Polar vs nonpolar lab report
advertisement

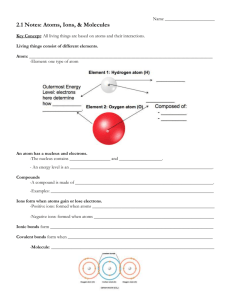
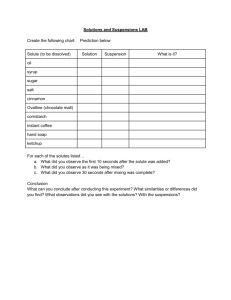
Polar vs nonpolar lab Background Some substances dissolve well in water while others do not. The answer lies in the polarity of the molecules in both the solvent and the solute. A molecule is polar if its center of positive charge is in a different location that its center of the electronegative charge. Water is the best example of this. The electronegativity of hydrogen is 2.1 while oxygen has 3.5. The charge separation in water is responsible for its unique properties. Some solvents are nonpolar and will not dissolve in water. A nonpolar solvent does not have this large electronegativity difference. These are considerations taken into account in the drycleaners business. They need to have solvents on hand that will dissolve different substances out of clothing. Remember that more is not better in this lab-you will have a hard time telling if things are dissolving Prelab 1.Make a sketch showing the attractions of water molecules to each other 2.Make separate sketches indicating the attractive forces between water molecules and anion and cations-such as water dissolving NaCl: Materials Copper chloride, sucrose, naphthalene, ethanol, vegetable oil, ammonium nitrate, water, hexane, goggles 1cm water + 8-10drops of solute/or 2-3 small grains of solute 1cm hexane + 9-10 drops of solute/2-3 small grains of solute Data Solute behavior in water H2O behavior in hexane Copper II chloride (CuCl2) Sucrose (C12H22O11) Naphthalene (C10H8) Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) Vegetable oil CH3(CH2)16COOH Ammonium nitrate NH4NO3 CH2CHCHCHCHCH2 Analysis 1.Divide the solutes into two groups(nonpolar and polar) and list: 2.What are some similarities between solutes that dissolve in water ONLYyou may include such aspects as electronegativity? 3.What are some similarities between solutes that dissolve in hexane ONLYyou may include such aspects as electronegativity? 4.For the solutes that had some affinity for both water and hexane, describe the structural reasoning as to why they behaved this way.