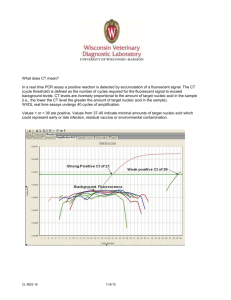
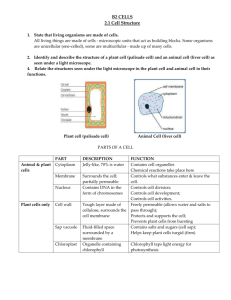
nucleic dominant
advertisement

1) All of the following hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle EXCEPT: estrogen LH prolactin progesterone FSH 2) DNA contains all the following molecules EXCEPT: uracil guanine adenine deoxyribose phosphate 3) In aerobic respiration, the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is: NAD+ O2 H2O NADP+ H2 4) All of the following statements are correct regarding alleles EXCEPT: A gene can have more than one allele. Two identical alleles are said to be heterozygous with respect to that gene. Alleles are found on corresponding loci of homologous chromosomes. Alleles are alternative forms of the same gene. One allele can be dominant and the other can be recessive. 5) The Krebs cycle in humans occurs in the intermembrane phase inner mitochondrial membrane outer mitochondrial membrane cytoplasm mitochondrial matrix 6) The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions is known as the thalamus cerebrum medulla cerebellum hypothalamus 7) A researcher performs a cross between 2 mice, both having black fur. Black for is dominant over white for. 75% of the offspring have black coats and 25% have white coats. The researcher can assume that the parents genotypes were most likely: BB x BB BB x Bb BB x bb Bb x Bb bb x bb 8) A feature of amino acids not found in carbohydrates is the presence of phosphorous nitrogen hydrogen oxygen carbon 9) Crossing over occurs during which of the following phases in sexual reproduction? Metaphase I Metaphase II Prophase I Prophase II Anaphase I 10) Which of the following are characteristics of both bacteria and fungi? cell wall, unicellularity, and mitochondria cell wall, DNA, and plasma membrane nucleus, organelles, and unicellularity plasma membrane, multicellularity, and Golgi apparatus nucleus, RNA, and cell wall 11) The major difference between cartilage and bone is that cartilage is a type of connective tissue. lacks blood vessels and nerves. secretes a rubbery matrix. is composed of collagen and salts. is part of the skeletal system. 12) A macromolecule which consists of a polymer of amino acids. Glycogen Cellulose Protein Triglyceride Nucleic Acid 13) The stored form of sugar in humans. Glycogen Cellulose Protein Triglyceride Nucleic Acid 14) Lipid which consists of three fatty acids covalently bonded to glycerol. Glycogen Cellulose Protein Triglyceride Nucleic acid 15) A substance that cannot be broken down by cows Glycogen Cellulose Protein Triglyceride Nucleic acid 16) The appendix of a human and the hipbone of a whale. Analogous structures Homologous structures Divergent evolution Convergent evolution Vestigial Structures