Psychopharmacology
advertisement

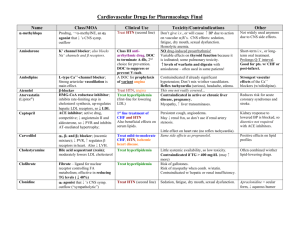
DEPRESSION Antidepressants Target symptomsSleep disturbance, appetite disturbance, fatigue, dec’d sex drive, psychomotor retardation or agitation, diurnal variations in mood, impaired concentration or forgetfulness, anhedonia Improvement may take 1-3 wks Primary considerations: Side effect profile, ease of administration, h/o past response, safety & medical considerations, specific subtype of depression Secondary considerations: Neurotransmitter specificity, family h/o response, blood level considerations, cost First-line agents: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI’s) Newer atypical antidepressants Cyclic antidepressants Second-line interventions: Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI’s) Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) SSRI’s- block neuronal uptake of serotonin; first line for all types except psychotic, melancholic & mild -lower anticholinergic s/e (dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention), less cardiotoxicity, faster onset than TCA’s -effective w/ anxiety features & psychomotor agitation -less dangerous when OD Common adverse rx-agitation, anxiety, sleep disturbance, tremor, sexual dysfunction, tension HA, autonomic rx (dry mouth, sweating, wt change, mild nausea, loose bm) Potential toxic effects- abd pain, diarrhea, sweating, fever, tachycardia, elevated BP, altered mental state, myoclonus, inc’d motor activity, irritability, hostility, mood change, hyperpyrexia, cardiovascular shock, death -risk inc when combined w/ 2nd serotonin-enhancing agent such as MAOI Serotonergic syndrome: inc HR, BP, fever, seizure -citalopram (Celexa) -fluoxetine (Prozac) -fluvoxamine (Luvox) -paroxetine (Paxil) -sertraline (Zoloft) -excitalopram (Lexapro) New Atypical Antidepressant- different neurotransmitters & side effects -bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) -trazadone (Desryl) -venlafaxine (Effexor) -mirtazapine (Remeron) -duloxetine (Cymbalta) -roboxetine (Vestra, Endronax) Tricylic antidepressants- inhibit reuptake of norepi & serotonin; takes 10-14 days or longer to start, full effect may not be seen for 4-8wks, start low go slow Adverse rx- anticholinergic (dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, constipation, urinary retention, esophageal reflux), postural hyptension Potential toxic effects- dysrhythmias, tachycardia, MI, heart block Adverse drug interactions- contraindicated w/ MAOI Contraindications- recent MI, narrow-angle glaucoma, h/o seizures, pregnant women -amitriptyline (Elavil, Endep) -amoxapine (Ascendin) -desipramine (Norpramin, Pertofrane) -doxepin (Adapin, Sinequan) -imipramine (Tofranil) -nortriptyline (Aventyl, Pamelor) -protriptyline (Vivactil) -trimipramine (Surmontil) -maprotiline (Ludiomil) MAOI- inc norepi, serotonin dopamine s/e-high BP, HTN crisis CVA -not often given as first-line tx; particularly effective for atypical depression Adverse rx- orthostatic hypotension, wt gain, edema, change in cardiac rate & rhythm, constipation, urinary hesitancy, sexual dysfunction, vertigo, overactivity, muscle twitching, hypomanic & manic behavior, insomnia, weakness, fatigue Potential toxic effects- inc’d BP, intracranial hemorrhage, hyperpyrexia, convulsion, coma, death, HTN crisis (starts w/ HA, stiff/sore neck, palpitations, inc/dec HR often w/ CP, N&V, inc temp) Contraindications- CVS, HTN, CHF, liver disease, consumption of foods w/ tyramine, tryptophan, dopamine; recurrent or severe HA; surgery previous 10-14days, <16yrs -phenelzine (Nardil) -tranylcypromine (Parnate) -moclobemide (Manerix, Aurorix) ECT-can achieve >90% remission rate w/in 1-2wks Indications- need for rapid, definitive response when suicidal/homicidal; extreme agitation/stupor; risks of other txs outweigh risks of ECT; h/o poor drug response, h/o good ECT response, or both; client prefers it -major depressive & bipolar, esp w/ psychotic symptoms; & clients w/ depression w/ marked psychomotor retardation & stupor -manics resistant to tx w/ litium & antipsychotic drugs & rapid cyclers -pregnant schizo -Parkinson’s Integrative approaches: -light therapy; St. John’s Wort; exercise; transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) BIPOLAR lithium (Lithobid)- acute tx of mania & depressive episodes & prevention of recurrent mania/dep epidsodes -less effective in people w/ mixed mania -effective in reducing: elation, grandiosity, expansiveness; flight of idea; irritability, manipulativeness; anxiety; (to a lesser extent)-insomnia; psychomotor agitation; threatening or assaultive behavior; distractibility; hypersexuality; paranoia Therapeutic levels- 7-14 days; 0.4-1.3mEq/L (toxicity @ 1.5, >2.0 is life threatening!) Adverse Rx- hypothyroidism, kidney impairment Contraindications- CV disease, brain damage, renal disease, thyroid disease, myasthenia gravis, pregnancy/breast feeding, children<12yrs Antiepileptic drugs: dysphoric manic, rapid cycling, EEG abnormalities, substance abuse, progression in frequency & severity of symptons, no family h/o -carbamazepine (Tegretol)- monitor blood levels first 8 wks -divalproex (Depakote) -lamotrigine (Lamictal) -gabapentin (Neurontin) -topiramate (Topamax)- does not appear to cause wt gain Anxiolytics-tx of acute mania w/ tx-resistant mania; should be avoided w/ h/o substance abuse -clonazepam (Klonopin) -lorazepam (Ativan) Antipsychotics- newer atypical have mood-stabilizing properties -olanzapine (Zyprexa) -quetiapine (Seroquel) ECT- severe manic behavior, esp w/ tx-resistant mania & rapid cyclers SCHIZOPHRENIA Antipsychotics -3-6wks for effect Side effects: akathesia, dystonia, akinesia, dyskinesia/tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome Peripheral nervous system effects: constipation, dry mouth, nasal congestion, clurred vision, mydriasis, photphobia, orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, urinary retention, urinary hesitation, wt gain, inhibition of ejaculation or impotence in men Anticholinergic effects: dry mouth, urinary retention & hesitancy, constipation, blurred vision, photosensitivity, dry eyes, inhibition of ejaculation or impotence in men Extrapyramidal Side Effects (EPS)-acute dystonic rx (opisthotonos, oculogyric crisis); -akathisia(internal restlessness & external pacing/fidgeting); -tardive dyskinesia (AIMS test); appears after prolonged tx, not always reversible: involuntary tonic muscular spasms of tongue, fingers, toes, neck, trunk or pelvis -psuedoparkinsonism Cardiovascular effects- hypotension, postural hypotension, tachycardia Rare & toxic effects- Agranulocytosis- sore throat, fever, malaise, mouth sores - Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)- dec’d LOC, greatly inc’d muscle tone, autonomic dysfxn: hyperpyrexia, labile HTN, tachycardia, tachypnea, diaphoresis, drooling -tx: early detection; bromocriptine (Parlodel) for mild; dantrolene (Dantrium) for more severe; ECT - cholestatic jaundice- Traditional- dopamine antagonist Advantages-target positive symptoms; becoming obsolete because of side effects; less expensive disadvantages-do not treat neg symptoms, EPS, tardive dyskinesia, anticholineergic effects, lower seizure threshold high potency= low sedation + low ACH + high EPS -haloperidol (Haldol)- least sedating, often used in lg dose for assaultive behavior -trifluoperazine (Stelazine) -fluphenazine (Prolixin) -thiothixene (Navane) Medium potency -loxapine (Loxitane) -molindone (Moban) -perphenazine (Trilafon) Low potency= high sedation + high ACH + low EPS -chlorpromazine (Thorazine) -thioridazine (Mellaril) -mesoridazine (Serentil) Decanoate= long acting -haloperidol decanoate (Haldol) -fluphenazine deconate (Prolixin) AtypicalAdvantages-diminish neg symptoms as well; fewer side effects; improve symptoms of anxiety/depression, dec suicidal Disadvantages- wt gain, metabolic abnormalities -clozapine (Clozaril)- s/e: agranulocytosis, seizures; weekly WBC for first 6 mos & frequently after -risperidone (Risperdal)-olanzapine (Zyprexa) -quetiapine (Seroquel) -ziprasidone (Geodon) -aripiprazole (Abilify) -paliperidone (Invega) Antiparkinsonian drugs- to tx s/e -trihexyphenidyl (Artane) -benztropine mesylate (Cogentin) -diphenhydramine hydrochloride (Benadryl) Amantadine hydrochloride (Symmetrel) Adjuncts: Antidepressants; antimanic agents; benzos (can improve symptoms by ~50%) Snake root- source of reserpine in antipsychotics