Evolution Unit Summary
advertisement
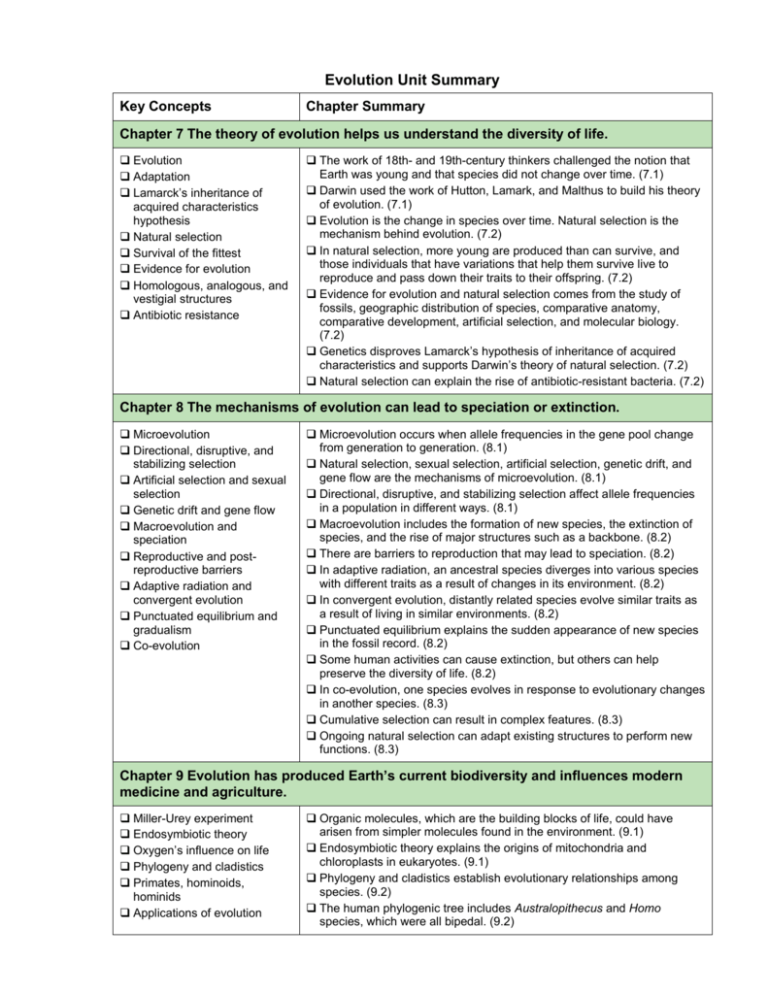
Evolution Unit Summary Key Concepts Chapter Summary Chapter 7 The theory of evolution helps us understand the diversity of life. Evolution Adaptation Lamarck’s inheritance of acquired characteristics hypothesis Natural selection Survival of the fittest Evidence for evolution Homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures Antibiotic resistance The work of 18th- and 19th-century thinkers challenged the notion that Earth was young and that species did not change over time. (7.1) Darwin used the work of Hutton, Lamark, and Malthus to build his theory of evolution. (7.1) Evolution is the change in species over time. Natural selection is the mechanism behind evolution. (7.2) In natural selection, more young are produced than can survive, and those individuals that have variations that help them survive live to reproduce and pass down their traits to their offspring. (7.2) Evidence for evolution and natural selection comes from the study of fossils, geographic distribution of species, comparative anatomy, comparative development, artificial selection, and molecular biology. (7.2) Genetics disproves Lamarck’s hypothesis of inheritance of acquired characteristics and supports Darwin’s theory of natural selection. (7.2) Natural selection can explain the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. (7.2) Chapter 8 The mechanisms of evolution can lead to speciation or extinction. Microevolution Directional, disruptive, and stabilizing selection Artificial selection and sexual selection Genetic drift and gene flow Macroevolution and speciation Reproductive and postreproductive barriers Adaptive radiation and convergent evolution Punctuated equilibrium and gradualism Co-evolution Microevolution occurs when allele frequencies in the gene pool change from generation to generation. (8.1) Natural selection, sexual selection, artificial selection, genetic drift, and gene flow are the mechanisms of microevolution. (8.1) Directional, disruptive, and stabilizing selection affect allele frequencies in a population in different ways. (8.1) Macroevolution includes the formation of new species, the extinction of species, and the rise of major structures such as a backbone. (8.2) There are barriers to reproduction that may lead to speciation. (8.2) In adaptive radiation, an ancestral species diverges into various species with different traits as a result of changes in its environment. (8.2) In convergent evolution, distantly related species evolve similar traits as a result of living in similar environments. (8.2) Punctuated equilibrium explains the sudden appearance of new species in the fossil record. (8.2) Some human activities can cause extinction, but others can help preserve the diversity of life. (8.2) In co-evolution, one species evolves in response to evolutionary changes in another species. (8.3) Cumulative selection can result in complex features. (8.3) Ongoing natural selection can adapt existing structures to perform new functions. (8.3) Chapter 9 Evolution has produced Earth’s current biodiversity and influences modern medicine and agriculture. Miller-Urey experiment Endosymbiotic theory Oxygen’s influence on life Phylogeny and cladistics Primates, hominoids, hominids Applications of evolution Organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life, could have arisen from simpler molecules found in the environment. (9.1) Endosymbiotic theory explains the origins of mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotes. (9.1) Phylogeny and cladistics establish evolutionary relationships among species. (9.2) The human phylogenic tree includes Australopithecus and Homo species, which were all bipedal. (9.2) Unit C Vocabulary Chapter 7 The theory of evolution helps us understand the diversity of life. Chapter 8 The mechanisms of evolution can lead to speciation or extinction. adaptation analogous structures artificial selection descent with modification ecological niche fitness fossil record fossils adaptive radiation biological species concept co-evolution cumulative selection directional selection disruptive selection founder effect gene flow gene pool genetic drift gradualism heritable homologous structures hypothesis natural selection survival of the fittest theory variation vestigial structures Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium hybrid microevolution mimicry phenotype punctuated equilibrium reproductive isolation sexual selection speciation stabilizing selection Chapter 9 Evolution has produced Earth’s current biodiversity and influences modern medicine and agriculture. aerobic bipedalism chemoautotroph clade cladistics cladogram continental drift derived characters era eukaryote geologic time scale hominids hominoids mass extinction organic molecule period phylogenetic tree phylogeny primary abiogenesis primates prokaryote stromatolite Unit Review Questions p 269 # 1, 4-9, 12, 14-15, 17-19, 20-25, 28-31, 32-38, 40-42, 44, 46,52, 54-56, 58-59, 62