Study_Guide_EARTHSCI_Earthquake_Mini_Quiz_web
advertisement

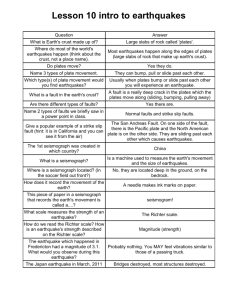
Study Guide: Earthquake Mini-Quiz Name: ___________________________________________________________ Section: _______ FYI: The quiz will include ten (10) of the following twenty (20) topics. 1. Know how to identify & label Hanging Wall (above the fault) and Foot Wall (below the fault) 2. Know how to identify & label Normal Fault (tension) and Reverse Fault (compression) and Strike-Slip Fault (shearing) 3. Know how to identify & label Divergent Plates (tension) and Convergent Plates (compression) and Transform Plates (shearing) 4. Know how to identify & label the three stresses that affect rocks underground: Tension, Compression, Shearing 5. Which fault caused the 1755 Cape Ann, Massachusetts earthquake? (The Bloody Bluff-Lake Char Fault) 6. The strongest earthquake was 9.5 on the Richter Scale (in Chile, 1960) 7. The deadliest earthquake was in Shanshi, China in 1556 (830,000+ died) 8. Aftershock = series of minor earthquakes after the main quake 9. Liquefaction = loose, sandy sediment that flows like a liquid due to shaking 10. Richter Scale (Charles Richter, 1934) magnitude of energy released compared to an equivalent amount of TNT explosive (0 to no upper limit) 11. Mercalli Scale (Giuseppe Mercalli, 1902) intensity of observed damage due to an earthquake (Roman numeral I to XII) 12. 90% of earthquakes occur along plate boundaries 13. 10% of earthquakes occur along faults 14. Primary Waves: fastest, slinky, least destructive, can go through anything 15. Secondary Waves are second fastest, very destructive, travel like a rope up and down, and also side to side, cannot travel through liquids 16. Surface Waves are slowest, most destructive, (Love and Rayleigh) and travel in a twisting and rolling motion 17. California: San Andreas Fault (Pacific Plate and North American Plate Boundary), Transform plate boundary (shearing) 18. Focus (underground) and Epicenter (on surface, above focus) 19. Seismoscope (dragon and toad), Seismograph, Seismogram, Seismometer 20. Tsunami Waves (caused by underwater earthquakes, asteroid impacts, or landslides), tide rushes out very quickly before >>> seek higher ground! BONUS: Earthquake Safety Procedure: Drop, Cover and Hold on