Assignment 1
advertisement

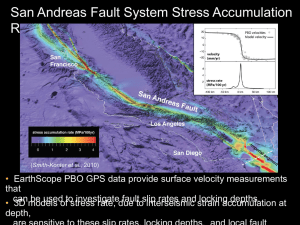
CE 5603 Seismic Hazard Assessment Middle East Technical University, Ankara,Turkey Department of Civil Engineering Prof. Dr. K. Önder Çetin ASSIGNMENT 1 – Review of Probabilistic Concepts 1. Earthquakes on a 150 km long fault occur as ruptures of length S, where S is anywhere between zero and half the length of the fault. A dam is located in the vicinity of the fault as shown in the figure given below. (a) In a two-dimensional coordinate system show the sample space of the rupture length S and the coordinate X of the center of the rupture (i.e.: x-axis shows the coordinate of the ruptured fault segment’s midpoint, X, y-axis shows the rupture length, S). Assume the rupture may not extend beyond the ends of the fault. (b) Show the event that the center of rupture is within 30 km of the dam. (c) Show the event that the shortest distance from the rupture to the dam is less than 30 km. 150 km X Fault Rupture S 20 km 50 km Dam 2. Two soil sites A and B are located in a seismic region. It is estimated that an earthquake in the region might be strong (S), moderate (M), or weak (W) with probabilities P(S) = 0.03, P(M) = 0.25 , and P(W) = 0.72. The probabilities of liquefaction of each soil site if these earthquakes occur are 0.30, 0.15, and 0.08, respectively. (a) Determine the probability of liquefaction of site A if the earthquake occurs. (b) If site A is liquefied, what is the probability that the earthquake was of weak strength? Assignment 1 : Review of probabilistic concepts CE 5603 Seismic Hazard Assessment Middle East Technical University, Ankara,Turkey Department of Civil Engineering Prof. Dr. K. Önder Çetin (c) Due to proximity of the sites to each other and similarities in the soil profile characteristics, it is estimated that if site A liquefies the probability that site B will also liquefy is 0.55, 0.16, and 0.04 for the three types of earthquakes. Determine the probability that both sites will liquefy in an earthquake. (d) If site A has liquefied and site B has not, what is the probability that the earthquake was not strong? 3. The highway system for transportation between Ankara and Istanbul includes two parallel bridges A and B that are crossed by a North Anatolian Fault system. In the event of an earthquake on NAF, each bridge will fail if the fault rupture crosses it. Assuming that the other parts of the highway system are not vulnerable to earthquakes, (a) Determine the probability of failure of the highway system, i.e., the probability that transportation between Ankara and Istanbul will be interrupted, if an earthquake caused by a 120 km long rupture occurs on the fault. Assume the rupture is equally likely to occur anywhere along the fault, but not extending beyond its ends. (b) Suppose bridge B is known to have failed, what is the probability that bridge A has survived? (c) If transportation between cities Ankara and Istanbul is known to be possible after the earthquake, what is the probability that both bridges survived? İstanbul 200 km 140 km A an 60 km bu l Assignment 1 : Review of probabilistic concepts B an bu l Ankara