Module 3 Lesson 2 Guided Notes
advertisement

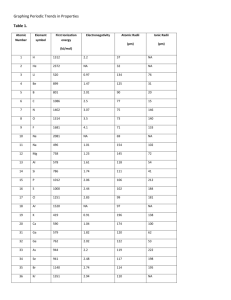
Module 3 Lesson 2 Guided Notes (Periodic Table Trends) Essential Standards Addressed: 1.3.2 Infer the physical properties of an element based on its position on the Periodic Table. 1.3.3 Infer the atomic radius, reactivity, electronegativity, and ionization energy of an element from its position on the Periodic Table. Slides 1 – 6 (Atomic Radius) 1. What is atomic radius (how is it defined) and what is its general trend? 2. Which element has the largest atomic radius on the Periodic Table? 3. Which element has the smallest atomic radius on the Periodic Table? 4. Why does atomic radius decrease across the periods of the Periodic Table? 5. Example: Which element has a larger atomic radius – silicon or sulfur? 6. Example: Which element has a larger atomic radius – sodium or potassium? Slides 7 – 10 (Ionization Energy) 7. What is an ion? Provide an example of one positive and negative ion. 8. What is the definition of ionization energy? 9. What is the ionization energy trend? 10.Which element and group have the lowest ionization energy? 11.Which element and group have the highest ionization energy? 12.Example: Which element has a higher ionization energy – aluminum or phosphorus? 13.Example: Which element has the lower ionization energy – calcium or strontium? Slides 11 – 14 (Electronegativity) 14.What is the electronegativity trend? 15.Which element has the highest electronegativity? 16.Which element has the lowest electronegativity? 17.Which element has a greater electronegativity value – carbon or nitrogen? 18.Which element has a lower electronegativity value – calcium or strontium? Slides 15 – 16 (Metallic Activity) 19.What is the general trend for metallic activity? 20.Which element has the greatest metallic activity? 21.Which element has the lowest metallic activity? Slides 17 – 19 (Ionic Radii) 22.What is a positive ion called and provide an example. 23.What is a negative ion called and provide an example. 24.How do neutral atoms become positive ions? 25.How do neutral atoms become negative ions? 26.Are positive ions larger/smaller than a neutral atom of that same element? 27.Are negative ions larger/smaller than a neutral atom of that same element? Slides 20 – 25 (Review) 28.Atomic radius trend increases _________ and to the ________________. Which element is the largest atom? 29.Ionization Energy increases ____________ and to the _________________. Which element has the largest ionization energy? 30.Electronegativity increases ____________ and to the ______________. Which element has the largest electronegativity? 31.Metallic activity increases ____________ and to the ______________. Which element has the greatest metallic activity? 32.Ionic Radii is a ___________ vs. _____________ trend. Metals lose electrons and become ____________ than the original atom. Non-metals gain electrons and become ____________ then the original atom.