KASAB Framework for School Administrators & Teachers
advertisement

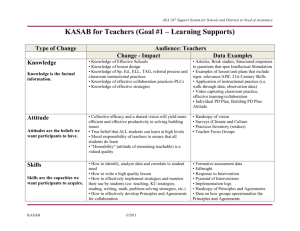
Iowa Support System for Schools and Districts in Need of Assistance KASAB (Examples/Possibilities) for Administrators and Teachers Type of Change Knowledge Audience: Administrators Changes - Impact Data Examples Attitude Skill Aspiration Behavior Design Phase: KASAB for Administrators and Teachers Understanding the magnitude of first and second order change Understanding the difference between instructional leadership compared to managerial duties Belief that all students can learn at high levels Believe that increasing their skill and ability in the essential responsibilities/practices and an understanding of change leadership will improve student achievement Conducting coaching conversations with teachers Know how to use data to facilitate change and make informed decisions Shares ideals and beliefs about schooling, teaching and learning with teachers, staff and parents All students in the school will achieve at high levels To be an instructional leader Consistent use of the special education process Participation in identified professional development Consistent use of standardized walk- ©2009 Evidence of attention to the responsibilities of communication, culture, input, and order through meeting notes, agendas, public communications, action steps, etc. Time audit – Administrative schedule Interview data Participation in learning opportunities for leadership Time audit – Administrative schedule Use of professional resources Teacher surveys Practices Inventory Meeting notes and other communications Data summaries and resulting decisions Individual Professional Development Plan Interview Reflection log/journal Time audit – Administrative schedule Participation in special education decisions Sign-in sheets/registration/grade for participation in professional development Analysis of walk-through data and Design - 145 Iowa Support System for Schools and Districts in Need of Assistance Type of Change Knowledge throughs Demonstration of coaching conversations with teachers Partnering with parents/families/community to achieve student expectations Articulation of shared vision Audience: Teachers Changes - Impact Data Examples Knowledge of Effective Schools Knowledge of lesson design Knowledge of Sp. Ed., ELL, TAG, referral process and classroom instructional practices Knowledge of effective collaboration practices Articles, Book studies, Structured responses to questions that spur Intellectual Stimulation Examples of lesson/unit plans that include rigor, relevance/AIW, 21st Century Skills Application of instructional practice (i.e. walk-through data) Video capturing classroom practice, effective teaming/collaboration Individual PD Plan, Building PD Plan Hardcopy of vision Surveys (Climate and Culture Practices Inventory (retakes) Teacher Focus Groups Formative assessment data Pyramid of Interventions Implementation logs Hardcopy of Principles and Agreements Data on how groups operationalize the Attitude Skills perception surveys Documentation of reflective/coaching conversations Evaluation of leadership standards Minutes of community/parent meetings Customer satisfaction survey Design Phase: KASAB for Administrators and Teachers Collective efficacy and a shared vision will yield more efficient and effective productivity in solving building issues True belief that ALL students can learn at high levels Moral responsibility of teachers to ensure that all students do learn “Honeability” (attitude of remaining teachable) is a valued quality How to identify, analyze data and correlate to student need How to write a high quality lesson How to effectively implement strategies and monitor their use by students (co- ©2009 Design - 146 Iowa Support System for Schools and Districts in Need of Assistance Aspirations Behaviors teaching, KU strategies, reading, writing, math, problem-solving strategies, etc.) How to effectively develop Principles and Agreements for collaboration Instruction is highly effective for each and every child Every child will learn to his/her maximum potential Frequent monitoring of student progress in order to create effective flexible instructional groups Maximum use of instructional time (including transitions) and professional development time Effectively operationalizing the principles and agreements of collaboration Principles and Agreements Modeling Effective Teaming Survey (Climate and Culture) Practices Inventory Walk-through data Time Audit – PD and Instructional Walk-through data Observation data Videotape – Reflections of self and group Data Team meeting artifacts Remember: Knowledge is the factual information. Attitudes are the beliefs we want participants to have. Skills are the capacities we want participants to acquire. Aspirations are the desires we want participants to have. Behaviors are the consistent application of the knowledge and skills that are driven by the attitudes and aspirations. Design Phase: KASAB for Administrators and Teachers ©2009 Design - 147