End of Chapter Questions
advertisement

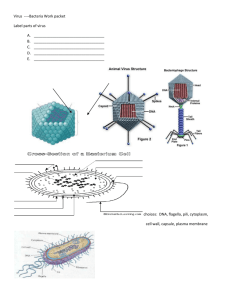
Chapter 24 and 25 Chapter Review Questions Chapter 24 End of Chapter Review Questions page 482 1. heterotroph, saprophyte, chemoautotroph: does not belong because the others describe bacteria that use food produced by other organisms. 2. spirochetes, enteric bacteria, methanogen: is an archaebacterium. The other terms refer to eubacteria-linkage of prokaryotes (lacks a nucleus) 3. archaebacterium, exotoxin, pathogen: refers to a group of bacteria. The others are related to diseases. 4. pilus, conjugation, endospore: conjugation is a process, the others are structures a pilus starts conjugation that does not involve an endospore. 5. cyanobacterium, anaerobe, enteric bacteria: anaerobe-an organism living under certain environmental conditions without oxygen. The other terms refer to groups of bacteria. 6. Bacteria produce yogurt from milk by fermentation. 7. Rod-shaped bacteria are called bacilli. 8. Thermoacidophiles are archaebacteria. 9. Gram-positive bacteria stain purple. 10. Eutrophication is the result of population explosions. 11. Bacterial DNA is a closed loop. 12. The glococalyx helps bacteria stick to surfaces. 13. During nitrogen fixation, gaseous nitrogen is converted to ammonia. 14. An organism that must have oxygen to survive is an obligate aerobe. 15. Genetic recombination in bacteria can occur during the process of conjugation. 17. List one distinguishing characteristics of each of the main groups of archaebacteria. The methanogens make methane as a byproduct. The halophiles require a salty environment. The thermoacidophiles require high temperatures and low pH (acid). 19. Describe the capsule of bacterium and its function. The capsule is a protective layer of polusaccharides that surrounds the bacterial cell wall. It protects the cell from harsh environments. 20. Explain how saprophytic bacteria contribute to the recycling of nutrients in the environment. By decomposing dead organic matter, saprophytic bacteria release carbon and other elements to the environment for reuse by other organisms. 22. Describe one was bacteria can exchange genetic information. In conjugation a portion of DNA from on bacterium passes across a conjugation bridge and into another bacterium. In transduction, a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another. In transformation, a bacterial cell picks up DNA from its environment. 23. Identify the metabolic process that bacteria use to make food products such as pickles and sauerkraut. Bacteria use fermentation, which is an anaerobic pathway. 24. List some diseases caused by bacteria, and list the organs they affect. Botulism -nerves Cholera -intestines Gonorrhea -urethra, fallopian tubes, epididymis Lyme disease -skin, joints heart Salmonella -intestines Tetanus -nerves 1 Chapter 24 and 25 Chapter Review Questions 25. Label the parts of the bacterium in the picture. A- cell wall B- DNA C- Cell membrane D- ribosome Chapter 25 End of Chapter Review Questions page 502 1. obligate- restricted to a single condition of life intracellular-something occurring within a cell parasite- an organism that lives at the expense of another organism inside of or on the host A virus is an infectious particle that multiplies only within a living cell. 2. Viral infection is usually very specific. Identify the structure of the cell surface that permits only specific viruses to infect it. Receptor sites are specific sites that viruses recognize and attach to on the host cell’s surface. If a virus does not find a receptor site, it cannot infect a host cell. 3. Distinguish a virus from a provirus. A virus is an infectious particle outside its host ell. A provirus is viral DNA integrated in the host cell’s chromosomes. 4. Use what you know about the meaning of the word lysis to explain the meanings of lytic and lysogenic cycles. Lysis- a process to destroy or disintegration. The lytic cycle ends with disintegration of the host cell. Lysogenic cycle- genic means “capable of” and the virus is capable of causing cell disintegration. 5. Explain the meaning of the term reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is when an enzyme that catalyzes the production of DNA from RNA, the opposite of transcription, hence the term reverse transcriptase. 6. A virus is a biologically active particle composed of protein and nucleic acid. 7. Which of the following was a key event in the development of virology? The crystallization of a virus. 8. The term icosahedron refers to the structure of the viral capsid. 9. Certain viruses have reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that synthesizes DNA using RNA as a template. 10. An essential aspect of viral replication is the release of the viral nucleic acid in the cytoplasm of the host cell. 11. Viroids differ from viruses in their absence of a capsid. 12. The head region of a bacteriophage is used to enclose the nucleic acid. 13. Lysis refers to the disintegration of the host cell. 14. Temperate viruses are those that integrate their viral genes into the DNA of the host cell. 15. One virus that participates in the lysogenic cycle is HIV. 16. Explain the activity of reverse transcriptase. Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that uses RNA as a template for DNA (opposite of transcription) 17. Describe the structure of HIV. HIV has an RNA genome, a protein capsid, an envelope, an envelope with glycoprotein, and reverse transcriptase. 2 Chapter 24 and 25 Chapter Review Questions 19. Name the animal diseases that result from prion activity. Both scrapie and mad cow disease are degenerative brain diseases associated with prion activity. Scrapie occurs in sheep. Mad cow disease occurs in cattle. 21. What are some of the useful attributes of viruses? Viruses provide clues to the biochemistry of living organisms, and they can be used in the development of antiviral medications. 22. Distinguish between a virulent virus and a temperate virus? A virulent virus is a virus that replicates the lytic cycle. A temperate virus is a virus that can replicate the lysogenic cycle. 23. What causes a temperate bacteriophage to become virulent? External stimuli like radiation and chemicals are responsible. 24. Explain the methods humans use to control viral diseases. Vaccines are used to prevent viral infections. Disease transmission is prevented by controlling animals that carry viruses. Certain viral diseases can be treated with antiviral drugs. 25. What agents can trigger cells to multiply uncontrollably? Lysogenic viruses, cigarette smoke, asbestos, sunlight, chemicals, and radiation. 3