supporting Details- The pieces of evidence that a writer uses to prove the main idea. These details can include facts, statistics, quotations, or anecdotes. 14. Primary Source- A firsthand account, such as a speech, an autobiography, or a letter. These are useful because they directly express the thoughts and feelings of a writer, and it may include details that only an eyewitness can provide. 15. Secondary Source- A second-hand account such as history books, biographies, newspapers, magazines, and textbook. They summarize or analyze events in which the writers did not participate. 16. Fact- These are objective and can be proven. 17. Opinion- These are subjective and cannot be proven. 18. Inference- To guess, to conclude from evidence. 19. Audience- The people who read a text. 20. Connotation- All the meanings, associations, or emotions that have come to be attached to some words, in addition to their literal dictionary definition. School: Homework, bells, tests, prom, etc. 21. Context Clue- Using the words around an unfamiliar word to figure out the meaning 22. Denotation- The literal, dictionary definition of a word. School: an institution of learning 23. Idiom- Expression peculiar to a particular language that means something different from the literal meaning of each word. “It’s raining cats and dogs” or “We heard it through the grapevine.” 24. Euphemism-The substitution of a mild, indirect, or vague expression for one thought to be offensive, harsh, or blunt. “To pass away” instead of “To croak, kick the bucket, or die.” “Aroma” instead of “smell.” “Upset stomach” instead of “puked, barfed, or upchucked.” 25. Essay- A short literary composition on a particular theme or subject usually written in prose. 26. Author’s Purpose- An author’s reason for writing: to inform, to persuade, to describe, to explain 27. Style- The particular way in which a writer uses language 28. Anecdote- Very, very brief story, usually told to make a point 29. Rhetorical Question- A question to which an answer is not expected or already known 30. Propaganda-Information, ideas, or rumors deliberately spread widely to help or harm a person, group, movement, institution, nation, etc. 31. Cliché- An overused expression that has lost its originality. “I thank you from the bottom of my heart.” 32. Synonym- Words that mean the same thing or almost the same thing. Nonfiction Terms (Use Literary Handbook on pp. 1019-1031 in blue/purple textbook, 1056-1072 in Green text books, and the dictionary) Nonfiction Fiction Autobiography Biography Memoir Bias Objective Subjective Speech Thesis Tone Main Idea Supporting Details Primary Source (p. 578 PB) Secondary Source (p.578 PB) Fact (p. 579 PB) Opinion (p. 579 PB) Inference Audience (p. 66 PB) Connotation Context Clue Denotation Idiom Euphemism Essay Author’s Purpose (p.66 PB) Style Anecdote Rhetorical Question Propaganda Cliché Synonym (p. 31 PB)