Test on the Periodic Table

Jenna Zukswert’s Comprehensive Test on the Periodic Table
Format
Multiple choice questions- 40%
Short answer- 15%
Label a periodic table- 20%
Reactions (ionization energy/ electron affinity)- 10%
Essay question (possible take-home)- 15%
Multiple choice questions = 20, worth 2 points each
atomic and/or ionic size/ mass
ionization energy and/or electron affinity
the families and/or characteristics of metals, metalloids, nonmetals
several topics integrated
Short answer = 3, worth 5 points each
Periodic table = label certain components and trends
atomic radius- 4 points
ionic radius- 4 points
ionization energy- 4 points
electronegativity-2 points
representative elements, transition metals, inner transition metals- 3 points
noble gases and alkali metals- 2 points
metals, non-metals, metalloids – 1 point
Reactions = 2 reactions worth 5 points each
ionization energy
electron affinity
Essay - worth 15 points total, may be take-home
The “Element”ary Exam
Answers to the multiple choice (2 points each):
1. ______ 2._______ 3._______ 4._______ 5._______
6._______ 7._______ 8._______ 9._______ 10.______
11.______ 12.______ 13.______ 14.______ 15.______
16.______ 17.______ 18.______ 19.______ 20.______
Reactions (5 points each)
1.
Write equations for the ionization of Mg to Mg
+1
and Mg
+1
to Mg
+2
. Then, calculate the energy required to remove all valence electrons from one gram of magnesium. The first ionization energy is 738.1 kJ/mol, the second ionization energy is 1,450 kJ/mol, and the third ionization energy is 7,730 kJ/mol.
2.
Write the equation for the formation of a fluoride anion from a fluorine atom.
Fluorine’s electron affinity is +328 kJ/mol. What is ΔH when electrons are added to two moles of fluorine?
Writing Section- Please Answer on a Separate Sheet
Short Answer (5 points each)-
1.
Explain how the modern periodic table came to be. Reference Moseley,
Newlands, and Mendeleev in your answer.
2.
What is ionization energy? How does ionization energy influence the type of ion that an element typically forms?
3.
What is effective nuclear charge? How does it affect the size of an element’s atomic radius?
Essay (15 Points)
Elements found in the same groups tend to share many of the same characteristics. a.) Describe the physical and chemical properties of the alkali metals b.) Describe the physical and chemical properties of the coinage metals c.) Compare and contrast the alkali metals with the coinage metals
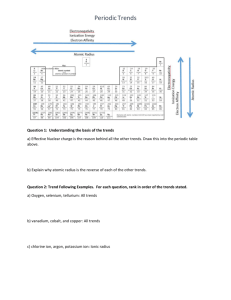
Periodic Table Trends to Label- Be as Detailed as You Can!
Trends and Families to Label:
Atomic Radius
Ionic Radius
Ionization Energy
Electronegativity
Representative Elements
Transition Metals
Inner Transition Metals
Noble Gases
Alkali Metals
Metals, metalloids, nonmetals (this can be generalized, does not need to be exact)
Multiple Choice
1. The size of an element’s atomic radius __________ from left to right across the periodic table. a. increases c. remains constant b. decreases d. is randomly assigned
2. Arrange the following elements from lowest to highest ionization energy: Be, Mg,
Ca, Rb, Sr a. Be, Mg, Ca, Rb, Sr c. Rb, Sr, Ca, Mg, Be b. Rb, Sr, Ca, Be, Mg d. Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Rb
3. The halogens tend to form anions because…. a. They have low first ionization energies b. They have low electron affinities c. They have high electron affinities d. They don’t; they form cations
4. Name the only element touching the stair-step line that is NOT a metalloid a. Aluminum c. Nitrogen b. Boron d. Astatine
5. When a metal atom becomes a cation… a. It gains an electron b. It becomes a different isotope c. Its atomic number changes d. Its ionic radius is smaller than its atomic radius
6. Ionization energy is measured in atoms when a. They are in a gaseous state b. They are ions c. They are in a solid state d. They are at 25°C
7.
Electron affinity… a.
Is always positive b.
May be positive or negative c.
Is always negative d.
Is typically higher in metals than nonmetals
8.
Al
2
O
3
is… a.
Called dialuminum trioxide b.
Impossible to form c.
Not a true oxide d.
Amphoteric
9.
How many valence electrons does one atom of copper have? a. 9 c. 2 b. 10 d. 1
10. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing effective nuclear charge: Bi,
As, P, N, Sb a. Bi, Sb, As, P, N c. Bi, As, P, N, Sb b. N, P, As, Sb, Bi d. N, As, P, Bi, Sb
11.
Of Fe, K, P, and Cl, which would you expect to have the greatest electron affinity? a. K b. Fe c. Cl d. P
12.
Unknown element X has four energy levels, five valence electrons, and is a metalloid.
What is element X? a. Si c. Se b. Ge d. As
13.
The electron affinity of chlorine is 349 kJ/mol. What is the correct equation for the formation of chloride? a.
Cl (s) + e
-
→ Cl
-
(s) + 349 kJ b.
Cl (g) + e
-
→ Cl
-
(g) + 349 kJ c.
Cl (s) + 349 kJ + e - → Cl (s) d.
Cl (g) + 349 kJ + e
-
→ Cl
-
(g)
14. The second ionization energy of sodium is much higher than the first ionization energy because… a. The second electron is removed from an already-stable noble gas core b. The second electron is a valence electron c. The atom has a larger radius after the first electron is removed d. It’s not higher than the first ionization energy
15. Boron and silicon form similar compounds and are very similar due to their
________ relationship a. periodic c. chemical b. familial d. diagonal
16. An element with a greater effective nuclear charge has a(n) ______ atomic radius a. larger c. undefined b. smaller d. undulating
17. Lanthanides and actinides have these kinds of orbitals: a. s only b. s, p and d c. s, p, d, and f d. f only
18. The first ionization energy of beryllium is 899 kJ/mol and the second ionization energy is 1,757 kJ/mol. How much energy would it take to remove the valence electrons from two moles of beryllium? a. 5,312 kJ c. 4,413 kJ b. 2,656 kJ d. 10,704 kJ
19. What is NOT true of the element rubidium? a. It is an alkali metal b. It has a low electron affinity b. It has one valence electron d. Its radius is larger than cesium’s
20. What is true of the oxide formed when magnesium reacts with oxygen? a. Its formula is Mg
2
O b. It is basic b. It is molecular d. It is amphoteric